The interpreter pattern (Interpreter Pattern), which is a behavioral pattern, provides a way to evaluate the syntax or expressions of a language. This pattern implements an expression interface that interprets a particular context. This pattern is used in SQL parsing, symbol processing engines, and so on. 意图: Given a language, define its grammatical representation and define an interpreter that uses the identity to interpret sentences in the language. 主要解决: Build an interpreter to interpret sentences for some fixed grammars. 何时使用: If a particular type of problem occurs frequently enough, it may be worthwhile to express each instance of the problem as a sentence in a simple language. This allows you to build an interpreter that solves the problem by interpreting these sentences. 如何解决: Construct the grammar tree and define the Terminator and non-Terminator. 关键代码: Build the environment class, which contains some global information outside the interpreter, usually HashMap. 应用实例: Compiler, operation expression evaluation. 优点: 1. Good expansibility and flexibility. 2. A new way to interpret the expression has been added. 3. It is easy to implement simple grammar. 缺点: 1. There are few available scenarios. 2. It is difficult to maintain complex grammar. 3. The interpreter pattern can cause class inflation. 4. The interpreter mode adopts the method of recursive call. 使用场景: 1. A sentence in a language that needs interpretation and execution can be represented as an abstract syntax tree. 2. Some recurrent problems can be expressed in a simple language. 3. A scenario that needs to be explained in a simple grammar. 注意事项: There are few available scenarios. If you encounter it in JAVA, you can use expression4J instead. We will create an interface Expression And realized Expression The entity class of the interface. Definition as the main interpreter in the context TerminalExpression Class. Other classes OrExpression 、 AndExpression Used to create composite expressions. InterpreterPatternDemo Our demo class uses the Expression Class to create rules and demonstrate the resolution of expressions. Create an expression interface. Create an entity class that implements the above interface. InterpreterPatternDemo Use Expression Class to create rules and parse them. Execute the program and output the result: 6.18.1. Introduction ¶
6.18.2. Realize ¶
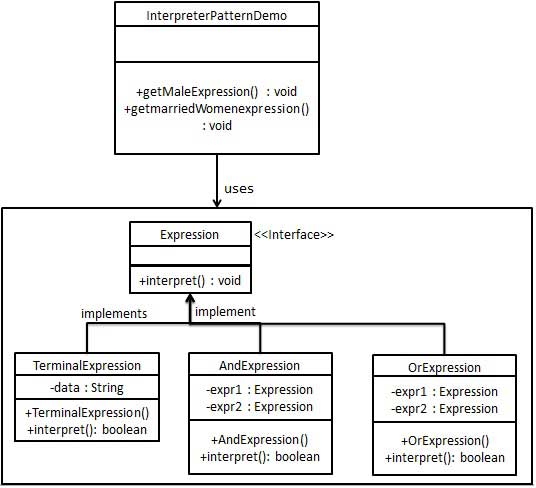
6.18.3. Step 1 ¶
Expression.java ¶
publicinterfaceExpression{publicbooleaninterpret(Stringcontext);}
6.18.4. Step 2 ¶
TerminalExpression.java ¶
publicclassTerminalExpressionimplementsExpression{privateStringdata;publicTerminalExpression(Stringdata){this.data=data;}@Overridepublicbooleaninterpret(Stringcontext){if(context.contains(data)){returntrue;}returnfalse;}}
OrExpression.java ¶
publicclassOrExpressionimplementsExpression{privateExpressionexpr1=null;privateExpressionexpr2=null;publicOrExpression(Expressionexpr1,Expressionexpr2){this.expr1=expr1;this.expr2=expr2;}@Overridepublicbooleaninterpret(Stringcontext){returnexpr1.interpret(context)\|\|expr2.interpret(context);}}
AndExpression.java ¶
publicclassAndExpressionimplementsExpression{privateExpressionexpr1=null;privateExpressionexpr2=null;publicAndExpression(Expressionexpr1,Expressionexpr2){this.expr1=expr1;this.expr2=expr2;}@Overridepublicbooleaninterpret(Stringcontext){returnexpr1.interpret(context)&&expr2.interpret(context);}}
6.18.5. Step 3 ¶
InterpreterPatternDemo.java ¶
publicclassInterpreterPatternDemo{//规则:Robert 和 John
是男性publicstaticExpressiongetMaleExpression(){Expressionrobert=newTerminalExpression("Robert");Expressionjohn=newTerminalExpression("John");returnnewOrExpression(robert,john);}//规则:Julie
是一个已婚的女性publicstaticExpressiongetMarriedWomanExpression(){Expressionjulie=newTerminalExpression("Julie");Expressionmarried=newTerminalExpression("Married");returnnewAndExpression(julie,married);}publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){ExpressionisMale=getMaleExpression();ExpressionisMarriedWoman=getMarriedWomanExpression();System.out.println("John
is male?"+isMale.interpret("John"));System.out.println("Julie is a
married women?"+isMarriedWoman.interpret("Married Julie"));}}
6.18.6. Step 4 ¶
John is male? true
Julie is a married women? true