The MySQL download address for all platforms is: MySQL 下载 . Pick what you need. MySQL Community Server Version and corresponding platform.
注意: During the installation process, we need to install it by turning on administrator privileges, otherwise it will not be able to install due to lack of permissions. It is recommended to use the RPM package for installation on the Linux platform. Mysql,MySQL AB provides the download address for the following RPM packages: MySQL -MySQL server. You need this option unless you only want to connect to the MySQL server running on another machine. MySQL-client -MySQL client program to connect to and operate the Mysql server. MySQL-devel -Libraries and include files, which you need to install if you want to compile other MySQL clients, such as Perl modules. MySQL-shared -this package contains shared libraries (libmysqlclient.so*) that some languages and applications need to load dynamically, using MySQL. MySQL-bench -benchmark and performance testing tools for MySQL database servers. Before installation, we can check whether the system comes with the installation MySQL: If your system is installed, you can choose to uninstall it: 安装 MySQL: Next, we use the yum command to install MySQL under the Centos7 system. It is important to note that the MySQL database in CentOS 7 has been removed from the default program list, so before installation, we need to download the Yum resource package from the official website at: https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/repo/yum/ . Permission settings: Initialize MySQL: Start MySQL: View the running status of MySQL: 注意: If this is the first time we start the mysql service, the mysql server will first do the initialization configuration. In addition, you can also use MariaDB instead, the MariaDB database management system is a branch of MySQL, mainly maintained by the open source community and licensed by GPL. One of the reasons for developing this branch is that after Oracle acquired MySQL, there is a potential risk of shutting down MySQL, so the community uses a branching approach to avoid this risk. The goal of MariaDB is to be fully compatible with MySQL, including API and the command line, making it an easy replacement for MySQL. The relevant commands for the mariadb database are: After successfully installing MySQL, some of the underlying tables will be initialized, and after the server starts, you can verify that MySQL is working properly through a simple test. Use the mysqladmin tool to get the server status: Use the mysqladmin command to check the version of the server, which is located in the / usr/bin directory on linux and C:mysqlbin on Windows. This command on linux will output the following result, which is based on your system information: If you do not output any information after the above command is executed, your Mysql is not installed successfully. You can use the mysql command in MySQL Client (Mysql client) to connect to the MySQL server. By default, the login password of the MySQL server is empty, so there is no need to enter a password for this example. The command is as follows: The mysql > prompt will be output after the above command is executed, which indicates that you have successfully connected to the Mysql server. You can execute the SQL command at the mysql > prompt: After Mysql is installed successfully, the default root user password is empty. You can use the following command to create a root user password: Now you can connect to the Mysql server with the following command: 注意: When entering the password, the password will not be displayed, you can enter it correctly. It is relatively easy to install MySQL on Windows, and the latest version can be found in MySQL 下载 View in the download ( 更详细安装: Windows 上安装 MySQL ). Click Download Click the button to enter the download page and click the No thanks, just start my download. You can download it immediately: After downloading, we unzip the zip package to the appropriate directory. Here, I will put the extracted folder in C:webmysql-8.0.11 Down. 