9.36.1. Brief introduction ¶
IOS maps help us locate locations, and IOS maps use the MapKit framework.
9.36.2. Instance step ¶
1.创建一个简单的 View based application
two。 Select the project file, then select the target, and then add MapKit.framework.
3.添加 Corelocation.framework
4.向 ViewController.xib 添加地图查看和创建 ibOutlet 并且命名为mapView。
5.通过”File-> New -> File… -> “选择 Objective C class创建一个新的文件,单击下一步
6.”sub class of”为 NSObject,类作命名为MapAnnotation
7.选择创建
8.更新MapAnnotation.h ,如下所示
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import <MapKit/MapKit.h>
@interface MapAnnotation : NSObject<MKAnnotation>
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *title;
@property (nonatomic, readwrite) CLLocationCoordinate2D coordinate;
- (id)initWithTitle:(NSString *)title andCoordinate:
(CLLocationCoordinate2D)coordinate2d;
@end
9.更新MapAnnotation.m ,如下所示
#import "MapAnnotation.h"
@implementation MapAnnotation
-(id)initWithTitle:(NSString *)title andCoordinate:
(CLLocationCoordinate2D)coordinate2d{
self.title = title;
self.coordinate =coordinate2d;
return self;
}
@end
10.更新ViewController.h ,如下所示
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
#import <MapKit/MapKit.h>
#import <CoreLocation/CoreLocation.h>
@interface ViewController : UIViewController<MKMapViewDelegate>
{
MKMapView *mapView;
}
@end
11.更新ViewController.m ,如下所示
#import "ViewController.h"
#import "MapAnnotation.h"
@interface ViewController ()
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
mapView = [[MKMapView alloc]initWithFrame:
CGRectMake(10, 100, 300, 300)];
mapView.delegate = self;
mapView.centerCoordinate = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.32, -122.03);
mapView.mapType = MKMapTypeHybrid;
CLLocationCoordinate2D location;
location.latitude = (double) 37.332768;
location.longitude = (double) -122.030039;
// Add the annotation to our map view
MapAnnotation *newAnnotation = [[MapAnnotation alloc]
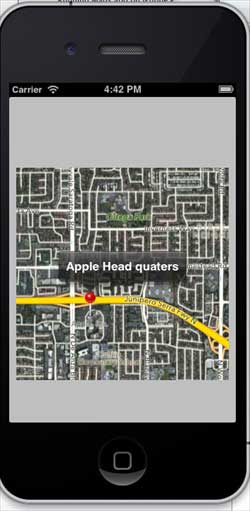
initWithTitle:@"Apple Head quaters" andCoordinate:location];
[mapView addAnnotation:newAnnotation];
CLLocationCoordinate2D location2;
location2.latitude = (double) 37.35239;
location2.longitude = (double) -122.025919;
MapAnnotation *newAnnotation2 = [[MapAnnotation alloc]
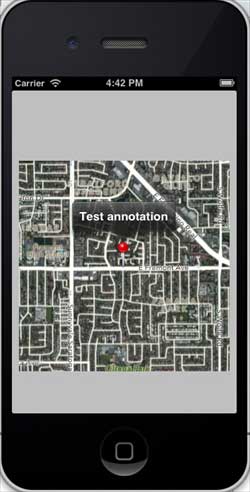
initWithTitle:@"Test annotation" andCoordinate:location2];
[mapView addAnnotation:newAnnotation2];
[self.view addSubview:mapView];
}
// When a map annotation point is added, zoom to it (1500 range)
- (void)mapView:(MKMapView *)mv didAddAnnotationViews:(NSArray *)views
{
MKAnnotationView *annotationView = [views objectAtIndex:0];
id <MKAnnotation> mp = [annotationView annotation];
MKCoordinateRegion region = MKCoordinateRegionMakeWithDistance
([mp coordinate], 1500, 1500);
[mv setRegion:region animated:YES];
[mv selectAnnotation:mp animated:YES];
}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning
{
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
@end
9.36.3. Output ¶
When you run the application, the output is as follows
When we scroll up the map, the output is as follows