In the previous chapters, we have learned how to read data in one table, which is relatively simple, but in real applications we often need to read data from multiple data tables.
In this section, we will show you how to use MySQL’s JOIN to query data in two or more tables.
You can use Mysql’s JOIN in SELECT, UPDATE and DELETE statements to federate multi-table queries.
JOIN is roughly divided into the following three categories according to its functions:
INNER JOIN(内连接,或等值连接) Gets the record of the field matching relationship in the two tables
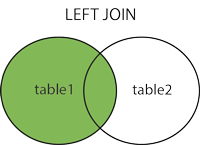
LEFT JOIN(左连接): Gets all the records in the left table, even if there are no matching records in the right table.
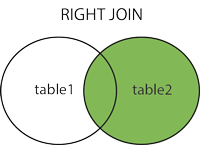
RIGHT JOIN(右连接): In contrast to LEFT JOIN, it is used to get all the records in the right table, even if there are no matching records in the left table.
The database structure and data download used in this chapter: runoob-mysql-join-test.sql . We have two tables tcount_tbl and runoob_tbl in the RUNOOB database. The data of the two data tables are as follows: Try the following example: Test instance data Next we will use MySQL’s INNER JOIN(也可以省略 INNER 使用 JOIN,效果一样) 来连接以上两张表来读取runoob_tbl表中所有runoob_author字段在tcount_tbl表对应的runoob_count字段值: INNER JOIN The above SQL statement is equivalent to: WHERE clause MySQL left join is different from join. MySQL LEFT JOIN reads all the data from the data table on the left, even if the table on the right has no corresponding data. Try the following example to runoob_tbl For the left table tcount_tbl For the right table, understand the application of MySQL LEFT JOIN: LEFT JOIN LEFT JOIN is used in the above example, and this statement reads all selected field data from the data table runoob_tbl on the left, even if there is no corresponding runoob_author field value in the table tcount_tbl on the right. MySQL RIGHT JOIN reads all the data from the data table on the right, even if the table on the left has no corresponding data. Try the following example to runoob_tbl For the left table tcount_tbl For the right table, understand the application of MySQL RIGHT JOIN: RIGHT JOIN RIGHT JOIN is used in the above example, and this statement reads all the selected field data from the data table tcount_tbl on the right, even if there is no corresponding runoob_author field value in the left table runoob_tbl. Used in PHP Try the following example: MySQL ORDER BY Test: The output is shown in the following figure:Use INNER JOIN from a command prompt ¶
Example ¶
mysql>useRUNOOB;Databasechangedmysql>SELECT\*FROMtcount_tbl;
+---------------+--------------+ \|runoob_author\|runoob_count\|
+---------------+--------------+ \| 菜鸟教程 \|10\| \|RUNOOB.COM\|20\|
\|Google\|22\|
+---------------+--------------+3rowsinset(0.01sec)mysql>SELECT\*fromrunoob_tbl;
+-----------+---------------+---------------+-----------------+
\|runoob_id\|runoob_title\|runoob_author\|submission_date\|
+-----------+---------------+---------------+-----------------+ \|1\|
学习PHP\| 菜鸟教程 \|2017-04-12\| \|2\| 学习MySQL\| 菜鸟教程
\|2017-04-12\| \|3\| 学习Java\|RUNOOB.COM\|2015-05-01\| \|4\|
学习Python\|RUNOOB.COM\|2016-03-06\| \|5\| 学习C\|FK\|2017-04-05\|
+-----------+---------------+---------------+-----------------+5rowsinset(0.01sec)
mysql>SELECTa.runoob_id,a.runoob_author,b.runoob_countFROMrunoob_tblaINNERJOINtcount_tblbONa.runoob_author=b.runoob_author;
+-------------+-----------------+----------------+
\|a.runoob_id\|a.runoob_author\|b.runoob_count\|
+-------------+-----------------+----------------+ \|1\| 菜鸟教程 \|10\|
\|2\| 菜鸟教程 \|10\| \|3\|RUNOOB.COM\|20\| \|4\|RUNOOB.COM\|20\|
+-------------+-----------------+----------------+4rowsinset(0.00sec)
mysql>SELECTa.runoob_id,a.runoob_author,b.runoob_countFROMrunoob_tbla,tcount_tblbWHEREa.runoob_author=b.runoob_author;
+-------------+-----------------+----------------+
\|a.runoob_id\|a.runoob_author\|b.runoob_count\|
+-------------+-----------------+----------------+ \|1\| 菜鸟教程 \|10\|
\|2\| 菜鸟教程 \|10\| \|3\|RUNOOB.COM\|20\| \|4\|RUNOOB.COM\|20\|
+-------------+-----------------+----------------+4rowsinset(0.01sec)
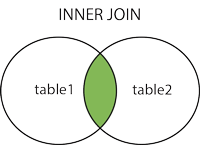
MySQL LEFT JOIN ¶
Example ¶
mysql>SELECTa.runoob_id,a.runoob_author,b.runoob_countFROMrunoob_tblaLEFTJOINtcount_tblbONa.runoob_author=b.runoob_author;
+-------------+-----------------+----------------+
\|a.runoob_id\|a.runoob_author\|b.runoob_count\|
+-------------+-----------------+----------------+ \|1\| 菜鸟教程 \|10\|
\|2\| 菜鸟教程 \|10\| \|3\|RUNOOB.COM\|20\| \|4\|RUNOOB.COM\|20\|
\|5\|FK\|NULL\|
+-------------+-----------------+----------------+5rowsinset(0.01sec)
MySQL RIGHT JOIN ¶
Example ¶
mysql>SELECTa.runoob_id,a.runoob_author,b.runoob_countFROMrunoob_tblaRIGHTJOINtcount_tblbONa.runoob_author=b.runoob_author;
+-------------+-----------------+----------------+
\|a.runoob_id\|a.runoob_author\|b.runoob_count\|
+-------------+-----------------+----------------+ \|1\| 菜鸟教程 \|10\|
\|2\| 菜鸟教程 \|10\| \|3\|RUNOOB.COM\|20\| \|4\|RUNOOB.COM\|20\|
\|NULL\|NULL\|22\|
+-------------+-----------------+----------------+5rowsinset(0.01sec)
Using JOIN in PHP scripts ¶
mysqli_query()
Function to execute the SQL statement, you can use the same SQL statement as the
mysqli_query()
The arguments to the function.<?php$dbhost='localhost';//mysql服务器主机地址$dbuser='root';//mysql用户名$dbpass='123456';//mysql用户名密码$conn=mysqli_connect($dbhost,$dbuser,$dbpass);if(!$conn){die('连接失败:'.mysqli_error($conn));}//设置编码,防止中文乱码mysqli_query($conn,"set
names utf8");$sql='SELECT a.runoob_id, a.runoob_author, b.runoob_count
FROM runoob_tbl a INNER JOIN tcount_tbl b ON a.runoob_author =
b.runoob_author';mysqli_select_db($conn,'RUNOOB');$retval=mysqli_query($conn,$sql);if(!$retval){die('无法读取数据:'.mysqli_error($conn));}echo'<h2>菜鸟教程
MySQL JOIN 测试<h2>';echo'<table border="1"><tr><td>教程
ID</td><td>作者</td><td>登陆次数</td></tr>';while($row=mysqli_fetch_array($retval,MYSQLI_ASSOC)){echo"<tr><td>{$row['runoob_id']}</td>"."<td>{$row['runoob_author']}</td>"."<td>{$row['runoob_count']}</td>"."</tr>";}echo'</table>';mysqli_close($conn);?>
