4.15.1. If…else statement #
Lua
if
statement can be associated with the
else
statement is usedtogether, in
if
conditional expression is
false
, when the execution
else
statement code block.
Lua
if...else
syntax format of the statement is as follows:
if(Booleans)
then
--[Execute the statement block when the Boolean expression is true--]
else
--[Execute the statement block when the Boolean expression is false--]
end
When the Boolean expression is
true
at that time,
if
block of code in is executed when the Boolean expression is
false
, The code block for
else
will be executed.
Lua
believes that
false
and
nil
are false,
true
and non
nil
are true. It should be noted that in Lua
0
for
true
.
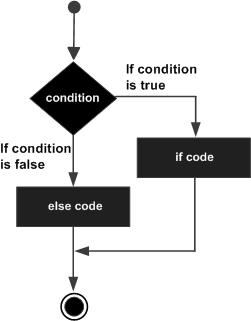
The flow chart of the if statement is as follows:
4.15.2. Example #
The following example is used to determine a variable The execution result of the above code is as follows:
a
value:Example #
--[Define variables--]
a = 100;
--[Check Condition--]
if( a < 20 )
then
--[Execute the statement block when the if condition is true--]
print("A less than 20" )
else
--[Execute the statement block when the if condition is false--]
print("A greater than 20" )
end
print("The value of a is:", a)
A greater than 20
The value of a is: 100
4.15.3. If…else statement #
Lua
if
statement can be associated with the
else
statement is usedtogether, in
if
conditional expression is
false
when the execution
else
statement code block to detect multiple conditional statements.
Lua
if...else
syntax format of the statement is as follows:
if(Boolean expression 1)
then
--[Execute this statement block when Boolean expression 1 is true--]
elseif(Boolean expression 2)
then
--[Execute this statement block when Boolean expression 2 is true--]
elseif(Boolean Expression 3)
then
--[Execute this statement block when Boolean expression 3 is true--]
else
--[If none of the above Boolean expressions are true, execute the statement block--]
end
4.15.4. Example #
The following example sets the variable The execution result of the above code is as follows:
a
to judge the value:Example #
--[Define variables--]
a = 100
--[Check Boolean conditions--]
if( a == 10 )
then
--[If the condition is true, print the following information--]
print("The value of a is 10" )
elseif( a == 20 )
then
--[Print the following information when the if else if condition is true--]
print("The value of a is 20" )
elseif( a == 30 )
then
--[If else if the condition is true, print the following information--]
print("The value of a is 30" )
else
--[Print the following information when none of the above conditional statements are true--]
print("No matching value for a" )
end
print("The true value of a is: ", a )
No matching value for a
The true value of a is: 100