One
switch
statement allows you to test when a variable is equal to multiple values. Each value is called a case, and the variable being tested will be for each
switch
case
check it out.
Install using CPAN Open a command window and enter Ubuntu usage The syntax format is as follows: The following is Any type of In a The scalar When the variable being tested is equal to When matching When matching Execute the above program, and the output is as follows: Next let’s take a look at the use of Execute the above program, and the output is as follows:
switch
case
execution is based on
Switch
module
Switch
the module is not installed by default. 5.17.1. Install the Switch.pm module #
cpan
command, and then enter
installSwitch
command:# cpan
cpan[1]> install Switch // install
cpan[2]> exit // exit
apt-get
installationsudo apt-get install libswitch-perl
5.17.2. Grammar #
Grammar #
Use Switch; Switch (argument) {case1 {print "number 1"} case "a" {print "string
{case [1.. 10,42] {print "Number in list"}case ( @ array) {print "Number in array"}case/ w+/
{print "Regular matching pattern"}caseqr/ w+/{
Print "regular matching pattern"} case ( % hash) {print "hash"}
case ( &sub) {print "child process"} else {print "does not match the previous condition"}}
switch
rules for the statement:
switch
scalar parameter can be used in parentheses of the statement.
switch
there can be any number of
case
statement. Every one of them.
case
followed by a value to be compared and a colon.
case
after the statement will match the
switch
the scalar of the statement is compared to determine whether it is equal.
case
Constant time in
case
The following statement will be executed until it is encountered
break
Statement.
switch
statement can have an optional
else
the statement is at the end, and the statement is in all
case
executed in the case of a mismatch.
case
after that, it will be executed
case
statement block code, jump out after execution
switch
statement.
case
later, if we need to continue with the next
case
statement, you need to add
next
statement. 5.17.3. Flow chart #
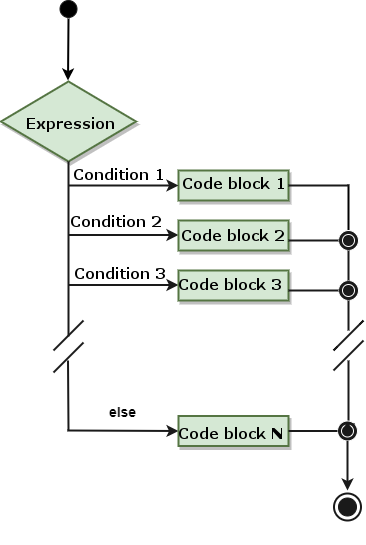
Example #
#/ Usr/bin/perluse
Switch$ Var=10@ Array=(10,20,30);% Hash=('key1 '=>10,'key2'=>20); Switch ($var) {case10 {print "number
10 n "{case" a "{print" string
{case [1.. 10,42] {print "Number in list"} case ( @ array) {print "Number in array"} case
( % hash) {print "In hash"}else {print "No matching condition"}}
Number 10
next
example:Example #
#/ Usr/bin/perluse
Switch$ Var=10@ Array=(10,20,30);% Hash=('key1 '=>10,'key2'=>20); Switch ($var) {case10 {print "number
10 n "; next;} # Continue executing case" a "{print" string after matching
{case [1.. 10,42] {print "Number in list"} case ( @ array) {print "Number in array"} case
( % hash) {print "In hash"}else {print "No matching condition"}}
Number 10
Numbers in the list