In this section, we will show you how to build an Angular form using components and templates.
Using Angular templates, we can create various types of forms, such as login forms, contact forms, product details forms, etc., and we also add data checks to the fields of these forms.
Next, let’s implement the function of the form step by step. Import initialization project. For a complete project creation, please refer to: Angular 2 TypeScript environment configuration Or download the source code directly: Click me to download After decompressing, change the directory name to angular-forms, and modify “name”: “angular-quickstart” in the angular-forms/package.json file to “name”: “angular-forms”. When it is finished, we execute A simple model class named In In the following code, labeled Each Angular form is divided into two parts: a HTML-based template and a code-based component that handles data and user interaction. In Instance is imported into the Modify Because template-driven forms have their own modules, we have to put The Modify the root component file Create a template file In open Execution Next, we use the Modify Every last Every last The output result of running the above instance is as follows: We can also pass through Status Class when it is true Class when it is false Control has already been accessed Ng-touched Ng-untouched The control value has changed Ng-dirty Ng-pristine The control value is valid Ng-valid Ng-invalid This allows us to add a custom CSS to reflect the state of the form. In open Modify In the template by setting the Delete Next, we create a form for adding a website, in the Bind the above button event to the component method: Let’s add one to the component We can use Angular’s instructions. We define a template reference variable This The The In the template, we put The main form is visible from the beginning because The final directory structure is: 1.7.1. Create a project ¶
cnpm
install
to load the dependency package. 1.7.2. Create a Site model ¶
Site
has been created, which includes three required fields:
id
,
name
, and
url
. One optional field is
alexa
.
angular-forms/app
create under the directory
site.ts
file, the code is as follows:
app/site.ts
file: ¶ export class Site {
constructor(
public id: number,
public name: string,
public url: string,
public alexa?: number
) { }
}
public
is a public field
alexa
, thenadd a question mark (?) Represents an optional field. 1.7.3. Create a form component ¶
angular-forms/app
create under the directory
site-form.component.ts
file, the code is as follows:
app/site-form.component.ts
file: ¶ import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { Site } from './site';
@Component({
moduleId: module.id,
selector: 'site-form',
templateUrl: 'site-form.component.html'
})
export class SiteFormComponent {
urls = ['www.runoob.com', 'www.google.com',
'www.taobao.com', 'www.facebook.com'];
model = new Site(1, 'Rookie Tutorial', this.urls[0], 10000);
submitted = false;
onSubmit() { this.submitted = true; }
// TODO: Remove after completion
get diagnostic() { return JSON.stringify(this.model); }
}
Component
decorator and
Site
model.
@Component
selector “site-form” indicates that we can pass through a
<site-form>
tag to throw this form into the parent template.
templateUrl
property points to a separate HTML template file called
site-form.component.html
.
diagnostic
property is used to return the JSON form of the model. 1.7.4. Define the root module of the application ¶
app.module.ts
to define the root module of the application, the module specifies the external referenced and declared components that belongto this module, such as
SiteFormComponent
.
FormsModule
added to this application
imports
array so that we can use the form.
app/app.module.ts
file code is as follows
app/app.module.ts
file: ¶ import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { SiteFormComponent } from './site-form.component';
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
FormsModule
],
declarations: [
AppComponent,
SiteFormComponent
],
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ]
})
export class AppModule { }
1.7.5. Create a root component ¶
app.component.ts
, set the
SiteFormComponent
put it in it.
