A conditional statement executes the program through one or more conditions set, executing the specified statement when the condition is true, and when the condition is
false
executes another specified statement when the.
You can use the following figure to briefly understand the execution of conditional statements:
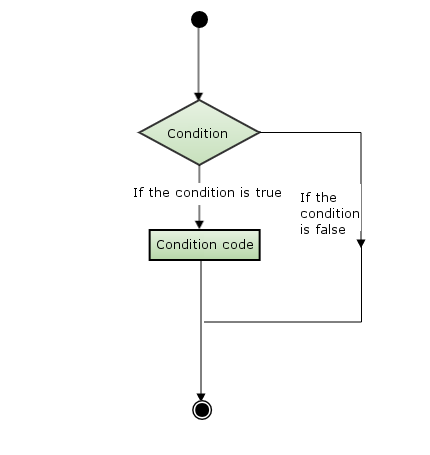
Swift provides the following types of conditional statements:
Cycle type | Description |
|---|---|
For-in | Iterate through all the elements in a set, such as intervals represented by numbers, elements in an array, characters in a string. |
For cycle | Used to repeat a series of statements until specific conditions are met, usually by increasing the value of the counter after each loop is completed. |
While cycle | Run a series of statements that, if the condition is true, run repeatedly until the condition becomes false. |
Repeat…while cycle | A similar while statement differs from a block of code that executes a loop before determining a loop condition. |
9.10.1.
?
:
Operator #
We have explained the conditional operator in the previous chapter
?
:
,can be used as a substitute
If.
Else
statement. Its general form is as follows:
Exp1 ? Exp2 : Exp3;
Where Exp1, Exp2, and Exp3 are expressions. Please note the use and locationof colons.
?
the value of the expression is determined by Exp1. If Exp1 is true, the value of Exp2 is calculated, and the result is the entire
?
the value of the expression. If Exp1 is false, the value of Exp3 is calculated, and the result is the entire
?
the value of the expression.