NoSQL (NoSQL = Not Only SQL), which means “not just SQL”.
In modern computing systems, a huge amount of data is generated on the network every day.
A large part of this data is processed by relational database management systems (RDBMS). The paper “A relational model of data for large shared data banks” of relational model proposed by E.F.Codd’s in 1970 makes data modeling and application programming easier.
Through the application practice, it is proved that the relational model is very suitable for client-server programming, far beyond the expected benefits. today, it is the leading technology of structured data storage in network and business applications.
NoSQL is a new revolutionary movement of database, and it was suggested in the early days that the trend became higher and higher in 2009. Proponents of NoSQL advocate the use of non-relational data storage, compared with the overwhelming use of relational databases, this concept is undoubtedly the injection of a new kind of thinking. Transaction is transaction in English, which is similar to real-world transaction. It has the following four features: 1、A (Atomicity) 原子性 Atomicity is easy to understand, that is, all operations in the transaction are either completed or not done. The condition for the success of a transaction is that all operations in the transaction are successful. As long as one operation fails, the whole transaction fails and needs to be rolled back. For example, a bank transfer of 100 yuan from An account to B account is divided into two steps: 1) withdraw 100 yuan from An account; 2) deposit 100 yuan to B account. These two steps are either completed together or not together. If only the first step is completed and the second step fails, the money will be inexplicably less than 100 yuan. 2、C (Consistency) 一致性 Consistency is also easy to understand, that is, the database should be in a consistent state all the time, and the operation of the transaction will not change the original consistency constraints of the database. For example, the existing integrity constraint a+b=10, if a transaction changes a, then b must be changed so that the transaction still satisfies a+b=10 after the transaction ends, otherwise the transaction fails. 3、I (Isolation) 独立性 The so-called independence means that concurrent transactions will not affect each other. If the data accessed by one transaction is being modified by another transaction, as long as another transaction is not committed, the data accessed by it will not be affected by the uncommitted transaction. For example, there is a transaction that transfers 100 yuan from An account to B account. In the case that the transaction has not been completed, if B inquires about his own account at this time, he will not see the new 100 yuan. 4、D (Durability) 持久性 Persistence means that once a transaction is committed, its changes will be permanently stored on the database and will not be lost even if there is an outage. A distributed system (distributed system) consists of multiple computers and communication software components connected through a computer network (local network or wide area network). Distributed system is a software system based on network. Because of the characteristics of the software, the distributed system has a high degree of cohesion and transparency. Therefore, the difference between a network and a distributed system has more to do with high-level software (especially the operating system) than hardware. Distributed systems can be applied to different platforms such as Pc, workstations, local area networks and wide area networks. 可靠性(容错) : An important advantage of distributed computing system is reliability. The system crash of one server does not affect the rest of the server. 可扩展性: In distributed computing systems, more machines can be added as needed. 