接下来我们需要配置下 MySQL 的配置文件 Open the folder you just unzipped C:webmysql-8.0.11 To create under this folder my.ini Configuration files, editin my.ini Configure the following basic information: 接下来我们来启动下 MySQL 数据库: Open the cmd command line tool as an administrator and change directories: Initialize the database: When the execution is complete, the initial default password of the root user is output, such as: APWCY5ws&hjQ is the initial password, which is needed for subsequent login, and you can also change the password after logging in. Enter the following installation command: Start and enter the following command: Note: the data directory needs to be initialized at 5.7: Initialize and then run net start mysql to start mysql. When the MySQL service is already running, we can log in to the MySQL database through the client tool that comes with MySQL. First, open a command prompt and enter a name in the following format: Parameter description: -h Specify the MySQL hostname to which the client wants to log in. Login to the local machine (localhost or 127.0.0.1) this parameter can be omitted -u User name of login -p Tell the server that a password will be used to log in, and this option can be ignored if the username and password you want to log in is empty. If we want to log in to the local MySQL database, we only need to enter the following command: Press enter to confirm that if the installation is correct and MySQL is running, you will get the following response: If the password exists, enter the password to log in, if it does not exist, press enter to log in directly. After logging in successfully, you will see Welcome to the MySQL monitor… It’s a prompt. Then the command prompt will always be Install MySQL on Linux/UNIX ¶
rpm -qa | grep mysql
rpm -e mysql // 普通删除模式
rpm -e --nodeps mysql // 强力删除模式,如果使用上面命令删除时,提示有依赖的其它文件,则用该命令可以对其进行强力删除
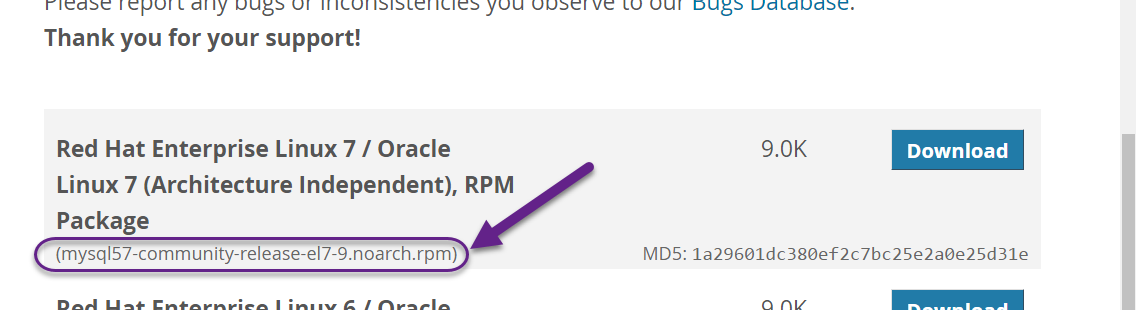
wget http://repo.mysql.com/mysql-community-release-el7-5.noarch.rpm
rpm -ivh mysql-community-release-el7-5.noarch.rpm
yum update
yum install mysql-server
chown -R mysql:mysql /var/lib/mysql/
mysqld --initialize
systemctl start mysqld
systemctl status mysqld
yum install mariadb-server mariadb
systemctl start mariadb #启动MariaDB
systemctl stop mariadb #停止MariaDB
systemctl restart mariadb #重启MariaDB
systemctl enable mariadb #设置开机启动
Verify MySQL installation ¶
[root@host]# mysqladmin --version
mysqladmin Ver 8.23 Distrib 5.0.9-0, for redhat-linux-gnu on i386
Use MySQL Client (Mysql client) to execute simple SQL commands ¶
[root@host]# mysql
mysql> SHOW DATABASES;
+----------+
| Database |
+----------+
| mysql |
| test |
+----------+
2 rows in set (0.13 sec)
What you need to do after Mysql installation ¶
[root@host]# mysqladmin -u root password "new_password";
[root@host]# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:*******
Install MySQL on Windows ¶
[client]
# 设置mysql客户端默认字符集
default-character-set=utf8
[mysqld]
# 设置3306端口
port = 3306
# 设置mysql的安装目录
basedir=C:\\web\\mysql-8.0.11
# 设置 mysql数据库的数据的存放目录,MySQL 8+ 不需要以下配置,系统自己生成即可,否则有可能报错
# datadir=C:\\web\\sqldata
# 允许最大连接数
max_connections=20
# 服务端使用的字符集默认为8比特编码的latin1字符集
character-set-server=utf8
# 创建新表时将使用的默认存储引擎
default-storage-engine=INNODB
cd C:\web\mysql-8.0.11\bin
mysqld --initialize --console
...
2018-04-20T02:35:05.464644Z 5 [Note] [MY-010454] [Server] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: APWCY5ws&hjQ
...
mysqld install
net start mysql
cd C:\web\mysql-8.0.11\bin
mysqld --initialize-insecure
Log in to MySQL ¶
mysql -h 主机名 -u 用户名 -p
mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
mysql>
Add a flashing cursor to wait for the input of the command, enter exit Or quit Log out and log in.