Django middleware is a hook that modifies Django request or response objects, which can be understood as a process between HttpRequest and HttpResponse processing.
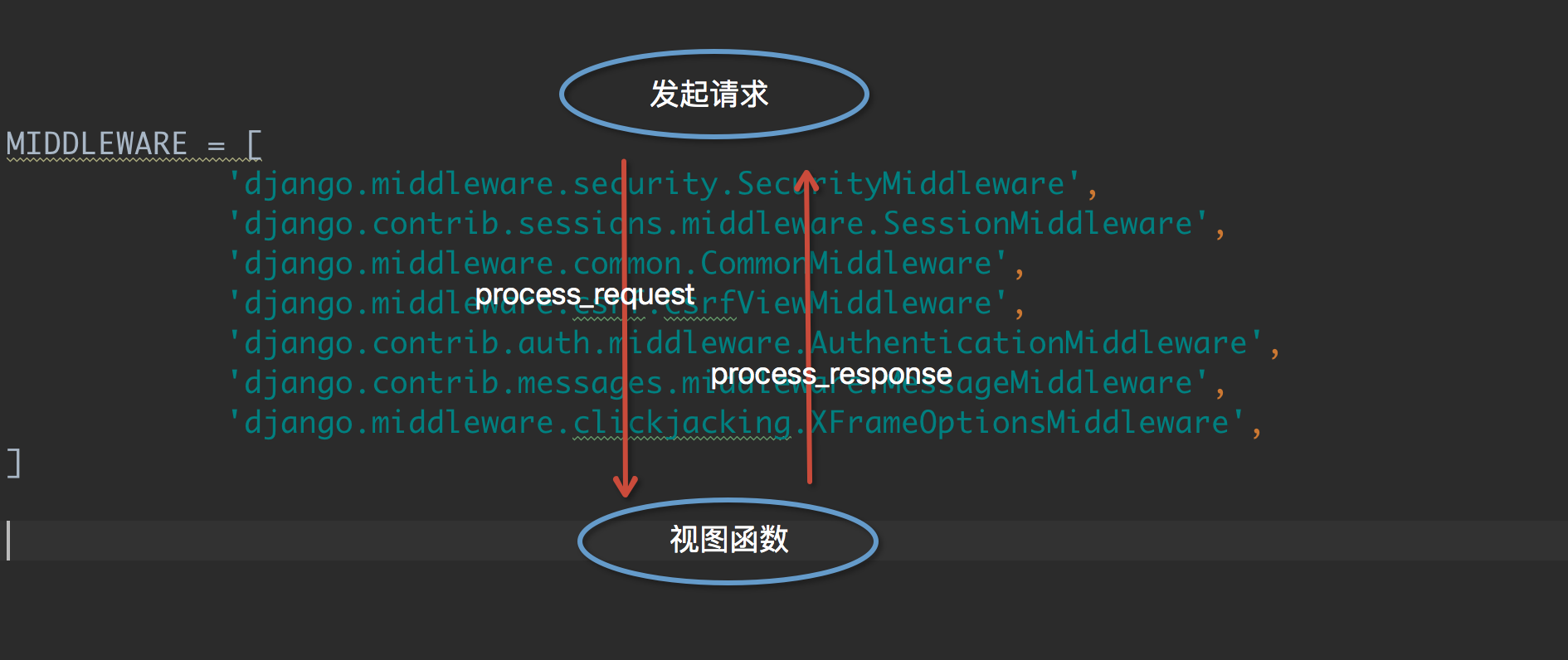
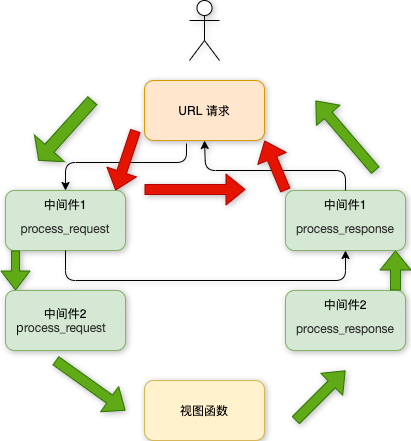
In the process of browser from request to response, Django needs to be processed through a lot of middleware, as shown in the following figure:

The role of Django middleware:
The modification request, which is passed to the HttpRequest object in view.
