Singleton pattern (Singleton Pattern) is one of the simplest design patterns in Java. This type of design pattern is a creative pattern, which provides the best way to create objects.
This pattern involves a single class that is responsible for creating its own objects while ensuring that only a single object is created. This class provides a way to access its unique object directly without instantiating the object of the class.
注意:
1、单例类只能有一个实例。
2、单例类必须自己创建自己的唯一实例。
3、单例类必须给所有其他对象提供这一实例。
6.5.1. Introduction ¶
意图: Ensure that there is only one instance of a class and provide a global access point to it.
主要解决: A class used globally is frequently created and destroyed.
何时使用: When you want to control the number of instances and save system resources.
如何解决: Determine whether the system already has this singleton, return if so, and create it if not.
关键代码: The constructor is private.
应用实例:
There is only one head teacher in a class.
2、Windows 是多进程多线程的,在操作一个文件的时候,就不可避免地出现多个进程或线程同时操作一个文件的现象,所以所有文件的处理必须通过唯一的实例来进行。
3、一些设备管理器常常设计为单例模式,比如一个电脑有两台打印机,在输出的时候就要处理不能两台打印机打印同一个文件。
优点:
1、在内存里只有一个实例,减少了内存的开销,尤其是频繁的创建和销毁实例(比如管理学院首页页面缓存)。
2、避免对资源的多重占用(比如写文件操作)。
缺点: There is no interface, can not be inherited, in conflict with the principle of single responsibility, a class should only care about internal logic, not how to instantiate outside.
使用场景:
1、要求生产唯一序列号。
2、WEB 中的计数器,不用每次刷新都在数据库里加一次,用单例先缓存起来。
3、创建的一个对象需要消耗的资源过多,比如 I/O 与数据库的连接等。
注意事项: The synchronization lock synchronized (Singleton.class) is required in the getInstance () method to prevent multithreading from entering at the same time, causing the instance to be instantiated multiple times.
6.5.2. Realize ¶
We will create a SingleObject Class. SingleObject The class has its private constructor and a static instance of itself.
SingleObject Class provides a static method for the outside world to obtain its static instance. SingletonPatternDemo Class usage SingleObject Class to get the SingleObject Object.
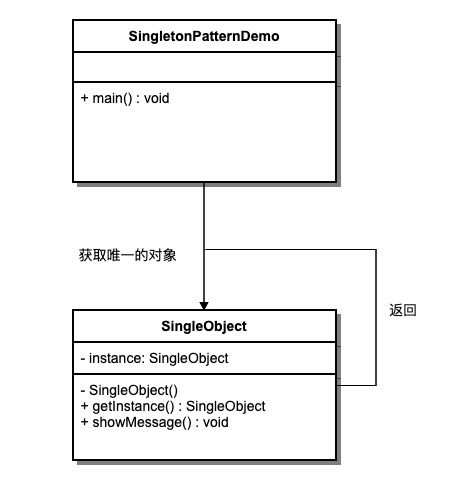
6.5.3. Step 1 ¶
Create a Singleton class.SingleObject.java ¶
publicclassSingleObject{//创建 SingleObject
的一个对象privatestaticSingleObjectinstance=newSingleObject();//让构造函数为
private,这样该类就不会被实例化privateSingleObject(){}//获取唯一可用的对象publicstaticSingleObjectgetInstance(){returninstance;}publicvoidshowMessage(){System.out.println("Hello
World!");}}
6.5.4. Step 2 ¶
Get a unique object from the singleton class.SingletonPatternDemo.java ¶
publicclassSingletonPatternDemo{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){//不合法的构造函数//编译时错误:构造函数
SingleObject() 是不可见的//SingleObject object = new
SingleObject();//获取唯一可用的对象SingleObjectobject=SingleObject.getInstance();//显示消息object.showMessage();}}
6.5.5. Step 3 ¶
Execute the program and output the result:
Hello World!
