5.22.1. I. the concept and its introduction ¶
And lookup set is a kind of tree data structure, which is used to deal with the merge and query of some disjoint sets.
The idea of searching sets is to use an array to represent the whole forest (parent). The root node of the tree uniquely identifies a set. As long as we find the root of an element, we can determine which set it is in.
5.22.2. II. Applicable instructions ¶
And check the collection to be used in some N In the application of the collection of elements, we usually start by making each element form a collection of single elements, and then merge the sets of elements that belong to the same group in a certain order, during which we repeatedly find out which set an element is in. This process does not seem to be complex, but the amount of data is extremely large, if described by other data structures, it is often too large in space, the computer can not bear, and can not calculate the results in a short time, so we can only use and look up sets to deal with.
5.22.3. Third, the basic data representation of parallel search sets ¶
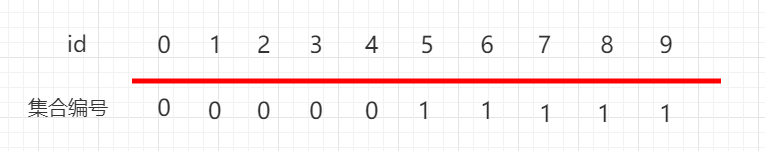
如上图 0-4 下面都是 0 , 5-9 下面都是 1 ,表示 0、1、2、3、4 这五个元素是相连接的, 5、6、7、8、9 这五个元素是相连的。

Again, as shown above. 0、2、4、6、8 It’s all below. 0 This collection represents 0、2、4、6、8 These five elements are connected. 1、3、5、7、9 It’s all below. 1 This collection represents 0,1、3、5、7、9 These five elements are connected.
Construct a class UnionFind, initialize each id [i] Point to yourself, there are no merged elements:
...
public UnionFind1(int n) {
count = n;
id = new int[n];
// 初始化, 每一个id[i]指向自己, 没有合并的元素
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
id[i] = i;
}
...
5.22.4. Java instance code ¶
源码包下载: Download UnionFind.java file code: ¶
package runoob.union;
public class UnionFind{
private int[] id;
// 数据个数
private int count;
public UnionFind1(int n) {
count = n;
id = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
id[i] = i;
}
}