Sometimes, we may need to execute the same piece of code multiple times. In general, statements are executed sequentially: the first statement in the function is executed first, then the second statement, and so on.
Programming languages provide a variety of control structures for more complex execution paths.
Loop statements allow us to execute a statement or group of statements multiple times. Here is a flowchart of loop statements in most programming languages:
The Swift language provides the following loop types. Click the link to viewa detailed description of each type: Cycle type Description For-in Iterate through all the elements in a set, such as intervals represented by numbers, elements in an array, characters in a string. For cycle Used to repeat a series of statements until specific conditions are met, usually by increasing the value of the counter after each loop is completed. While cycle Run a series of statements that, if the condition is true, run repeatedly until the condition becomes false. Repeat…while cycle A similar while statement differs from a block of code that executes a loop before determining a loop condition. Loop control statements change the order in which your code is executed, through which you can jump the code. Swift has the following loop control statements: Control statement Description Continue statement Tell a loop body to stop this loop iteration immediately and restart the next loop iteration. Break statement Interrupts the current loop. Fallthrough statement If you continue to execute the following case after a case has been executed, you need to use the fallthrough keyword.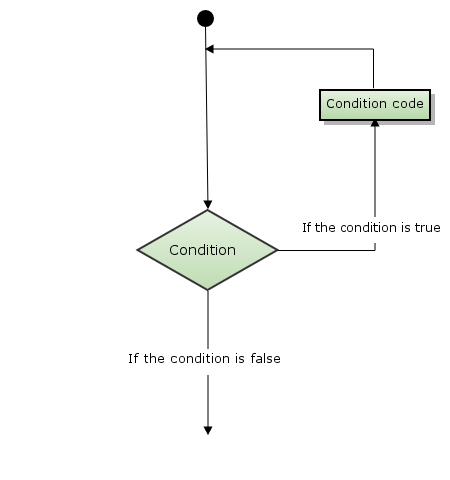
9.16.1. Cycle type #
9.16.2. Loop control statement #