资源共享: Sharing data is essential for applications such as banking and booking systems. 灵活性: Because the system is very flexible, it is easy to install, implement and debug new services. 更快的速度: A distributed computing system can have the computing power of multiple computers, which makes it faster than other systems. 开放系统: Because it is an open system, the service can be accessed locally or remotely. 更高的性能: Compared with centralized computer network clusters, it can provide higher performance (and better cost performance). 故障排除: Troubleshooting and diagnosing problems. 软件: Less software support is the main disadvantage of distributed computing systems. 网络: Network infrastructure problems, including: transmission problems, high load, information loss and so on. 安全性: The characteristics of open systems make distributed computing systems have some problems such as data security and risk of sharing. NoSQL refers to a non-relational database. NoSQL, sometimes referred to as the abbreviation of Not Only SQL, is a general term for database management systems that are different from traditional relational databases. NoSQL is used to store very large-scale data. Google or Facebook, for example, collect terabytes of data for their users every day. These types of data stores do not require fixed schemas and can be scaled out without redundant operations. Today we can easily access and grab data through third-party platforms (such as Google,Facebook, etc.). Users’ personal information, social networks, geographic locations, user-generated data and user action logs have increased exponentially. If we want to mine these user data, then SQL database is no longer suitable for these applications, but the development of NoSQL database can well deal with these large data. Social networking: Wikipedia page: RDBMS Highly organized structured data Structured query language (SQL) (SQL) Data and relationships are stored in separate tables. Data definition language Strict consistency Basic affairs NoSQL It represents more than just SQL. No declarative query language There are no predefined patterns Key-value pair storage, column storage, document storage, graphic database Final consistency, not ACID attribute Unstructured and unpredictable data CAP theorem High performance, high availability and scalability The term NoSQL, which first appeared in 1998, is a lightweight, open-source relational database developed by Carlo Strozzi that does not provide SQL functions. In 2009, Last.fm ‘s Johan Oskarsson launched a discussion on distributed open source databases [2] Eric Evans from Rackspace once again put forward the concept of NoSQL. At this time, NoSQL mainly refers to non-relational, distributed, database design patterns that do not provide ACID. The “no:sql (east)” seminar held in Atlanta in 2009 was a milestone with the slogan “select fun, profit from real_world where relational=false;”. Therefore, the most common interpretation of NoSQL is “non-relational”, emphasizing the advantages of Key-Value Stores and document databases, rather than simply opposing RDBMS. In computer science, CAP Theorem (CAP theorem), also known as Brewer’s theorem Theorem, points out that it is impossible for a distributed computing system to satisfy the following three points: 一致性(Consistency) (all nodes have the same data at the same time) 可用性(Availability) (ensure that every request responds regardless of success or failure) 分隔容忍(Partition tolerance) (the loss or failure of any information in the system will not affect the continued operation of the system) The core of CAP theory is that a distributed system can not meet the three requirements of consistency, availability and partition fault tolerance at the same time, but can only meet two at the same time. Therefore, according to the CAP