In iOS, action and Outlet refer to ibActions and ibOutlets, where the ib interface generator is located. All of these are related to the UI element, and we will learn about them visually and explore how to implement them. Step =
Let’s use the first iPhone application.
2、从导航部分中的文件中选择ViewController.xib文件
3、从右手边得窗口下面显示的窗口格库中选择UI元素
4、拖拽UI元素到界面生成器的可视框中
5、添加标签和红色圆形按钮到可视图中
6、在工作区工具栏的右上角找到编辑器选择按钮,如下图所示
选择编辑器按钮
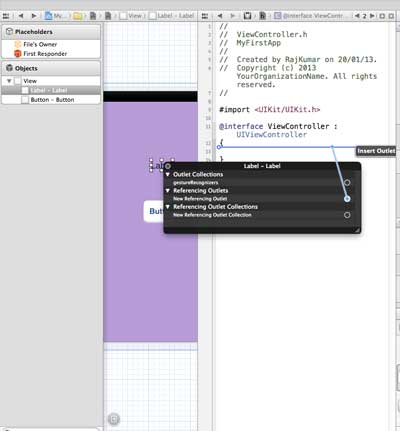
7、编辑器区域中心有两个窗口,ViewController.xib文件和ViewController.h
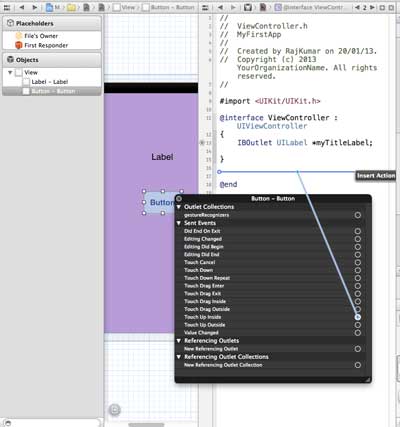
8、右击标签上的选择按钮,按住并拖动新引用参照,如下所示
9、现在放在ViewController.h之间的大括号中。也可以放在文件中,如果是这样,必须在做这个之前已经添加了。如下所示
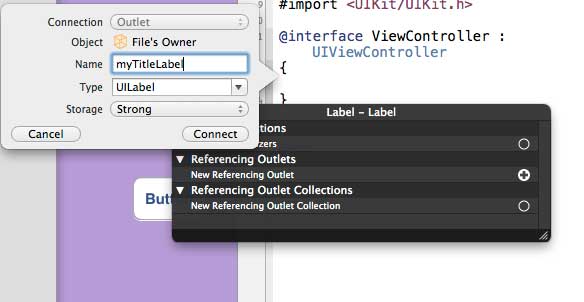
10. 输入输出口(Outlet)的标签名称,这里给出的是myTitleLable。单击链接,完成ibOutlet
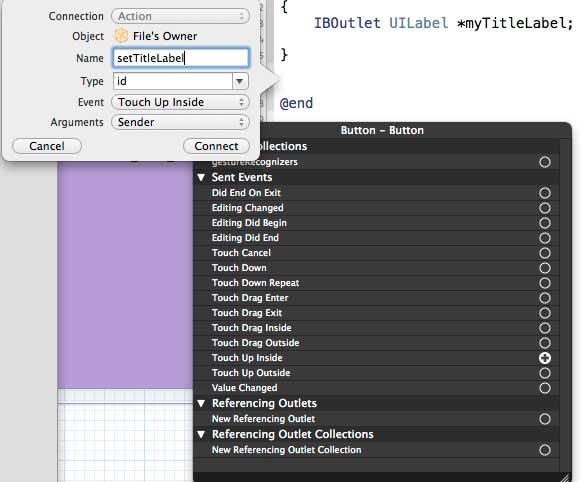
Similarly, to add an operation, simply right-click the rounded rectangle and choose to touch the heart and drag the curly braces below it
12、重新命名为setTitleLable
13、 选择ViewController.m文件,有一种方法,如下所示
-(IBAction) setTitleLabel:(id)sender{
}
14、在上述的方法内,如下所示,添加一个语句
[myTitleLabel setTitleText:@"Hello"];
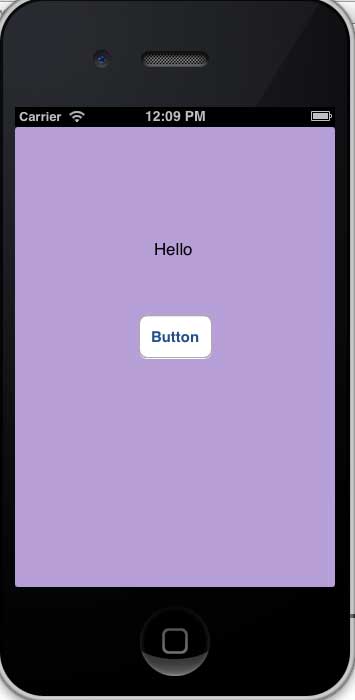
15、选择运行按钮运行该程序,得到如下的输出
16、单击按钮
17.、创建的参照(outlets)按钮标签已更改为对按钮执行的操作(actions)
As you can see from the above, IBOutlet will create a reference to UIElement (in this case, UILable), and the same IBAction and UIButton will be linked to UIButton by performing actions.
When creating an action, you can do different actions by selecting different events.