9.43.1. Brief introduction ¶
The basic idea of memory management under iOS is reference counting, which controls the life cycle of memory objects through reference counting of objects. When it comes to programming time, there are two main ways:
1:MRR (manual retain-release), manual reference counting, object generation, destruction, and changes in reference count are all done by developers.
2:ARC (Automatic Reference Counting), automatic reference counting, is only responsible for the generation of objects. Other process developers no longer need to care about their destruction. They are used in a manner similar to garbage collection, but the essence is reference counting.
9.43.2. The problems faced by ¶
According to Apple’s documentation, the two main problems are:
Data released or overwritten is still in use. This will cause memory corruption, usually in the event of an application crash, or, worse, user data.
Not releasing data that is no longer in use can lead to memory leaks. Allocated memory, memory leaks will not be released, even if it is never used again. Leaks can lead to increasing memory usage of applications, which in turn can lead to poor system performance or panic.
9.43.3. Memory management rules ¶
We create our own objects and release them when they no longer need them.
Keep the objects you need to use. These objects must be released if not necessary.
Don’t release objects we don’t have.
9.43.4. Use memory management tools ¶
Memory usage can be analyzed with the help of Xcode tools and instruments. It includes tools such as activity monitors, distributions, leaks, zombies, etc.
9.43.5. To analyze memory allocation ¶
Open an existing application.
Select the product, and the configuration file is as follows
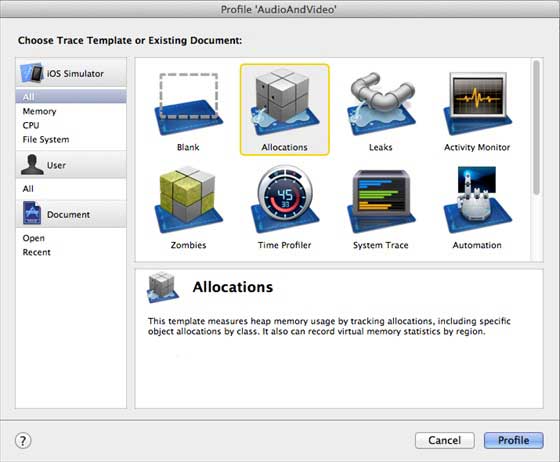
3.在以下界面中选择 Allocations 和 Profile。
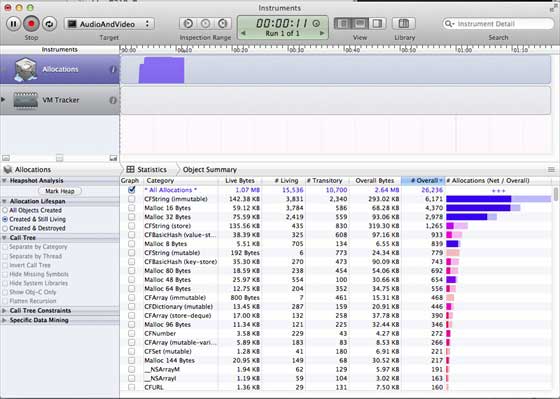
We can see the memory usage of different objects.
You can switch the view controller to see if memory is freed.
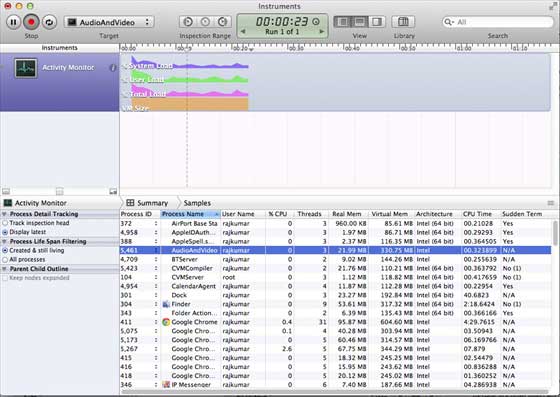
6.同样我们可以使用 Activity Monitor 来查看内存在应用程序中的分配的情况。
These tools can help us understand how memory is being used and where leaks may occur.