principle, the NoSQL database is divided into three categories: meeting the CA principle, meeting the CP principle and meeting the AP principle. CA-A single point of cluster, a system that meets consistency and availability, and is usually not very scalable. CP-A system that satisfies consistency and partition tolerance, usually with low performance. AP-Systems that meet availability and partition tolerance may generally require less consistency. Advantages: High scalability Distributed computing Low cost Architectural flexibility, semi-structured data There are no complicated relationships. Disadvantages: There is no standardization Limited query capabilities (so far) Ultimate consistency is an unintuitive program. BASE:Basically Available, Soft-state, Eventually Consistent . Defined by Eric Brewer. The core of CAP theory is that a distributed system can not meet the three requirements of consistency, availability and partition fault tolerance at the same time, but can only meet two at the same time. BASE is the general principle of weak availability and consistency requirements for NoSQL databases: Basically Available-basically available Soft-state-soft state / flexible transactions. “Soft state” can be understood as “connectionless”, while “Hard state” is “connection-oriented” Eventually Consistency-the ultimate consistency, is also the ultimate goal of ACID. ACID BASE Atomicity (Atomicity) Basic available (Basically Available) Consistency (Consistency) Soft state / flexible transaction (Soft state) Isolation (Isolation) Final consistency (Eventual consistency) Persistence (Durable) Types Partial representative Characteristics Column storage Hbase Cassandra Hypertable As the name implies, data is stored in columns. The biggest feature is that it is convenient to store structured and semi-structured data, and it is convenient to do data compression. It has great IO advantages for queries against a certain column or columns. Document storage MongoDB CouchDB Document storage is generally stored in a format similar to json, and the stored content is document-based. This gives you the opportunity to index some fields and implement some of the functions of a relational database. Key-value storage Tokyo Cabinet / Tyrant Berkeley DB MemcacheDB Redis Its value can be quickly queried through key. Generally speaking, storage is accepted according to order, regardless of value format. (Redis includes other features) Graph storage Neo4J FlockDB The best storage of graphic relationships. If the traditional relational database is used to solve the problem, the performance is low, and the design and use is not convenient. Object storage Db4o Versant Manipulate the database through a syntax similar to that of an object-oriented language and access data in the way of objects. Xml database Berkeley DB XML BaseX Store XML data efficiently and support XML’s internal query syntax, such as XQuery,Xpath. 3.2.1. Relational databases follow ACID rules ¶
3.2.2. Distributed system ¶
3.2.3. Advantages of distributed Computing ¶
3.2.4. Disadvantages of distributed Computing ¶
3.2.5. What is NoSQL? ¶
3.2.6. Why use NoSQL? ¶
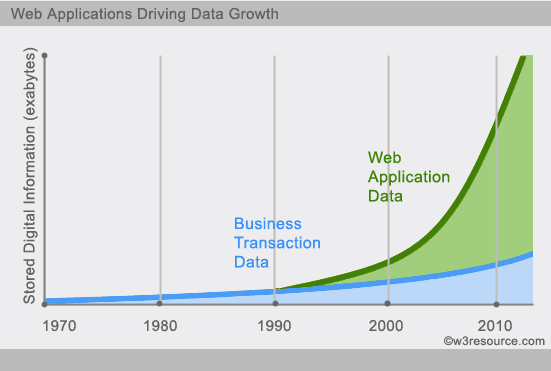
3.2.7. Example ¶
Each record: UserID1, UserID2
Separate records: UserID, first_name,last_name, age, gender,...
Task: Find all friends of friends of friends of ... friends of a given
user.
Large collection of documents
Combination of structured and unstructured data
Task: Retrieve all pages regarding athletics of Summer Olympic before
1950.
3.2.8. RDBMS vs NoSQL ¶
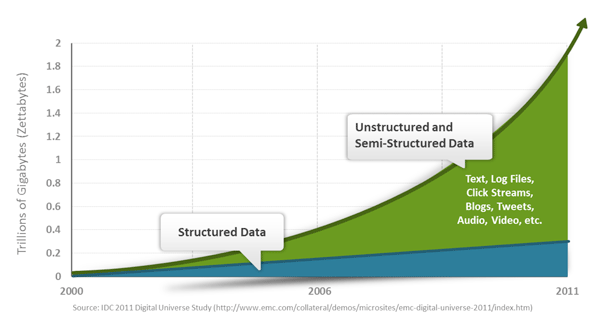
3.2.9. A brief history of NoSQL ¶
3.2.10. CAP theorem (CAP theorem) ¶
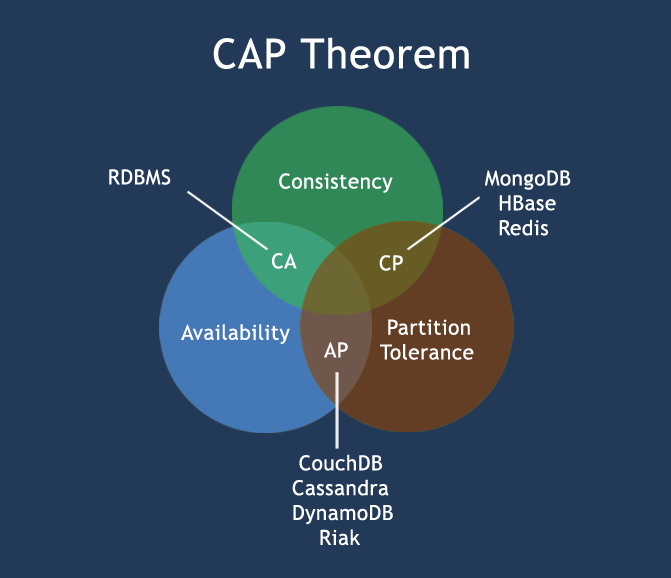
3.2.11. Advantages / disadvantages of NoSQL ¶
3.2.12. BASE ¶
3.2.13. ACID vs BASE ¶
3.2.14. NoSQL database classification ¶