6.5.6. Several ways to realize the singleton pattern ¶
The singleton pattern can be implemented in several ways, as follows:
6.5.7. 1. Lazy, thread unsafe ¶
是否 Lazy 初始化: Yes
是否多线程安全: No
实现难度: Easy
描述: This is the most basic implementation, and the biggest problem with this implementation is that it does not support multithreading. Because synchronized is not locked, it is not strictly a singleton pattern. In this way, lazy loading is obvious, does not require thread safety, and does not work properly in multithreading. 接下来介绍的几种实现方式都支持多线程,但是在性能上有所差异。 Example ¶
publicclassSingleton{privatestaticSingletoninstance;privateSingleton(){}publicstaticSingletongetInstance(){if(instance==null){instance=newSingleton();}returninstance;}}
6.5.8. 2. Lazy, thread safe ¶
是否 Lazy 初始化: Yes
是否多线程安全: Yes
实现难度: Easy
描述: This approach has a good lazy loading and works well in multithreading, but it is inefficient and does not require synchronization in 99% of the cases. Advantages: initialize only the first call to avoid memory waste. Disadvantages: synchronized must be locked to guarantee singletons, but locking will affect efficiency. The performance of getInstance () is not critical to the application (this method is used infrequently).Example ¶
publicclassSingleton{privatestaticSingletoninstance;privateSingleton(){}publicstaticsynchronizedSingletongetInstance(){if(instance==null){instance=newSingleton();}returninstance;}}
6.5.9. 3. Hungry Han style ¶
是否 Lazy 初始化: No
是否多线程安全: Yes
实现难度: Easy
描述: This method is more commonly used, but it is easy to produce junk objects. Advantages: without locking, the execution efficiency will be improved. Disadvantages: initialize the class when it is loaded, wasting memory. It avoids the problem of multi-thread synchronization based on the classloader mechanism, but instance is instantiated when the class is loaded. Although there are many reasons for class loading, most of them call the getInstance method in the singleton mode, but it is not sure that there are other ways (or other static methods) that lead to class loading. At this time, initializing instance obviously does not achieve the effect of lazy loading.Example ¶
publicclassSingleton{privatestaticSingletoninstance=newSingleton();privateSingleton(){}publicstaticSingletongetInstance(){returninstance;}}
6.5.10. 4. Double check lock / double check lock (DCL, i.e. double-checked locking) ¶
JDK 版本: From JDK1.5
是否 Lazy 初始化: Yes
是否多线程安全: Yes
实现难度: More complex
描述: This approach uses a double-lock mechanism, which is safe and can maintain high performance in the case of multithreading. The performance of getInstance () is critical to the application.Example ¶
publicclassSingleton{privatevolatilestaticSingletonsingleton;privateSingleton(){}publicstaticSingletongetSingleton(){if(singleton==null){synchronized(Singleton.class){if(singleton==null){singleton=newSingleton();}}}returnsingleton;}}
6.5.11. 5. Registered / static inner class ¶
是否 Lazy 初始化: Yes
是否多线程安全: Yes
实现难度: General
描述: This method can achieve the same effect of double check lock, but it is easier to implement. Use delayed initialization for static domains, which should be used instead of double locking. This method is only applicable to static domains, and double locking can be used when the instance domain needs to be deferred for initialization. This method also uses the classloader mechanism to ensure that there is only one thread when initializing the instance, which is different from the third method: in the third method, as long as the Singleton class is loaded, then the instance will be instantiated (not achieving the lazy loading effect), while in this way, the Singleton class is loaded and the instance is not necessarily initialized. Because the SingletonHolder class is not actively used, the SingletonHolder class is only explicitly loaded by explicitly calling the getInstance method, thus instantiating the instance. Imagine that if instantiating instance is resource-consuming and you want it to delay loading, on the other hand, you don’t want to instantiate when the Singleton class loads, because there is no guarantee that the Singleton class may be actively used and loaded elsewhere, then instantiating instance at this time is obviously not appropriate. At this point, this approach is more reasonable than the third way.Example ¶
publicclassSingleton{privatestaticclassSingletonHolder{privatestaticfinalSingletonINSTANCE=newSingleton();}privateSingleton(){}publicstaticfinalSingletongetInstance(){returnSingletonHolder.INSTANCE;}}
6.5.12. 6. Enumerate ¶
JDK 版本: From JDK1.5
是否 Lazy 初始化: No
是否多线程安全: Yes
实现难度: Easy
描述: This implementation has not been widely adopted, but it is the best way to implement the singleton pattern. It is more concise, automatically supports serialization mechanisms, and absolutely prevents multiple instantiations. This approach is advocated by Effective Java author Josh Bloch, which not only avoids the problem of multithreaded synchronization, but also automatically supports serialization mechanisms to prevent deserialization from recreating new objects and absolutely prevent multiple instantiations. However, because the enum feature was added after JDK1.5, writing in this way is unfamiliar and rarely used in practice. Private constructors cannot be called through reflection attack. 经验之谈: In general, the first and second lazy methods are not recommended, and the third hungry way is recommended. The fifth registration method is used only if you want to explicitly achieve the lazy loading effect. If deserialization is involved in creating objects, you can try using the sixth enumeration method. If you have other special needs, you can consider using the fourth double lock method.Example ¶
publicenumSingleton{INSTANCE;publicvoidwhateverMethod(){}}