Perl
redo
statement directly to the first line of the body of the loop to repeat the execution of the loop
redo
statement after the statement is no longer executed
continue
statement blocks are no longerexecuted.
The syntax format is as follows: Among them Labeled modifier No label modifier If it is in Execute the above program, and the output is as follows:
continue
statement can be used in the
while
and
foreach
in a loop. 5.28.1. Grammar #
redo [LABEL]
LABEL
is optional.
LABEL
of
redo
statement indicates that the loop control flow is transferred directly to the label modifier
LABEL
execution begins at the first line of the associated statement block and no longer executes
redo
statement and the statement after the
continue
sentence block;
LABEL
of
redo
statement means that the loop control flow is transferred directly to the first line of the current statement block to start execution instead of execution
redo
statement and the statement after the
continue
sentence block
for
loop or with
continue
statement block, then the
for
incremental list in the loop and
continue
statement blocks are no longer executed; 5.28.2. Flow chart #
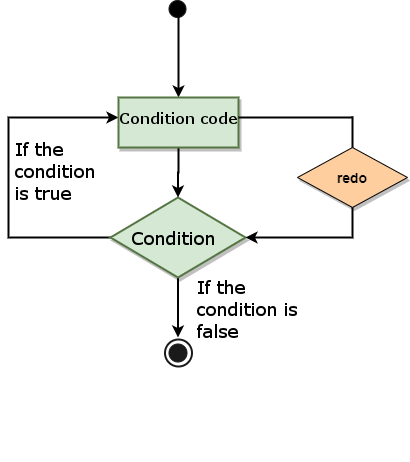
Example #
#/usr/bin/perl$a=0;while($a<10){if($a==5){$a=$a+1;redo;}print"a
=$a\\n";}continue{$a=$a+1;}
a = 0
a = 1
a = 2
a = 3
a = 4
a = 6
a = 7
a = 8
a = 9