app/app.component.ts
file: ¶ import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
template: '<site-form></site-form>'
})
export class AppComponent { }
1.7.6. Create an initial HTML form template ¶
site-form.component.html
the code is as follows:
app/site-form.component.html
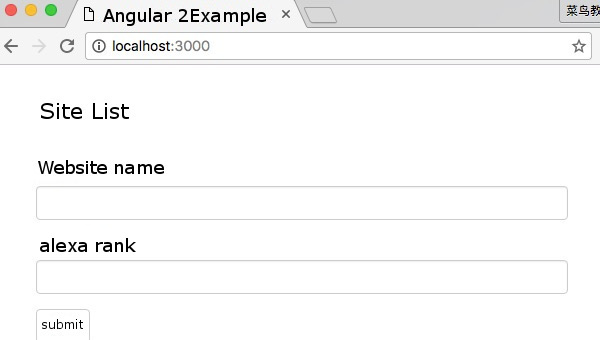
file: ¶ <div class="container">
<h1>Website Forms</h1>
<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="name">Website Name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="name" required>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="alexa">alexa ranking</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="alexa">
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-default">submit to</button>
</form>
</div>
required
property is a required field, or optional if it is not set.
angular-forms
enter the following command in the directory:cnpm install bootstrap --save
index.html
file, add the following style links to the
<head>
:<linkrel="stylesheet"href="node_modules/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css">
npm
start
visit: http://localhost:3000/ , and the output effect is as follows: 1.7.7. Use
ngModel
perform two-way data binding ¶
ngModel
perform two-way data binding to update the properties of the component by listening for DOM events.
app/site-form.component.html
, using the
ngModel
bind our form to the model. The code is as follows:
app/site-form.component.html
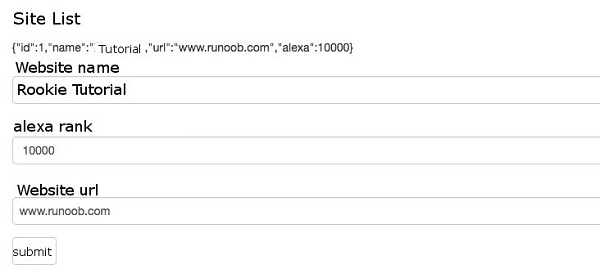
file: ¶ <div class="container">
<h1>Website Forms</h1>
<form>
{{diagnostic}}
<div class="form-group">
<label for="name">Website Name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="name"
required
[(ngModel)]="model.name" name="name">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="alexa">alexa ranking</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="alexa"
[(ngModel)]="model.alexa" name="alexa">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="url">website URL </label>
<select class="form-control" id="url"
required
[(ngModel)]="model.url" name="url">
<option *ngFor="let p of urls" [value]="p">{{p}}</option>
</select>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-default">submit to</button>
</form>
</div>
input
every element has one.
id
property, which is defined by the
label
of the element
for
property is used to match the tag to the corresponding
input
.
input
every element has one.
name
property, which is needed by Angular’s form module to register the controller for the form.
{{diagnostic}}
is only used to output data during testing.
ngModel
tracking modification status and validation, it uses three CSS classes to update the control to reflect the current state.
angular-forms
create under the directory
forms.css
file, the code is as follows:
forms.css
file: ¶ .ng-valid[required], .ng-valid.required {
border-left: 5px solid #42A948; /* green */
}
.ng-invalid:not(form) {
border-left: 5px solid #a94442; /* red */
}
index.html
file, add the following style links to the
<head>
:<linkrel="stylesheet"href="forms.css">
app/site-form.component.html
code is as follows:
app/site-form.component.html
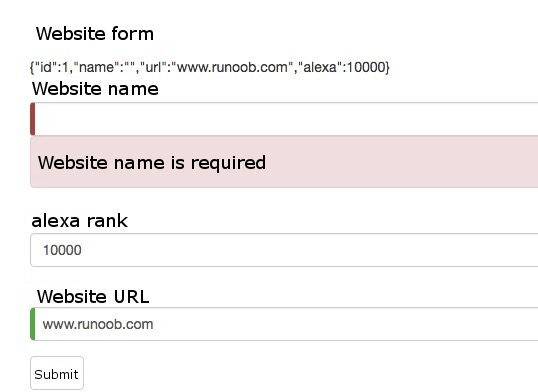
file: ¶ <div class="container">
<h1>Website Forms</h1>
<form>
{{diagnostic}}
<div class="form-group">
<label for="name">Website Name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="name"
required
[(ngModel)]="model.name" name="name"
#name="ngModel" >
<div [hidden]="name.valid || name.pristine"
class="alert alert-danger">
Website name is required
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="alexa">alexa ranking</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="alexa"
[(ngModel)]="model.alexa" name="alexa">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="url">website URL </label>
<select class="form-control" id="url"
required
[(ngModel)]="model.url" name="url">
<option *ngFor="let p of urls" [value]="p">{{p}}</option>
</select>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-default">submit to</button>
</form>
</div>
div
of the element
hidden
property is bound to the
name
control, we can control the visibility of error messages in the “name” field.
