5.3.1. I. the concept and its introduction ¶
Hill sorting (Shell Sort) is a kind of insertion sorting, which is an improvement on the direct insertion sorting algorithm.
Hill ranking is also known as reduced incremental sorting, which is named after DL.Shell proposed in 1959.
It is carried out by comparing elements at certain intervals, and the distance used for each comparison decreases with the progress of the algorithm, until only the last ranking of adjacent elements is compared.
5.3.2. II. Applicable instructions ¶
Hill sorting time complexity is O (n ^ (1.3-2)) and space complexity is constant order O (1). Hill sorting is not as fast as the fast sorting algorithm with O (n (logn)) time complexity, so it performs well for medium size, but sorting for very large data is not the best choice, which is much faster than the general O (n ^ 2) complexity algorithm.
5.3.3. III. Process diagram ¶
The purpose of Hill sorting is to improve the insertion sort in order to speed up, exchange non-adjacent elements to sort the local array, and finally use the insertion sort to sort the locally ordered array.
Here we choose the increment gap=length/2, reduce the increment by gap= gap/2, and use the sequence. {n/2,(n/2)/2…1} To show.
An example is shown in the figure:
(1)初始增量第一趟 gap = length/2 = 4
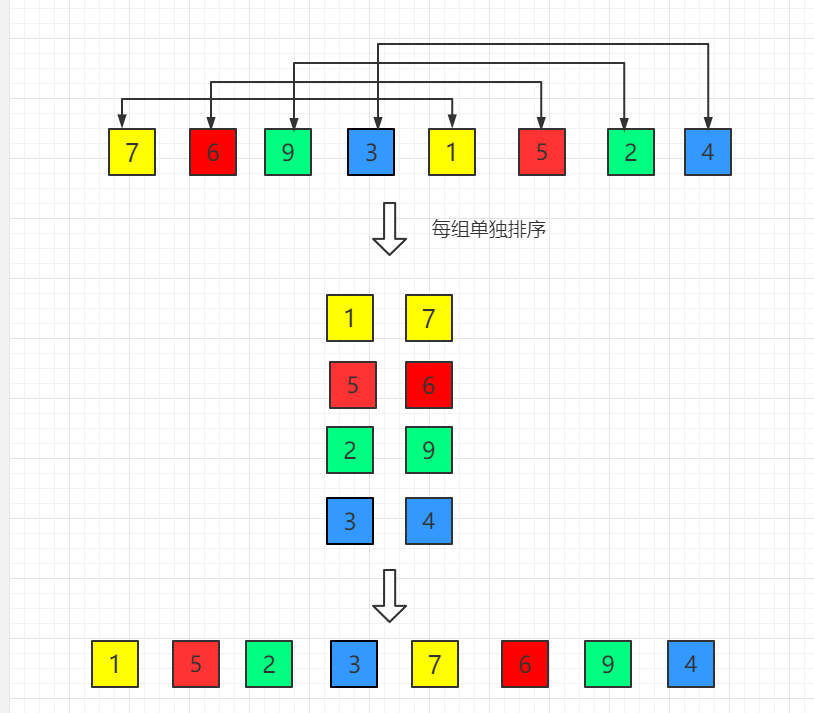
(2)第二趟,增量缩小为 2
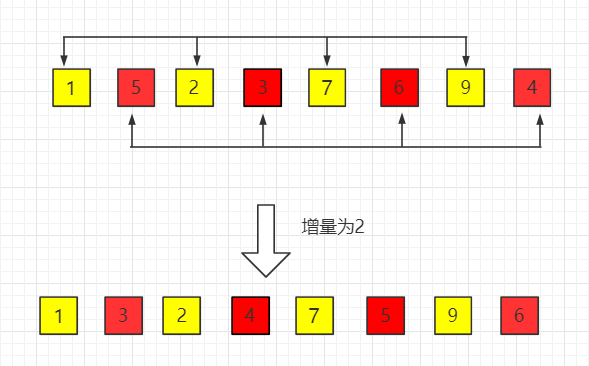
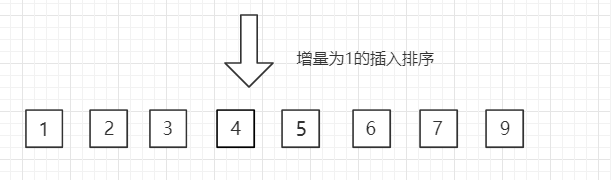
(3)第三趟,增量缩小为 1,得到最终排序结果
5.3.4. 4. Java instance code ¶
源码包下载: Download
The innermost loop is actually the insertion sort:ShellSort.java file code: ¶
public class ShellSort {
//核心代码---开始
public static void sort(Comparable[] arr) {
int j;
for (int gap = arr.length / 2; gap > 0; gap /= 2) {
for (int i = gap; i < arr.length; i++) {
Comparable tmp = arr[i];
for (j = i; j >= gap && tmp.compareTo(arr[j - gap]) < 0;
j -= gap) {
arr[j] = arr[j - gap];
}
arr[j] = tmp;
}
}
}
//核心代码---结束
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 2000;
Integer[] arr = SortTestHelper.generateRandomArray(N, 0, 10);
ShellSort.sort(arr);
for( int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i ++ ){
System.out.print(arr[i]);
System.out.print(' ');
}
}
}