In the visitor pattern (Visitor Pattern), we use a visitor class that changes the execution algorithm of the element class. In this way, the execution algorithm of the element can change as the visitor changes. This type of design pattern belongs to behavioral pattern. According to the pattern, the element object has accepted the visitor object so that the visitor object can handle operations on the element object. 意图: The data structure is mainly separated from the data operation. 主要解决: The coupling problem of stable data structure and variable operation. 何时使用: You need to do many different and unrelated operations on objects in an object structure, and you need to avoid letting these operations “pollute” the classes of these objects, and use the visitor pattern to encapsulate them in the class. 如何解决: Add an interface to the visited class that provides reception to the visitor. 关键代码: There is a method in the data base class that accepts the visitor and passes its own reference to the visitor. 应用实例: You are a guest at a friend’s house, you are a visitor, a friend accepts your interview, and you make a judgment on the friend’s description through the friend’s description, which is the visitor pattern. 优点: 1. Comply with the principle of single responsibility. 2. Excellent expansibility. 3. Flexibility. 缺点: 1. The disclosure of details by specific elements to visitors violates the Dimitt principle. 2. It is difficult to change specific elements. 3. It violates the principle of dependency inversion, relies on concrete classes, and does not rely on abstraction. 使用场景: 1. The class corresponding to the object in the object structure rarely changes, but it is often necessary to define new operations on this object structure. 2. You need to perform many different and irrelevant operations on the objects in an object structure, and you need to avoid letting these operations “pollute” the classes of these objects, and you don’t want to modify these classes when adding new operations. 注意事项: Visitors can unify the functions and can do reports, UI, interceptors and filters. We will create a definition that accepts the operation ComputerPart Interface. Keyboard 、 Mouse 、 Monitor And Computer It came true. ComputerPart The entity class of the interface. We will define another interface ComputerPartVisitor Which defines the operation of the visitor class Computer Use entity visitors to perform the appropriate actions. VisitorPatternDemo Our demo class uses the Computer 、 ComputerPartVisitor Class to demonstrate the use of the visitor pattern. Define an interface that represents an element. Create an entity class that extends the above class. Define an interface that represents visitors. Create entity visitors that implement the above classes. Use ComputerPartDisplayVisitor To show Computer An integral part of. Execute the program and output the result: 6.27.1. Introduction ¶
6.27.2. Realize ¶
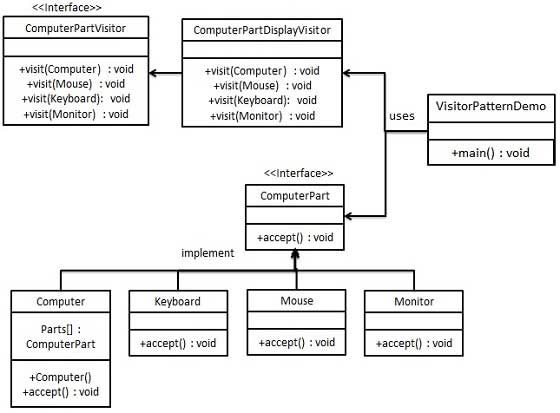
6.27.3. Step 1 ¶
ComputerPart.java ¶
publicinterfaceComputerPart{publicvoidaccept(ComputerPartVisitorcomputerPartVisitor);}
6.27.4. Step 2 ¶
Keyboard.java ¶
publicclassKeyboardimplementsComputerPart{@Overridepublicvoidaccept(ComputerPartVisitorcomputerPartVisitor){computerPartVisitor.visit(this);}}
Monitor.java ¶
publicclassMonitorimplementsComputerPart{@Overridepublicvoidaccept(ComputerPartVisitorcomputerPartVisitor){computerPartVisitor.visit(this);}}
Mouse.java ¶
publicclassMouseimplementsComputerPart{@Overridepublicvoidaccept(ComputerPartVisitorcomputerPartVisitor){computerPartVisitor.visit(this);}}
Computer.java ¶
publicclassComputerimplementsComputerPart{ComputerPart[]parts;publicComputer(){parts=newComputerPart[]{newMouse(),newKeyboard(),newMonitor()};}@Overridepublicvoidaccept(ComputerPartVisitorcomputerPartVisitor){for(inti=0;i<parts.length;i++){parts[i].accept(computerPartVisitor);}computerPartVisitor.visit(this);}}
6.27.5. Step 3 ¶
ComputerPartVisitor.java ¶
publicinterfaceComputerPartVisitor{publicvoidvisit(Computercomputer);publicvoidvisit(Mousemouse);publicvoidvisit(Keyboardkeyboard);publicvoidvisit(Monitormonitor);}
6.27.6. Step 4 ¶
ComputerPartDisplayVisitor.java ¶
publicclassComputerPartDisplayVisitorimplementsComputerPartVisitor{@Overridepublicvoidvisit(Computercomputer){System.out.println("Displaying
Computer.");}@Overridepublicvoidvisit(Mousemouse){System.out.println("Displaying
Mouse.");}@Overridepublicvoidvisit(Keyboardkeyboard){System.out.println("Displaying
Keyboard.");}@Overridepublicvoidvisit(Monitormonitor){System.out.println("Displaying
Monitor.");}}
6.27.7. Step 5 ¶
VisitorPatternDemo.java ¶
publicclassVisitorPatternDemo{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){ComputerPartcomputer=newComputer();computer.accept(newComputerPartDisplayVisitor());}}
6.27.8. Step 6 ¶
Displaying Mouse.
Displaying Keyboard.
Displaying Monitor.
Displaying Computer.