Recommended for Vue version
axios
to finish
ajax
request.
Axios is a Promise-based HTTP library that can be used in browsers and
node.js
.
Github open source address: https://github.com/axios/axios Use Or Use Use Use How to use it: We can simply read JSON data: Use It can be done by calling the For ease of use, the official provides aliases for all supported request methods, and you can directly use aliases to initiate requests: Note: when using alias methods Helper functions that handle concurrent requests: You can create a new one using a custom configuration The following are the available instance methods. The specified configuration is merged with the configuration of the instance: The following are the configuration options available when creating a request, note that only Use When use You can specify the configuration default values that will be used for each request. Global Custom instance defaults: Configurations are merged in a priority order. The order is: in After the request or response is If you want to remove the interceptor later, you can do this: Can be customized for Error handling: Can be used Use Axios’s Can be used You can also pass a Note: you can use the same browser In a browser environment, you can use URLSearchParams API: In addition, you can use the In Of course, like browsers, you can also use the If your environment does not support ES6 Promise, you can use the `polyfill<https://github.com/jakearchibald/es6-promise>`__ . 2.19.1. Installation method ¶
cdn
:<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/axios/0.18.0/axios.min.js"></script>
npm
:$ npm install axios
bower
:$ bower install axios
yarn
:$ yarn add axios
Vue.axios.get(api).then((response) => {
console.log(response.data)
})
this.axios.get(api).then((response) => {
console.log(response.data)
})
this.$http.get(api).then((response) => {
console.log(response.data)
})
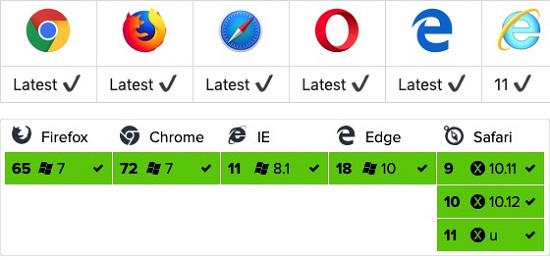
2.19.2. Browser support ¶
2.19.3. GET method ¶
GET instance ¶
constapp={data(){return{info:'Ajax
test!!'}},mounted(){axios.get('https://www.runoob.com/try/ajax/json_demo.json').
then(response=>(this.info=response)).catch(function(error)
{//Request failure handling console.log(error);});}}Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')
response.data
read JSON data:GET instance ¶
<divid="app"><h1>Website List</h1><divv-for="site in info">{{ site.name
}}</div></div><scripttype="text/javascript">const app = { data() {
return { info: 'Ajax test!!' } }, mounted () { axios
.get('https://www.runoob.com/try/ajax/json_demo.json') .then(response =>
(this.info = response)) .catch(function (error) { // Request failure handling
console.log(error); }); } } Vue.createApp(app).mount('#app')</script>
GET
format of parameters passed by the method is as follows:Pass parameter description ¶
//Add parameters directly to the URL
ID=12345axios.get('/user?ID=12345').then(function(response){console.log(response);}).
catch(function(error){console.log(error);});//It can also be achieved through
params
Set parameters:axios.get('/user',{params:{ID:12345}}).then(function(response)
{console.log(response);}).catch(function(error){console.log(error);});
2.19.4. POST method ¶
POST instance ¶
newVue({el:'#app',data(){return{info:null}},mounted(){axios.post
('https://www.runoob.com/try/ajax/demo_axios_post.php').then(response=>(this.info=response)).
catch(function(error){//Request failure handling console.log(error);});}})
POST
format of parameters passed by the method is as follows:Pass parameter description ¶
axios.post('/user',{firstName:'Fred',//parameter
firstNamelastName:'Flintstone'//parameter
lastName}).then(function(response){console.log(response);}).
catch(function(error){console.log(error);});
2.19.5. Execute multiple concurrent requests ¶
Example ¶
functiongetUserAccount(){returnaxios.get('/user/12345');}functiongetUserPermissions()
{returnaxios.get('/user/12345/permissions');}axios.all([getUserAccount(),
getUserPermissions()]).then(axios.spread(function(acct,perms){//Both requests are now completed}));
2.19.6. Axios API ¶
axios
pass the relevant configuration to create the request.Example ¶
axios(config)//sending POST
request axios({method:'post',url:'/user/12345',data:{firstName:'Fred',lastName:'Flintstone'}});//GET
Request remote image axios({method:'get',url:'http://bit.ly/2mTM3nY',responseType:'stream'}).
