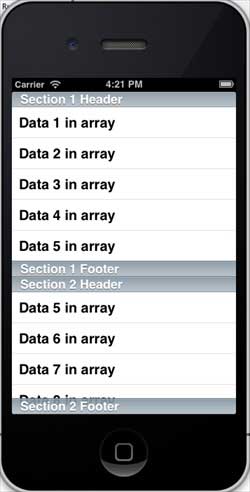
The IOS table view consists of cells (generally reusable) that display views scrolling vertically.
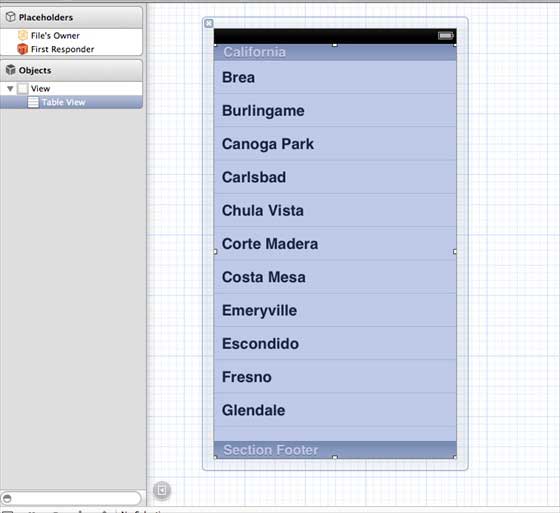
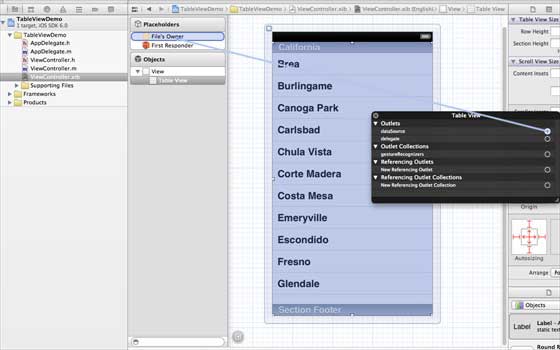
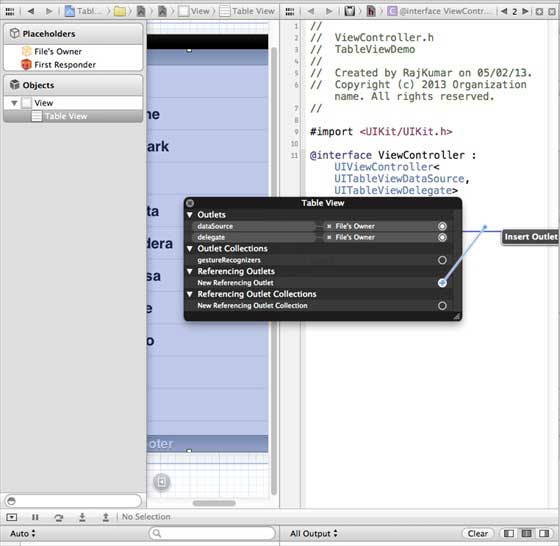
In iOS, the table view is used to display a list of data, such as a list of contacts, to-dos, or shopping items. Delegate DataSource RowHeight SectionFooterHeight SectionHeaderHeight SeparatorColor TableHeaderView TableFooterView 1.在ViewController.xib中添加表格视图,如下所示 two。 Set the delegate and data source to File’s Owner (owner of the file) by right-clicking and selecting the data source and delegate. Set up the data source as follows 3.为表格视图创建IBOutlet的并将其命名为myTableView。如以下图片中所示 To own the data, add a NSMutableArray so that it can be displayed in the list grid view 5.ViewController应采用的UITableViewDataSource和UITableViewDelegate协议。ViewController.h代码如下所示 6.执行所需的表格视图委托和数据源的方法。更新ViewController.m,如下所示 7.现在当我们运行应用程序时我们就会得到下面的输出 9.19.1. Important attribute ¶
An important method ¶
- (UITableViewCell *)cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
- (void)deleteRowsAtIndexPaths:(NSArray *)indexPaths
withRowAnimation:(UITableViewRowAnimation)animation
- (id)dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:(NSString *)identifier
- (id)dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:(NSString *)identifier
forIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath
- (void)reloadData
- (void)reloadRowsAtIndexPaths:(NSArray *)indexPaths
withRowAnimation:(UITableViewRowAnimation)animation
- (NSArray *)visibleCells
9.19.2. Sample code and steps ¶

#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
@interface ViewController : UIViewController<UITableViewDataSource,
UITableViewDelegate>
{
IBOutlet UITableView *myTableView;
NSMutableArray *myData;
}
@end
#import "ViewController.h"
@interface ViewController ()
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
// table view data is being set here
myData = [[NSMutableArray alloc]initWithObjects:
@"Data 1 in array",@"Data 2 in array",@"Data 3 in array",
@"Data 4 in array",@"Data 5 in array",@"Data 5 in array",
@"Data 6 in array",@"Data 7 in array",@"Data 8 in array",
@"Data 9 in array", nil];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning
{
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
#pragma mark - Table View Data source
- (NSInteger)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView numberOfRowsInSection:
(NSInteger)section{
return [myData count]/2;
}
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:
(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{
static NSString *cellIdentifier = @"cellID";
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:
cellIdentifier];
if (cell == nil) {
cell = [[UITableViewCell alloc]initWithStyle:
UITableViewCellStyleDefault reuseIdentifier:cellIdentifier];
}
NSString *stringForCell;
if (indexPath.section == 0) {
stringForCell= [myData objectAtIndex:indexPath.row];
}
else if (indexPath.section == 1){
stringForCell= [myData objectAtIndex:indexPath.row+ [myData count]/2];
}
[cell.textLabel setText:stringForCell];
return cell;
}
// Default is 1 if not implemented
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInTableView:(UITableView *)tableView{
return 2;
}
- (NSString *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView titleForHeaderInSection:
(NSInteger)section{
NSString *headerTitle;
if (section==0) {
headerTitle = @"Section 1 Header";
}
else{
headerTitle = @"Section 2 Header";
}
return headerTitle;
}
- (NSString *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView titleForFooterInSection:
(NSInteger)section{
NSString *footerTitle;
if (section==0) {
footerTitle = @"Section 1 Footer";
}
else{
footerTitle = @"Section 2 Footer";
}
return footerTitle;
}
#pragma mark - TableView delegate
-(void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView didSelectRowAtIndexPath:
(NSIndexPath *)indexPath{
[tableView deselectRowAtIndexPath:indexPath animated:YES];
UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:indexPath];
NSLog(@"Section:%d Row:%d selected and its data is %@",
indexPath.section,indexPath.row,cell.textLabel.text);
}
@end