name
field, and the display result is as follows: 1.7.8. Add a website ¶
app/site-form.component.html
add a button:
app/site-form.component.html
file: ¶ <button type="button" class="btn btn-default" (click)="newSite()">Add a Site</button>
app/site-form.component.ts
file: ¶ active = true;
newSite() {
this.model = new Site(5, '', '');
this.active = false;
setTimeout(() => this.active = true, 0);
}
active
tag, initializing it to
true
. When we add a new website, it puts
active
tag is set to
false
and then through a fast
setTimeout
function quickly sets it back to
true
. 1.7.9. Pass through
ngSubmit
to submit the form ¶
NgSubmit
to submit the form and bind it to the
SiteFormComponent.submit()
in a way.<form *ngIf="active" (ngSubmit)="onSubmit()" #siteForm="ngForm">
#siteForm
and initialize it to “ngForm”
siteForm
variable now refers to
NgForm
instruction, which represents the form as a whole.
site-form.component.ts
complete code of the file is as follows:
app/site-form.component.ts
file: ¶ import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { Site } from './site';
@Component({
moduleId: module.id,
selector: 'site-form',
templateUrl: 'site-form.component.html'
})
export class SiteFormComponent {
urls = ['www.runoob.com', 'www.google.com',
'www.taobao.com', 'www.facebook.com'];
model = new Site(1, 'Rookie Tutorial', this.urls[0], 10000);
submitted = false;
onSubmit() { this.submitted = true; }
// TODO: Remove after completion
get diagnostic() { return JSON.stringify(this.model); }
active = true;
newSite() {
this.model = new Site(5, '', '');
this.active = false;
setTimeout(() => this.active = true, 0);
}
}
app/site-form.component.html
complete code is as follows:
app/site-form.component.html
file: ¶ <div class="container">
<div [hidden]="submitted">
<h1>Website Forms</h1>
<form *ngIf="active" (ngSubmit)="onSubmit()" #siteForm="ngForm">
{{diagnostic}}
<div class="form-group">
<label for="name">Website Name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="name"
required
[(ngModel)]="model.name" name="name"
#name="ngModel" >
<div [hidden]="name.valid || name.pristine"
class="alert alert-danger">
Website name is required
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="alexa">alexa ranking</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="alexa"
[(ngModel)]="model.alexa" name="alexa">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="url">website URL </label>
<select class="form-control" id="url"
required
[(ngModel)]="model.url" name="url">
<option *ngFor="let p of urls" [value]="p">{{p}}</option>
</select>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-default" [disabled]="!siteForm.form.valid">submit to</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-default" (click)="newSite()">New website added</button>
</form>
</div>
<div [hidden]="!submitted">
<h2>The information you submitted is as follows:</h2>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-3">Website Name</div>
<div class="col-xs-9 pull-left">{{ model.name }}</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-3">Website alexa Ranking</div>
<div class="col-xs-9 pull-left">{{ model.alexa }}</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-xs-3">Website URL </div>
<div class="col-xs-9 pull-left">{{ model.url }}</div>
</div>
<br>
<button class="btn btn-default" (click)="submitted=false">edit</button>
</div>
</div>
hidden
property is bound to the
SiteFormComponent.submitted
property.
submitted
the property is
false
, when we submit this form, it is hidden
submitted
the property is
true
:submitted = false;
onSubmit() { this.submitted = true; }