A Slice is a partial reference to a data value.
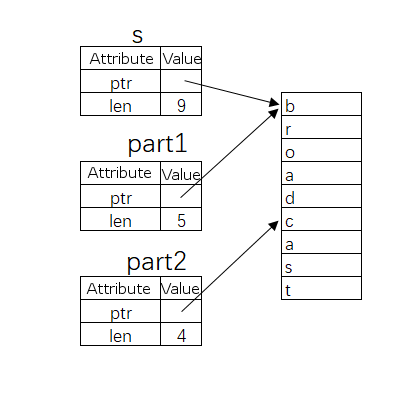
The name “slice” often appears in biology class. When we make sample slides, we have to take sections from organisms for observation under a microscope. In Rust, slicing means roughly the same thing, except that it isreferenced from data. The simplest and most commonly used data slicing type is string slicing. Running result: The figure above illustrates the principle of string slicing (Note: string types in Rust essentially record the starting position and length of characters in memory, as we learned for the time being). Use Note: so far, try not to use non-English characters in strings because of coding problems. The specific reasons will be described in the “string” section. A string referenced by a slice prohibits changing its value: This procedure is incorrect. S is partially referenced and it is forbidden to change its value. In fact, so far you must be wondering why you have to write this every time you use a string. At this point, we must tell the difference between the two concepts. There are two common string types in Rust: The overall type property of all string constants enclosed in double quotes is Here Note: the slicing result must be a reference type, but the developer must make this clear for himself: There is a quick way to change the In addition to strings, some other linear data structures also support slicing operations, such as arrays: Running result: 7.12.1. String slicing #
Example #
fn main() {
let s = String::from("broadcast");
let part1 = &s[0..5];
let part2 = &s[5..9];
println!("{}={}+{}", s, part1, part2);
}
broadcast=broad+cast
..
syntax for indicating the scope has appeared in the looping chapter.
x..y
represents the mathematical meaning of
[x,
y)
There can be no operands on
..
both sides:.. Y is equivalent to 0.. Y
x. Equivalent to position x to end of data
Equivalent to position 0 to end
Example #
fn main() {
let mut s = String::from("runoob");
let slice = &s[0..3];
s.push_str("yes!"); // error
println!("slice = {}", slice);
}
String::from("runoob")
write directly
"runoob"
, Can’t you?
str
and
String
.
str
is the Rust core language type, which is the string slicing (String Slice) thatthis chapter has been talking about, often in the form of references (& str).
&str
:let s = "hello";
s
is just one.
&str
a variable of type.
String
type is a data type provided by the Rust standard common library,and it is more functional-it supports practical operations such as string appending and emptying.
String
and
str
in addition to having a character start position attribute and a string length attribute, there is also a capacity attribute.
String
and
str
are all support slicing, and the result of slicing is
&str
type of data.let slice = &s[0..3];
String
convert to
&str
:let s1 = String::from("hello");
let s2 = &s1[..];
7.12.2. Non-string slice #
Example #
fn main() {
let arr = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9];
let part = &arr[0..3];
for i in part.iter() {
println!("{}", i);
}
}
1
3
5