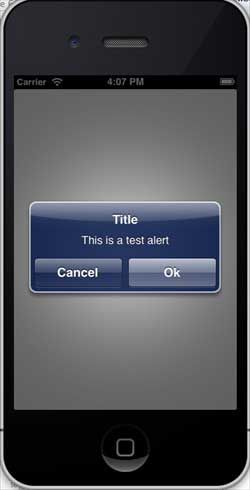
The warning dialog box is used to provide important information to the user.
You can proceed to further use the application only after you select an option in the warning dialog box view. AlertViewStyle CancelButtonIndex Delegate Message NumberOfButtons Title 让类符合警告对话框视图的委托协议,如下所示,在ViewController.h中添加<UIAlertViewDelegate> Now when we run the application, we will see the following output: 9.26.1. Important attribute ¶
An important method ¶
- (NSInteger)addButtonWithTitle:(NSString *)title
- (NSString *)buttonTitleAtIndex:(NSInteger)buttonIndex
- (void)dismissWithClickedButtonIndex:
(NSInteger)buttonIndex animated:(BOOL)animated
- (id)initWithTitle:(NSString *)title message:
(NSString *)message delegate:(id)delegate
cancelButtonTitle:(NSString *)cancelButtonTitle
otherButtonTitles:(NSString*)otherButtonTitles, ...
- (void)show
9.26.2. Update ViewController.h, as shown below ¶
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
@interface ViewController : UIViewController<UIAlertViewDelegate>{
}
@end
Add a custom method addAlertView ¶
-(void)addAlertView{
UIAlertView *alertView = [[UIAlertView alloc]initWithTitle:
@"Title" message:@"This is a test alert" delegate:self
cancelButtonTitle:@"Cancel" otherButtonTitles:@"Ok", nil];
[alertView show];
}
Execute the delegate method for the warning dialog view ¶
#pragma mark - Alert view delegate
- (void)alertView:(UIAlertView *)alertView clickedButtonAtIndex:
(NSInteger)buttonIndex{
switch (buttonIndex) {
case 0:
NSLog(@"Cancel button clicked");
break;
case 1:
NSLog(@"OK button clicked");
break;
default:
break;
}
}
Modify the viewDidLoad in ViewController.m, as follows ¶
(void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
[self addAlertView];
}
9.26.3. Output ¶