Modify the response, that is, the HttpResponse object returned by view.
Middleware components are configured in the list of MIDDLEWARE options in the settings.py file.
Each string option in the configuration is a class, that is, a middleware. Django default middleware configuration:
MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware',
'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware',
'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware',
'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware',
'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware',
]
7.17.1. Custom middleware ¶
Middleware can define four methods, which are:
process_request(self,request)
process_view(self, request, view_func, view_args, view_kwargs)
process_exception(self, request, exception)
process_response(self, request, response)
Customize the middle steps:
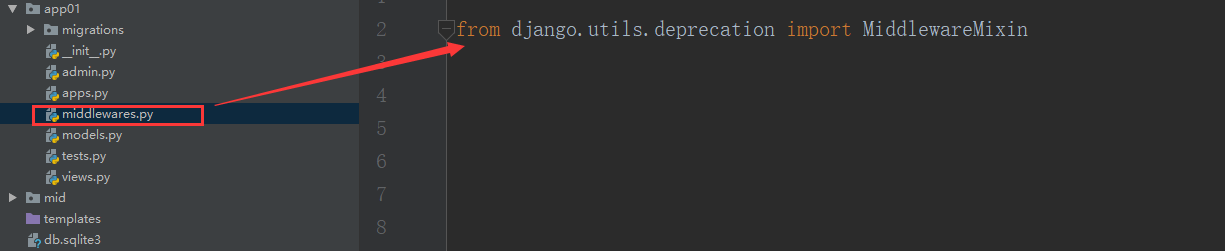
Create a new py file under the app directory with a custom name, and import MiddlewareMixin into the py file:
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
A custom middleware class that inherits the parent class MiddlewareMixin:
class MD1(MiddlewareMixin):
pass
