Go
language provides data structures of array types.
An array is a sequence of numbered and fixed-length data items of the same unique type, which can be any primitive type such as an integer, a string, or a custom type.
As opposed to declaring
number0,
number1,
...,
number99
in the form of an array
numbers[0],
numbers[1]
...,
numbers[99]
, it is more convenient and easy to expand.
Array elements can be read (or modified) by index (position), which starts at 0, the first element index is 0, the second index is 1, and so on.
The above is how one-dimensional arrays are defined. For example, the following defines an array The following demonstrates array initialization: We can also quickly initialize the array while declaring it literally: If the length of the array is uncertain, you can use the If the length of the array is set, we can also initialize the element by specifying the subscript: Initialize the array If you ignore The above example reads the fifth element. Array elements can be read (or modified) by index (position), which starts at 0, the first element index is0, the second index is 1, and so on. Array elements can be read by index (position). The format is the array namefollowed by parentheses, and the value of the index is in the brackets. Forexample: The above example reads the array The following shows an example of a complete operation of an array (declaration, assignment, access): The execution result of the above example is as follows: The execution result of the above example is as follows: Array pair Content Description Multidimensional array The Go language supports multidimensional arrays, and the simplest multidimensional array is a two-dimensional array. Pass an array to a function You can pass array parameters to the function
2.29.1. Declare array #
Go
language array declaration needs to specify the element type and the number of elements. The syntax format is as follows:var variable_name [SIZE] variable_type
balance
, the length is 10 and the type is
float32
:var balance [10] float32
2.29.2. Initialize array #
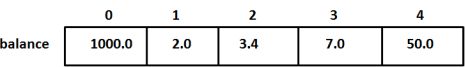
var balance = [5]float32{1000.0, 2.0, 3.4, 7.0, 50.0}
balance := [5]float32{1000.0, 2.0, 3.4, 7.0, 50.0}
...
instead of the length of the array, the compiler deduces the length of the array based on the number of elements:var balance = [...]float32{1000.0, 2.0, 3.4, 7.0, 50.0}
or
balance := [...]float32{1000.0, 2.0, 3.4, 7.0, 50.0}
// Initialize elements with indexes 1 and 3
balance := [5]float32{1:2.0,3:7.0}
{}
number of elements in cannot be greater than
[]
number in.
[]
number in does not set the size of the array
Go
language sets the size of the array based on the number of elements:balance[4] = 50.0
2.29.3. Access array elements #
var salary float32 = balance[9]
balance
value of the 10th element.Example 1 #
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var n [10]int /* n is an array with a length of 10 */
var i,j int
/* Initialize elements for array n */
for i = 0; i < 10; i++ {
n[i] = i + 100 /* Set element to i + 100 */
}
/* Output the value of each array element */
for j = 0; j < 10; j++ {
fmt.Printf("Element[%d] = %d\\n", j, n[j] )
}
}
Element[0] = 100
Element[1] = 101
Element[2] = 102
Element[3] = 103
Element[4] = 104
Element[5] = 105
Element[6] = 106
Element[7] = 107
Element[8] = 108
Element[9] = 109
Example 2 #
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var i,j,k int
// Quickly initialize an array while declaring it
balance := [5]float32{1000.0, 2.0, 3.4, 7.0, 50.0}
/* Output array elements */ ...
for i = 0; i < 5; i++ {
fmt.Printf("balance[%d] = %f\\n", i, balance[i] )
}
balance2 := [...]float32{1000.0, 2.0, 3.4, 7.0, 50.0}
/* Output the value of each array element */
for j = 0; j < 5; j++ {
fmt.Printf("balance2[%d] = %f\\n", j, balance2[j] )
}
// Initialize elements with indexes 1 and 3
balance3 := [5]float32{1:2.0,3:7.0}
for k = 0; k < 5; k++ {
fmt.Printf("balance3[%d] = %f\\n", k, balance3[k] )
}
}
balance[0] = 1000.000000
balance[1] = 2.000000
balance[2] = 3.400000
balance[3] = 7.000000
balance[4] = 50.000000
balance2[0] = 1000.000000
balance2[1] = 2.000000
balance2[2] = 3.400000
balance2[3] = 7.000000
balance2[4] = 50.000000
balance3[0] = 0.000000
balance3[1] = 2.000000
balance3[2] = 0.000000
balance3[3] = 7.000000
balance3[4] = 0.000000
2.29.4. More content #
Go
language is very important, and we will introduce more about the array below: