5.15.1. I. the concept and its introduction ¶
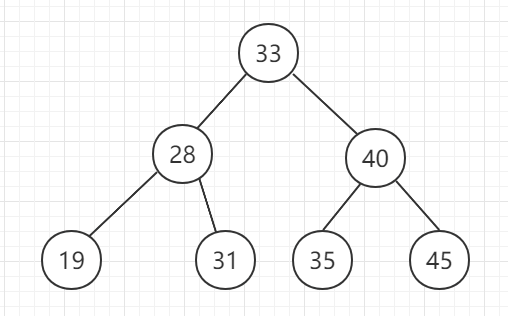
Binary search tree (English: Binary Search Tree), also known as binary search tree, binary search tree, ordered binary tree, or sorted binary tree. The following conditions are met:
If its left subtree is not empty, the value of all nodes on the left subtree is less than its root node.
If its right subtree is not empty, the value of all nodes on the right subtree is greater than its root node.
Its left and right subtrees are also binary search trees.
As shown in the following figure:
5.15.2. II. Applicable instructions ¶
Binary search tree has efficient insert, delete and query operations.
The average time complexity is O (log n), and the worst case is O (n). The binary search tree is different from the heap, it is not necessarily a complete binary tree, and the bottom layer is not easy to be directly represented by an array, so the linked list is used to realize the binary search tree.
Find element | Insert element | Delete element | |
|---|---|---|---|
Ordinary array | O (n) | O (n) | O (n) |
Sequential array | O (logn) | O (n) | O (n) |
Binary search tree | O (logn) | O (logn) | O (logn) |
The following first introduces the binary search method in the form of array as a reference, and then continues to introduce the search method of binary search tree.
5.15.3. Diagram of the process of three-part search method ¶
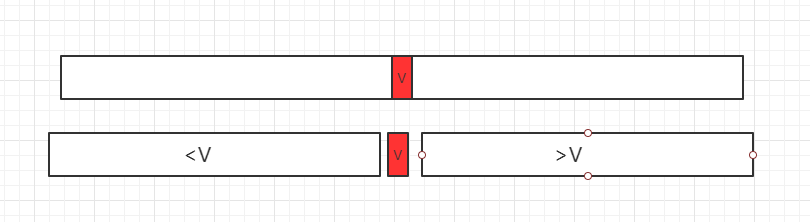
The idea of binary search method was put forward in 1946. Search problem is a very important basic problem in computers. For ordered sequences, binary search method can be used. If we want to find an element, first look at the relationship between the value V in the middle of the array and the size of the data we need to find, in three cases:
1、等于所要查找的数据,直接找到
2、若小于 V,在小于 V 部分分组继续查询
2、若大于 V,在大于 V 部分分组继续查询
5.15.4. 4. Java instance code ¶
源码包下载: Download Src/runoob/binary/BinarySearch.java file code: ¶
package runoob.binarySearch;
/*\*
\* 二分查找法
*/
public class BinarySearch {
// 二分查找法,在有序数组arr中,查找target
// 如果找到target,返回相应的索引index
// 如果没有找到target,返回-1
public static int find(Comparable[] arr, Comparable target) {
// 在arr[l...r]之中查找target
int l = 0, r = arr.length-1;
while( l <= r ){
//int mid = (l + r)/2;
// 防止极端情况下的整形溢出,使用下面的逻辑求出mid
int mid = l + (r-l)/2;
if( arr[mid].compareTo(target) == 0 )
return mid;
if( arr[mid].compareTo(target) > 0 )
r = mid - 1;
else
l = mid + 1;
}
return -1;
}
}