Register the custom middleware class in MIDDLEWARE in settings.py:
MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware',
'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware',
'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware',
'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware',
'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware',
'app01.middlewares.MD1',
]
7.17.2. Methods for customizing middleware classes ¶
The methods to customize the middleware class are: process_request and process_response.
7.17.3. Process_request method ¶
The process_request method has a parameter request, which is the same as the request in the view function.
The return value of the process_request method can be either a None or a HttpResponse object.
If the return value is None, follow the normal process and give it to the next middleware for processing.
The return value is the HttpResponse object, and Django will not execute the methods and view functions executed before the subsequent view functions, but directly start with the middleware and execute the middleware in reverse order, and execute the methods executed after the view functions.
The process_request method is executed before the view function.
When multiple middleware is configured, it is executed according to the registration order in MIDDLEWARE, that is, the index value of the list.
The request parameters passed between different middleware are all the same request object.Example ¶
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse
class MD1(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print("md1 process_request 方法。", id(request)) #在视图之前执行
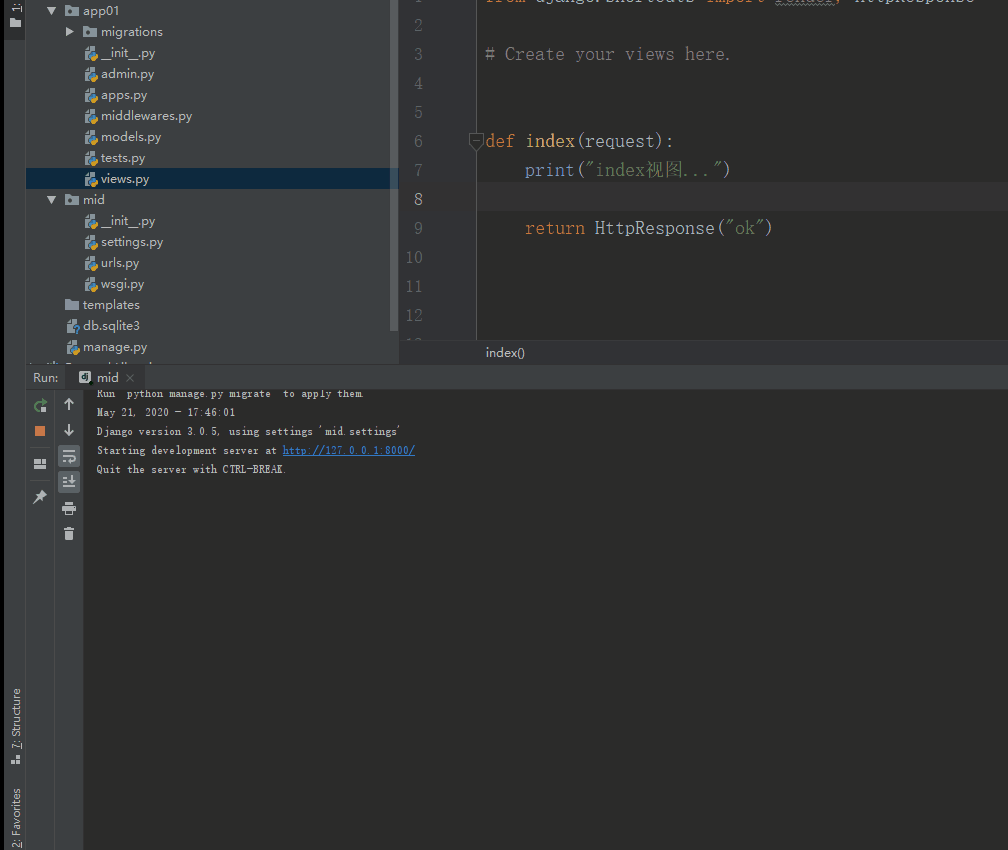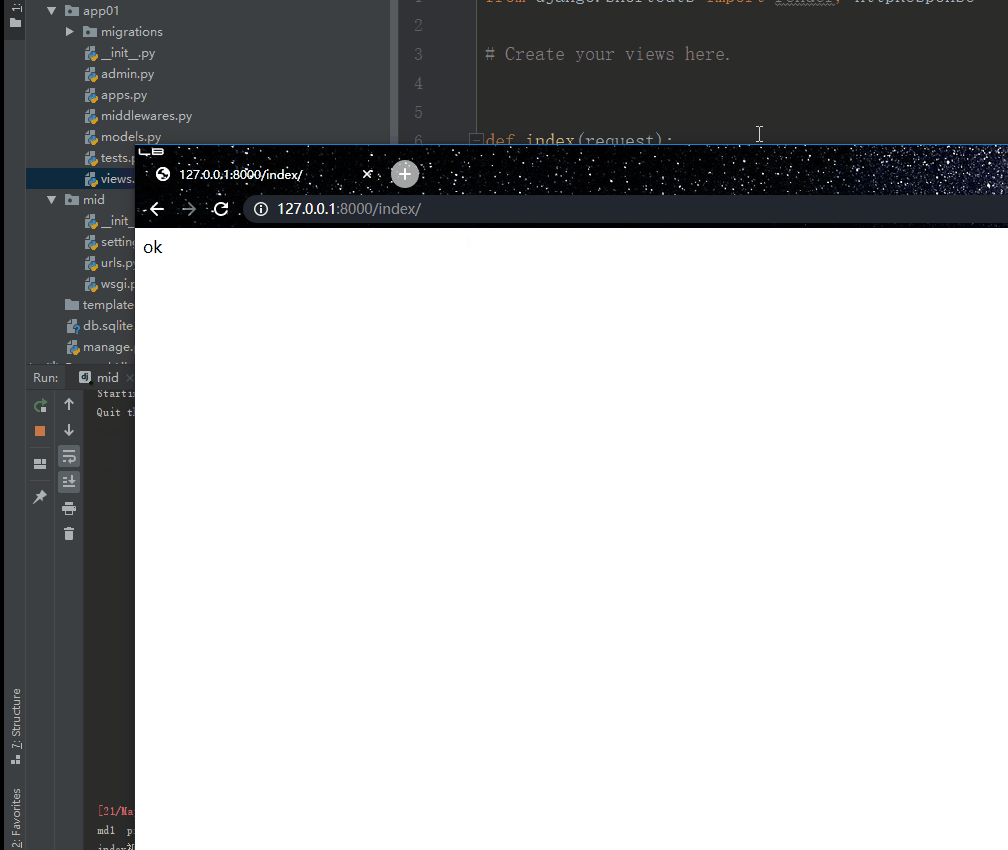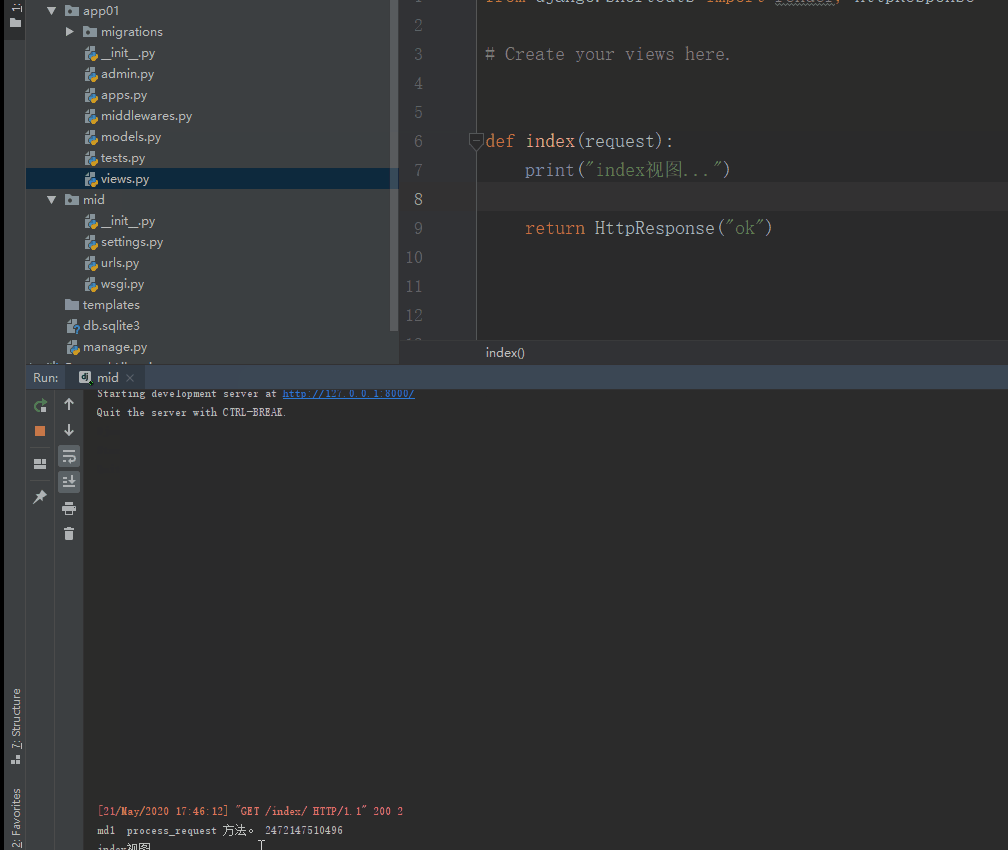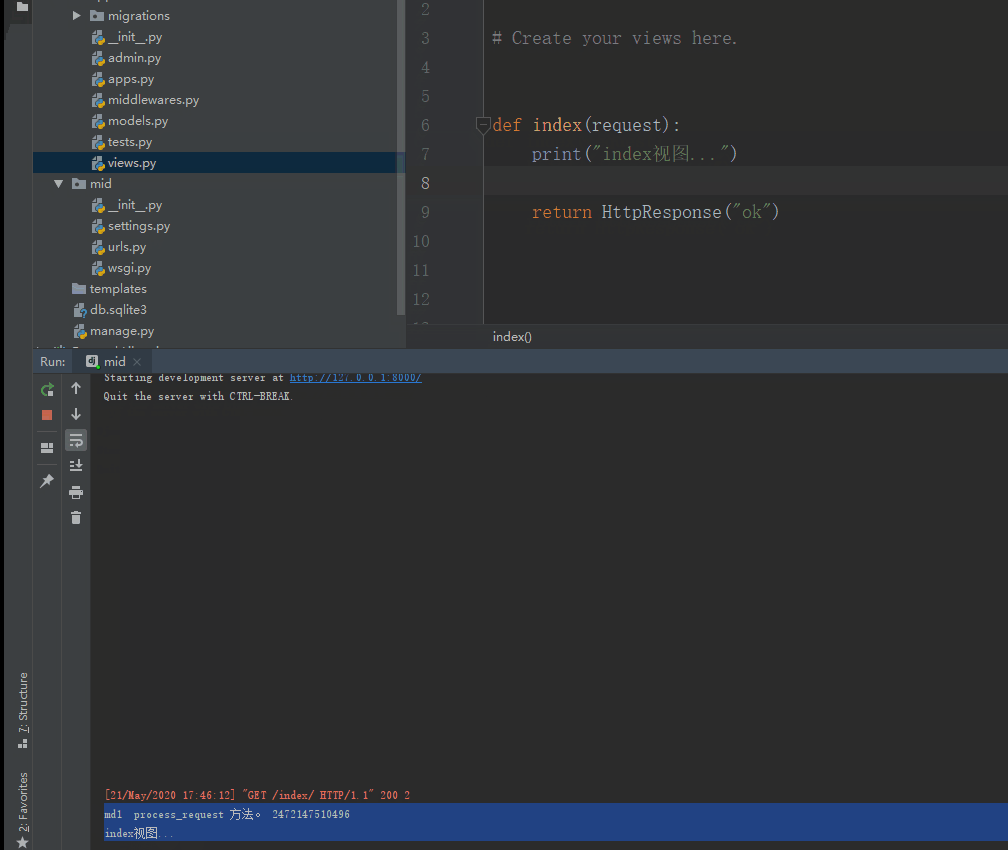
7.17.4. process_response ¶
The process_response method has two parameters, one is request, the other is response,request is the request object, and response is the HttpResponse object returned by the view function. The method must have a return value and must be response.
The process_response method is executed after the view function.
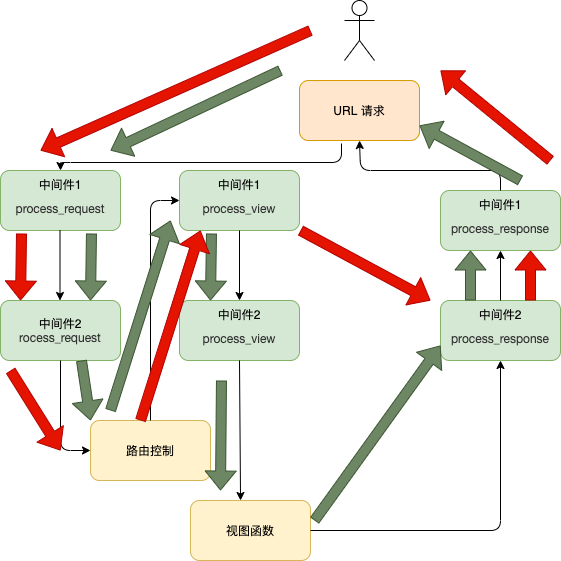
When configuring multiple middleware, it will be executed in reverse order according to the registration order in MIDDLEWARE, that is, the index value of the list. From the figure below, the green route is normally followed, assuming 中间件1 If there is a return value, follow the red route and directly execute the return of the process_response method under this class, and other middleware will not be executed.Example ¶
class MD1(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print("md1 process_request 方法。", id(request))
#在视图之前执行
def process_response(self,request, response): :#基于请求响应
print("md1 process_response 方法!", id(request)) #在视图之后
return response
7.17.5. process_view ¶
The format of the process_view method is as follows:
process_view(request, view_func, view_args, view_kwargs)
The process_view method has four parameters:
Request is a HttpRequest object.
View_func is the view function that Django will use.
View_args is a list of positional parameters that will be passed to the view.
View_kwargs is a dictionary of keyword parameters to be passed to the view.
Neither view_args nor view_kwargs contains the first view parameter (request).
The process_view method is executed before the view function and after the process_request method.
The return value can be a None, view_func (request), or HttpResponse object.
If the return value is None, follow the normal process and give it to the next middleware for processing.
