In this section, we will introduce you to the connection to the Perl database.
In Perl 5 we can use the DBI module to connect to the database.
The full name of DBI is Database Independent Interface in English and database independent interface in Chinese.
As a standard interface to communicate with database in Perl language, DBI defines a series of methods, variables and constants, and provides a database persistence layer independent of specific database platform. DBI has nothing to do with the specific database platform, we can apply it in DBI in the chart gets all the API (Application Programming) The following sets the more common variable name naming methods: Next, let’s take MySQL database as an example to demonstrate how Perl operates on the database. Here we create in the MySQL database Download the data sheet: https://static.runoob.com/download/websites_perl.sql Next, we use the following code to connect to the database: Perform the steps: Use Use Use Finally, if all goes well, the above actions will be submitted. The application can also bind output and input parameters, as shown in the following example by replacing the Perform the steps: Use Use Use Finally, if all goes well, the above actions will be submitted. The application can also bind output and input parameters, as shown in the following example by replacing the Of course, we can also bind the value to be set, as shown below Perform the steps: Use Use Use Finally, if all goes well, the above actions will be submitted. The following data will The If an error occurs during SQL execution, you can roll back the data without making any changes: Business 5.43.1. DBI structure #
Oracle
, MySQL or Informix, etc.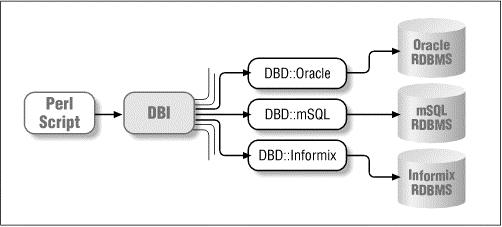
Interface
. The SQL data sent by the API is then distributed to the corresponding driverfor execution, and finally the data is obtained and returned.Variable name convention #
Handle to dsn driver object
$dbh Handle to a database object
$sth Handle to a statement or query object
$h universal handle ($dbh, $sth, or $drh), context dependent
The Bush value returned by the $rc operation code (true or false)
The integer value returned by the $rv operation code
@Array (list) of a row of values returned by an ary query
The row value returned by the $rows operation code
$fh file handle
Undef NULL value indicates undefined
\%Attr references the hash value of the attribute and passes it to the method
5.43.2. Database connection #
RUNOOB
database, the datasheet isthe
Websites
table structure and data are shown in the following figure: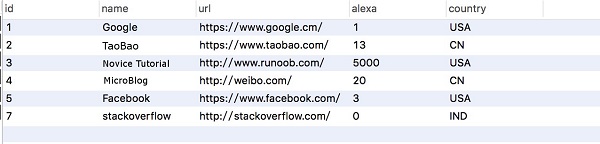
Example #
#/ Usr/bin/perl - wuse strict; Use DBI; My $host="localhost"#
Host address my $driver="mysql"# The interface type defaults to
Localhost $database="RUNOOB"# Database#
The handle of the driver object, my $dsn="DBI: $driver: database=$database: $host"; My $userid="root"#
Database username my $password="123456"# Database password#
Connect to database my $dbh=DBI ->connect ($dsn, $userid, $password) order $DBI:: errstr; My $sth=$dbh ->prepare ("SELECT
*From Websites "; # Preprocessing SQL Statement $sth ->execute(); # Executing SQL Operations#
The annotation section uses the binding value operation # $alexa=20# My $sth=
$dbh ->prepare ("SELECT name, URL # From Websites # WHERE alexa>?")#
Execute ($alexa) or die $DBI:: errstr#
Loop out all data while( my@row =$sth ->fetchrow_ Array() {printjoin (' t', @ row). " n";} $th ->finish()$ Dbh ->disconnect();
5.43.3. Insert operation #
prepare()
API preprocesses SQL statements.
execute()
API executes the SQL statement.
finish()
API releases the statement handle.my $sth = $dbh->prepare("INSERT INTO Websites
(name, url, alexa, country )
values
('Twitter', 'https://twitter.com/', 10, 'USA')");
$sth->execute() or die $DBI::errstr;
$sth->finish();
$dbh->commit or die $DBI::errstr;
?
placeholder to execute an insert query:my $name = "Twitter";
my $url = "https://twitter.com/";
my $alexa = 10;
my $country = "USA";
my $sth = $dbh->prepare("INSERT INTO Websites
(name, url, alexa, country )
values
(?,?,?,?)");
$sth->execute($name,$url,$alexa, $country)
or die $DBI::errstr;
$sth->finish();
$dbh->commit or die $DBI::errstr;
5.43.4. Update operation #
prepare()
API preprocesses SQL statements.
execute()
API executes the SQL statement.
finish()
API releases the statement handle.my $sth = $dbh->prepare("UPDATE Websites
SET alexa = alexa + 1
WHERE country = 'CN'");
$sth->execute() or die $DBI::errstr;
print "Number of updated records:" + $sth->rows;
$sth->finish();
$dbh->commit or die $DBI::errstr;
?
placeholder to execute an update query:$name = 'Novice Tutorial';
my $sth = $dbh->prepare("UPDATE Websites
SET alexa = alexa + 1
WHERE name = ?");
$sth->execute('$name') or die $DBI::errstr;
print "Number of updated records :" + $sth->rows;
$sth->finish();
country
for
CN
of
alexa
are modified to
1000
:$country = 'CN';
$alexa = 1000:;
my $sth = $dbh->prepare("UPDATE Websites
SET alexa = ?
WHERE country = ?");
$sth->execute( $alexa, '$country') or die $DBI::errstr;
print "Number of updated records :" + $sth->rows;
$sth->finish();
5.43.5. Delete data #
prepare()
API preprocesses SQL statements.
execute()
API executes the SQL statement.
finish()
API releases the statement handle.
Websites
in
alexa
data greater than 1000 is deleted:$alexa = 1000;
my $sth = $dbh->prepare("DELETE FROM Websites
WHERE alexa = ?");
$sth->execute( $alexa ) or die $DBI::errstr;
print "Number of records deleted :" + $sth->rows;
$sth->finish();
$dbh->commit or die $DBI::errstr;
5.43.6. Use the do statement #
do
statement can perform operations such as
UPDATE
,
INSERT
, or
DELETE
. It is relatively short to use and returns’ true’ for successful execution and
false
for failed execution. The example is as follows:“$dbh->do('DELETE FROM Websites WHERE alexa>1000');
5.43.7. COMMIT operation #
commit
to commit the transaction, complete the operation of the database:$dbh->commit or die $dbh->errstr;
5.43.8. ROLLBACK operation #
$dbh->rollback or die $dbh->errstr;