then(function(response){response.data.pipe(fs.createWriteStream('ada_lovelace.jpg'))});axios(url[,config])//sent
GET Request (default method) axios('/user/12345');
2.19.7. Alias of the request method ¶
axios.request(config)
axios.get(url[, config])
axios.delete(url[, config])
axios.head(url[, config])
axios.post(url[, data[, config]])
axios.put(url[, data[, config]])
axios.patch(url[, data[, config]])
url
、
method
、
data
none of these properties need to be specified in the configuration. 2.19.8. Concurrence ¶
axios.all(iterable)
axios.spread(callback)
2.19.9. Create an instance ¶
axios
example:axios.create([config])
const instance = axios.create({
baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/',
timeout: 1000,
headers: {'X-Custom-Header': 'foobar'}
});
2.19.10. Example method ¶
axios#request(config)
axios#get(url[, config])
axios#delete(url[, config])
axios#head(url[, config])
axios#post(url[, data[, config]])
axios#put(url[, data[, config]])
axios#patch(url[, data[, config]])
2.19.11. Request configuration item ¶
url
is necessary. If not specified
method
the request will be used by default
get
method.{
// `url` is a server used for requests URL
url: "/user",
// `method` is the method used when creating a request
method: "get", // Default is get
// `BaseURL` will automatically be added before `URL` unless `URL` is an absolute URL.
// It can facilitate passing relative URLs for axios instance methods by setting a `baseURL`
baseURL: "https://some-domain.com/api/",
// `transformRequest` Allow modification of request data before sending to the server
// Can only be used in request methods such as "PUT", "POST", and "PATCH"
// The function in the subsequent array must return a string, or ArrayBuffer,or Stream
transformRequest: [function (data) {
// Perform arbitrary conversion processing on data
return data;
}],
// `transformResponse` allow modification of response data before passing to then/catch
transformResponse: [function (data) {
// Perform arbitrary conversion processing on data
return data;
}],
// `headers` is the custom request header that will be sent soon
headers: {"X-Requested-With": "XMLHttpRequest"},
// `params` is the URL parameter to be sent together with the request
// Must be a plain object or URLSearchParams object
params: {
ID: 12345
},
// `paramsSerializer` is a function responsible for serializing `params`
// (e.g. https://www.npmjs.com/package/qs, http://api.jquery.com/jquery.param/)
paramsSerializer: function(params) {
return Qs.stringify(params, {arrayFormat: "brackets"})
},
// `data` is the data sent as the requesting subject
// Only applicable to these request methods "PUT", "POST", and "PATCH"
// When `transformRequest` is not set, it must be one of the following types:
// - string, plain object, ArrayBuffer, ArrayBufferView, URLSearchParams
// - Browser exclusive:FormData, File, Blob
// - Node exclusive: Stream
data: {
firstName: "Fred"
},
// `timeout` Specify the number of milliseconds for request timeout (0 indicates no timeout)
// If the request takes more than 'timeout', the request will be interrupted
timeout: 1000,
// `withCredentials` indicates whether credentials are required for cross domain requests
withCredentials: false, // default
// `adapter` allow custom processing of requests to make testing easier
// Return a promise and apply a valid response (refer to [response docs](#response-api)).
adapter: function (config) {
/* ... */
},
// `auth` indicates that HTTP basic authentication should be used and credentials should be provided
// This will set an `Authorization` header to overwrite any existing custom `Authorization` headers set using `headers`
auth: {
username: "janedoe",
password: "s00pers3cret"
},
// `responseType` The data type representing the server response can be "arraybuffer", "blob", "document", "json", "text", "stream"
responseType: "json", // default
// `xsrfCookieName` the name of the cookie used as the value for the xsrf token
xsrfCookieName: "XSRF-TOKEN", // default
// `xsrfHeaderName` the name of the HTTP header that carries the value of the xsrf token
xsrfHeaderName: "X-XSRF-TOKEN", // default
// `onUploadProgress` allow processing progress events for uploading
onUploadProgress: function (progressEvent) {
// Handling native progress events
},
// `onDownloadProgress` allow processing progress events for downloads
onDownloadProgress: function (progressEvent) {
// Handling native progress events
},
// `maxContentLength` Define the maximum size of allowed response content
maxContentLength: 2000,
// `validateStatus` define whether the given HTTP response status code is resolve or reject promise.
If `validateStatus` return `true` (Or set to `null` or `undefined`),promise will be resolve;
Otherwise, the promise will be rejected
validateStatus: function (status) {
return status >= 200 && status < 300; // default
},
// `maxRedirects` define the maximum number of redirects to follow in node.js
// If set to 0, no redirection will be followed
maxRedirects: 5, // default
// `httpAgent` and `httpsAgent` used in node.js to define custom proxies to be
used when executing HTTP and HTTPS, respectively. Allow configuration options like this:
// `keepAlive` is not enabled by default
httpAgent: new http.Agent({ keepAlive: true }),
httpsAgent: new https.Agent({ keepAlive: true }),
// "proxy" define the host name and port of the proxy server
// `auth` indicates that HTTP basic authentication should be used to connect to the proxy and provide credentials
// This will set a `Proxy Authorization` header,Overwrite existing custom `Proxy Authorization` headers set by using `header`.