The return value is the HttpResponse object, and Django will not execute the methods and view functions executed before the subsequent view functions, but directly start with the middleware and execute the middleware in reverse order, and execute the methods executed after the view functions.
c.返回值是 view_func(request),Django 将不执行后续视图函数之前执行的方法,提前执行视图函数,然后再倒序执行视图函数之后执行的方法。
When the process_request of the last middleware arrives at the routing relationship map, it returns to the first middleware process_view, and then goes down to the view function.
Example ¶
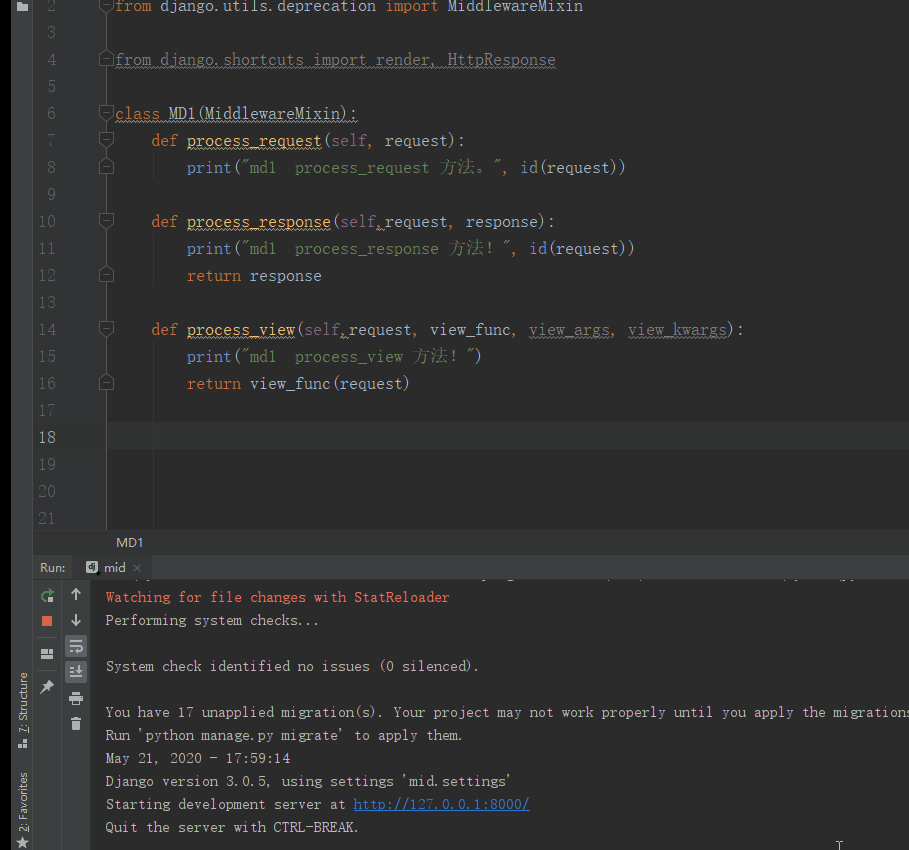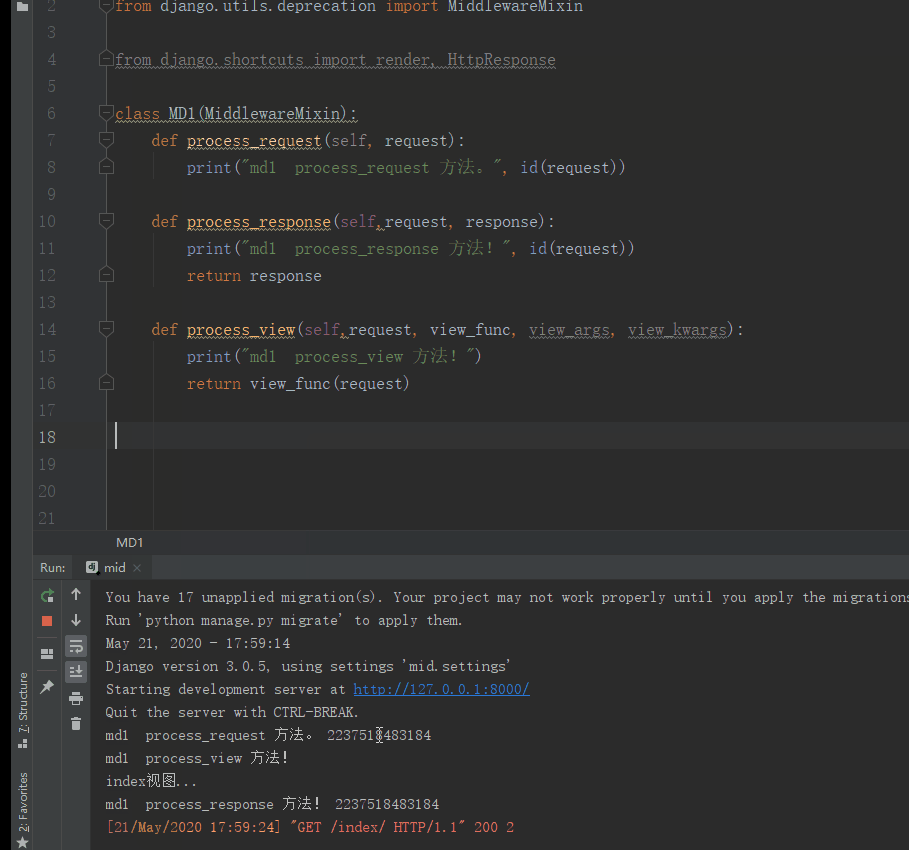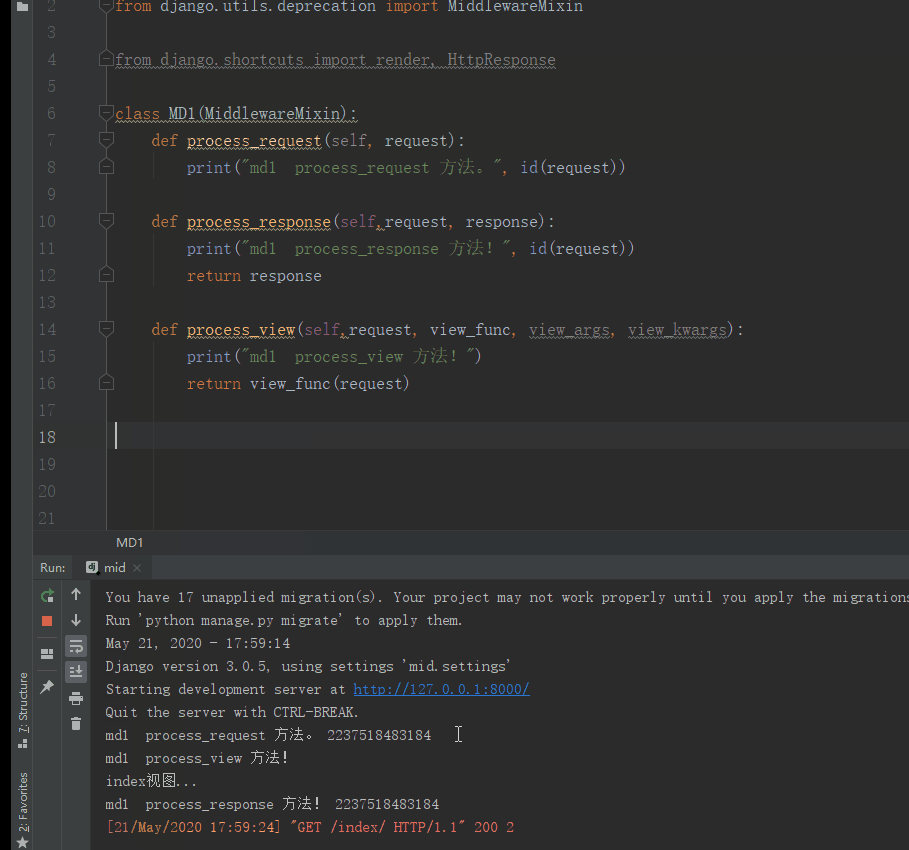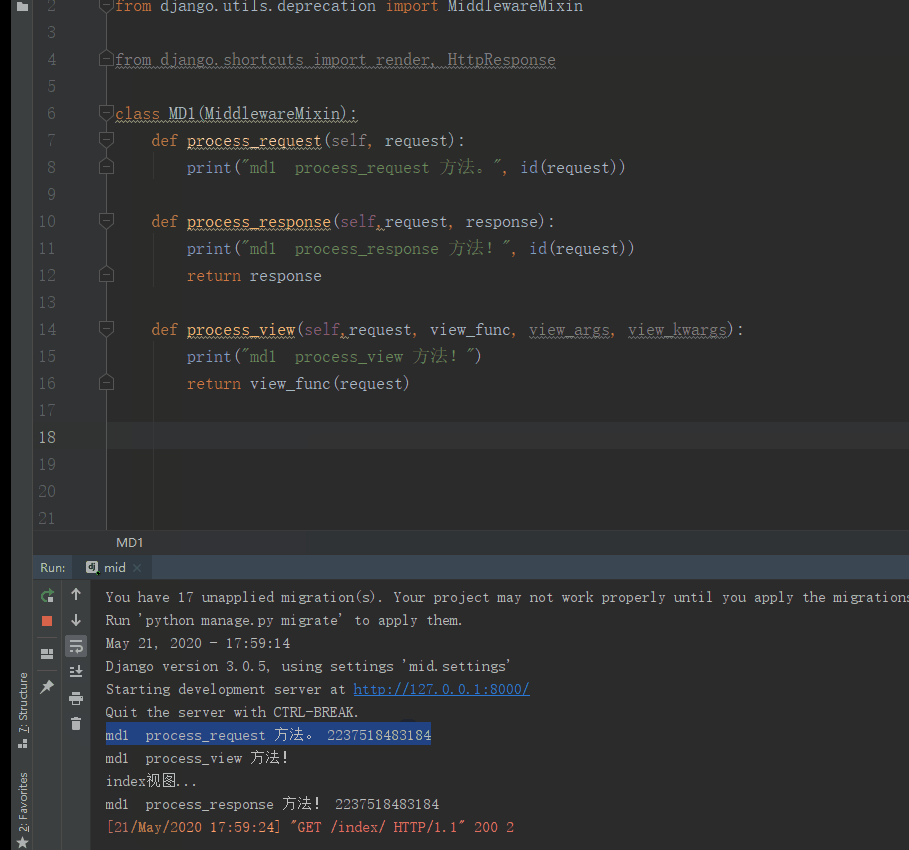
class MD1(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print("md1 process_request 方法。", id(request))
#在视图之前执行
def process_response(self,request, response): :#基于请求响应
print("md1 process_response 方法!", id(request))
#在视图之后
return response
def process_view(self,request, view_func, view_args,
view_kwargs):
