There are three forms of Just like the Same as Same as C’s 1.Match the expression first 2.Discriminant assignment expression The format of the Calculate the sum of numbers from The output is as follows: The following example is found in the The output is as follows: Infinite loop: To stop an infinite loop, press in the command window Loops in this format can iterate over strings, arrays, slices, and so on. The output of the above instance is as follows:
for
loop is a loop control structure that can execute a specified number of loops. 2.24.1. Grammar #
For
loops in the
Go
language, with only one using a semicolon.
for
in C language:for init; condition; post { }
while
in C:for condition { }
for(;;)
:for { }
init
is generally an assignment expression that assigns an initial value to a control variable;
condition
relational or logical expressions, loop control conditions;
post
is generally an assignment expression that increments or decrements the control variable.
for
statement execution process is as follows:
1
assign initial value;
init
whether the given condition is satisfied, if its value is true and the loop condition is satisfied, the statement inside the loop is executed and then executed
post
enter the second cycle and then judge
condition
; otherwise judge
condition
if the value is false, if the condition is not met, it will be terminated.
for
loop to execute the extra corporeal statement.
range
loop for
for
can be applied to
slice
、
map
, arrays, strings, and so on. The format is as follows:for key, value := range oldMap {
newMap[key] = value
}
for
statement syntax flow is shown in the following figure: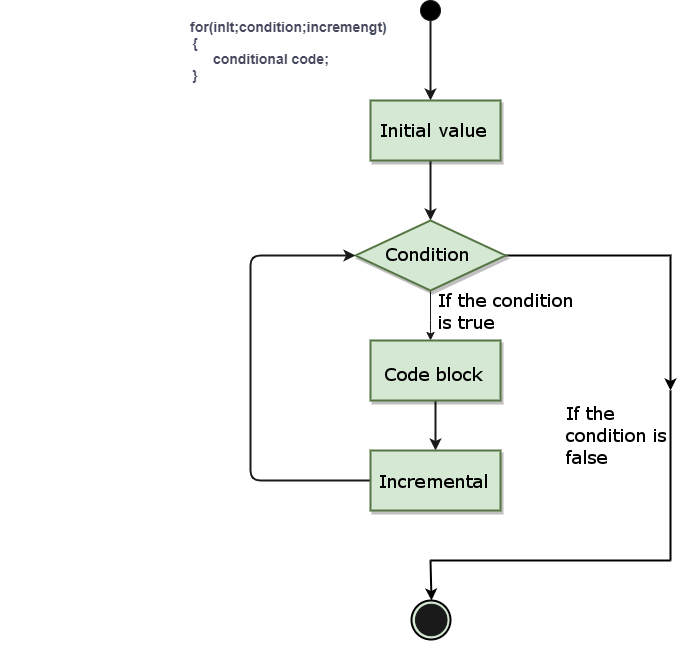
2.24.2. Example #
1
to
10
:Example #
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
sum := 0
for i := 0; i <= 10; i++ {
sum += i
}
fmt.Println(sum)
}
55
init
and
post
parameter is optional, and we can omit it directly, similar to
While
statement.
sum
less than
10
time calculation
sum
self-added value:Example #
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
sum := 1
for ; sum <= 10; {
sum += sum
}
fmt.Println(sum)
// It can also be written this way,
more like a While statement form
for sum <= 10{
sum += sum
}
fmt.Println(sum)
}
16
16
Example #
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
sum := 0
for {
sum++ // Endless cycle
}
fmt.Println(sum) // Unable to output
}
ctrl-c
.
For-each
range
cycleExample #
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
strings := []string{"google", "runoob"}
for i, s := range strings {
fmt.Println(i, s)
}
numbers := [6]int{1, 2, 3, 5}
for i,x:= range numbers {
fmt.Printf("Value of x in position% d=%d\\n", i,x)
}
}
0 Google
1 runoob
The value of position 0 x=1
The value of the first digit x=2
The value of the second digit x=3
The value of the third digit x=5
The value of the 4th digit x=0
Value of 5th digit x=0