proxy: {
host: "127.0.0.1",
port: 9000,
auth: : {
username: "mikeymike",
password: "rapunz3l"
}
},
// `cancelToken` specify for canceling requests cancel token
// (Check out the Cancellation section later to learn more)
cancelToken: new CancelToken(function (cancel) {
})
}
2.19.12. Response structure ¶
axios
response to the request contains the following information:{
// `data` response provided by the server
data: {},
// `status` HTTP status
status: 200,
// `statusText` HTTP status information from server response
statusText: "OK",
// `headers` server response header
headers: {},
// `config` is the configuration information provided for the request
config: {}
}
then
the following response is received:axios.get("/user/12345")
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response.data);
console.log(response.status);
console.log(response.statusText);
console.log(response.headers);
console.log(response.config);
});
catch
,or pass rejection callback as
then
the response can pass through the second parameter of
error
object can be used. 2.19.13. Default values for configuration ¶
axios
default value:axios.defaults.baseURL = 'https://api.example.com';
axios.defaults.headers.common['Authorization'] = AUTH_TOKEN;
axios.defaults.headers.post['Content-Type'] = 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded';
// Set default values for configuration when creating an instance
var instance = axios.create({
baseURL: 'https://api.example.com'
});
// Modify default values after the instance has been created
instance.defaults.headers.common['Authorization'] = AUTH_TOKEN;
2.19.14. Priority of configuration ¶
lib/defaults.js
the default value of the library found, followed by the instance’s
defaults
property, and finally the requested
config
parameters. The latter will take precedence over the former. Here is an example:// Create an instance using the default values of the configuration provided by the library
// The default value for timeout configuration at this time is `0`
var instance = axios.create();
// Overwrite library timeout default value
// Now, before timeout, all requests will wait for 2.5 seconds
instance.defaults.timeout = 2500;
// Overwrite timeout settings for requests that are known to take a long time
instance.get('/longRequest', {
timeout: 5000
});
2.19.15. Interceptor ¶
then
or
catch
intercept them before processing.// Add request interceptor
axios.interceptors.request.use(function (config) {
// What to do before sending a request
return config;
}, function (error) {
// What to do about request errors
return Promise.reject(error);
});
// Add response interceptor
axios.interceptors.response.use(function (response) {
// Do something about the response data
return response;
}, function (error) {
// Do something about response errors
return Promise.reject(error);
});
var myInterceptor = axios.interceptors.request.use(function () {/*...*/});
axios.interceptors.request.eject(myInterceptor);
axios
instance to add an interceptor.var instance = axios.create();
instance.interceptors.request.use(function () {/*...*/});
axios.get('/user/12345')
.catch(function (error) {
if (error.response) {
// The request has been sent, but the status code of the server response is not within the range of 2xx
console.log(error.response.data);
console.log(error.response.status);
console.log(error.response.headers);
} else {
// Something happened in setting up the request that triggered an Error
console.log('Error', error.message);
}
console.log(error.config);
});
validateStatus
the configuration option defines an error range for a custom HTTP status code.axios.get('/user/12345', {
validateStatus: function (status) {
return status < 500; // Only reject when the status code is greater than or equal to 500
}
})
2.19.16. cancel ¶
cancel
token
cancel the request.
cancel
token
API based on cancelable promises proposal
CancelToken.source
factory method creation
cancel
token
, like this:var CancelToken = axios.CancelToken;
var source = CancelToken.source();
axios.get('/user/12345', {
cancelToken: source.token
}).catch(function(thrown) {
if (axios.isCancel(thrown)) {
console.log('Request canceled', thrown.message);
} else {
// process error
}
});
// Cancel request (message parameter is optional)
source.cancel('Operation canceled by the user.');
executor
function to
CancelToken
to create a
cancel
,
token
:var CancelToken = axios.CancelToken;
var cancel;
axios.get('/user/12345', {
cancelToken: new CancelToken(function executor(c) {
// executor The function takes a cancel function as a parameter
cancel = c;
})
});
// Cancel request
cancel();
cancel
token
cancel multiple requests. 2.19.17. Use when requesting
application/x-www-form-urlencoded
¶
axios
JavaScript object is serialized to JSON by default. If you want to use the
application/x-www-form-urlencoded
format, you can use the following configuration.const params = new URLSearchParams();
params.append('param1', 'value1');
params.append('param2', 'value2');
axios.post('/foo', params);
URLSearchParams
not all browsers support it.
qs
library to encode the data:const qs = require('qs');
axios.post('/foo', qs.stringify({ 'bar': 123 }));
// Or in another way (ES6),
import qs from 'qs';
const data = { 'bar': 123 };
const options = {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'content-type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded' },
data: qs.stringify(data),
url,
};
axios(options);
2.19.18.
Node.js
environment ¶
node.js
can use the
querystring
module:const querystring = require('querystring');
axios.post('http://something.com/', querystring.stringify({ foo: 'bar' }));
qs
library. 2.19.19. Promises ¶
axios
relying on the native ES6 Promise implementation supported . 2.19.20. TypeScript support ¶
axios
contains the definition of TypeScript.import axios from "axios";
axios.get("/user?ID=12345");