print("md1 process_view 方法!") #在视图之前执行 顺序执行
#return view_func(request)

7.17.6. process_exception ¶
The process_exception method is as follows:
process_exception(request, exception)
Parameter description:
Request is a HttpRequest object.
Exception is an Exception object generated by a view function exception.
The process_exception method is executed only if there is an exception in the view function, in reverse order of the registration of the settings.
Execute after the view function and before the process_response method.
The return value of the process_exception method can be either a None or a HttpResponse object.
The return value is None, the page will report a 500 status code error, and the view function will not be executed.
The process_exception method is executed in reverse order, and then the process_response method is executed in reverse order.
The return value is a HttpResponse object, the page will not report an error, and the return status code is 200.
The view function is not executed, and the subsequent process_exception methods of the middleware are not executed, directly starting from the reverse order of the process_response methods of the last middleware.
If the process_view method returns the view function, the view function is executed in advance, and the view function reports an error, no matter what the return value of the process_exception method is, the page will report an error, and the view function and the process_exception method will not be executed.
Start directly from the process_response method of the last middleware in reverse order:Example ¶
class MD1(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print("md1 process_request 方法。", id(request))
#在视图之前执行
def process_response(self,request, response): :#基于请求响应
print("md1 process_response 方法!", id(request))
#在视图之后
return response
def process_view(self,request, view_func, view_args,
view_kwargs):
print("md1 process_view 方法!") #在视图之前执行 顺序执行
#return view_func(request)
def process_exception(self, request, exception):#引发错误
才会触发这个方法
print("md1 process_exception 方法!")
# return HttpResponse(exception) #返回错误信息