One In C # If the Boolean expression is When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following results: One When using One One Once someone In C # When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following results:
if
statement can be followed by an optional
else
statement
else
statement is executed when the Boolean expression is false. 1.12.1. Grammar #
if...else
syntax of the statement:if(boolean_expression)
{
/* The statement to be executed if the Boolean expression is true */
}
else
{
/* The statement to be executed if the Boolean expression is false */
}
true
, then execute
if
the code within the block. If the Boolean expression is
false
,then execute
else
code within the block. 1.12.2. Flow chart #
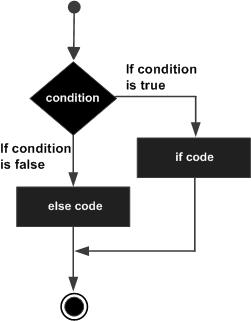
Example #
using System;
namespace DecisionMaking
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* Definition of Local Variables */
int a = 100;
/* Check Boolean conditions */
if (a < 20)
{
/* If the condition is true, output the following statement */
Console.WriteLine("A less than 20");
}
else
{
/* If the condition is false, output the following statement */
Console.WriteLine("A greater than 20");
}
Console.WriteLine("The value of a is {0}", a);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
A greater than 20
The value of a is 100
1.12.3.
if...else
if...else
statement #
if
statement can be followed by an optional
else
if...else
statement, which can be used to test a variety of conditions
if...else
if...else
statement, the following points need to be noted:
if
can be followed by zero or one.
else
must be in any one
else
if
after that.
if
can be followed by zero or more
else
if
must be in the
else
before.
else
if
, the match is successful, and the rest
else
if
or
else
will not be tested. 1.12.4. Grammar #
if...else
if...else
syntax of the statement:if(boolean_expression 1)
{
/* Execute when Boolean expression 1 is true */
}
else if( boolean_expression 2)
{
/* Execute when Boolean expression 2 is true */
}
else if( boolean_expression 3)
{
/* Execute when Boolean expression 3 is true */
}
else
{
/* Execute when none of the above conditions are true */
}
1.12.5. Example #
using System;
namespace DecisionMaking
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* Definition of Local Variables */
int a = 100;
/* Check Boolean conditions */
if (a == 10)
{
/* If the if condition is true, output the following statement */
Console.WriteLine("The value of a is 10");
}
else if (a == 20)
{
/* If the else if condition is true, output the following statement */
Console.WriteLine("The value of a is 20");
}
else if (a == 30)
{
/* If the else if condition is true, output the following statement */
Console.WriteLine("The value of a is 30");
}
else
{
/* If none of the above conditions are true, output the following statement */
Console.WriteLine("No matching values");
}
Console.WriteLine("The exact value of a is {0}", a);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
No matching values
The accurate value of a is 100