2.15.1. Introduction to Compose ¶
Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications. With Compose, you can use the YML file to configure all the services your application needs. Then, with a single command, you can create and start all services from the YML file configuration.
If you don’t know the YML file configuration, you can read it first. YAML 入门教程 .
There are three steps used by Compose:
Use Dockerfile to define the environment of the application.
Use docker-compose.yml to define the services that make up the application so that they can run together in an isolated environment.
Finally, execute the docker-compose up command to start and run the entire application.
The configuration example of docker-compose.yml is as follows (refer to the following for configuration parameters):
Example
# yaml 配置实例
version:'3'
services:
web:
build:.
ports:
- "5000:5000"
volumes:
- .:/code
- logvolume01:/var/log
links:
- redis
redis:
image:redis
volumes:
logvolume01:{}
Compose installation ¶
On Linux, we can download its binary package from Github to use, the latest release address: https://github.com/docker/compose/releases .
Run the following command to download the current stable version of Docker Compose:
$ sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/v2.2.2/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
To install another version of Compose, replace v2.2.2.
Apply executable permissions to binaries:
$ sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Create a soft chain:
$ sudo ln -s /usr/local/bin/docker-compose /usr/bin/docker-compose
Test whether the installation is successful:
$ docker-compose --version
cker-compose version 1.24.1, build 4667896b
注意 For alpine, the following dependency packages are required: py-pip,python-dev,libffi-dev,openssl-dev,gcc,libc-dev, and make.
2.15.2. MacOS ¶
The Docker desktop version of Mac and Docker Toolbox already include Compose and other Docker applications, so Mac users do not need to install Compose separately. Docker installation instructions can be found in MacOS Docker 安装 .
2.15.3. Windows PC ¶
The Docker desktop version of Windows and Docker Toolbox already include Compose and other Docker applications, so Windows users do not need to install Compose separately. Docker installation instructions can be found in Windows Docker 安装 .Use ¶
2.15.4. 1. Prepare ¶
Create a test directory:
$ mkdir composetest
$ cd composetest
Create a file named app.py in the test directory and copy and paste the following:
Composetest/app.py file code
import time
import redis
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(\__name_\_)
cache = redis.Redis(host='redis', port=6379)
def get_hit_count():
retries = 5
while True:
try:
return cache.incr('hits')
except redis.exceptions.ConnectionError as exc:
if retries == 0:
raise exc
retries -= 1
time.sleep(0.5)
@app.route('/')
def hello():
count = get_hit_count()
return 'Hello World! I have been seen {} times.\\n'.format(count)
In this example, redis is the hostname of the redis container on the application network, which uses port 6379.
Create another file called requirements.txt in the composetest directory as follows:
flask
redis
2.15.5. 2. Create a Dockerfile file ¶
In the composetest directory, create a file called Dockerfile with the following contents:
FROM python:3.7-alpine
WORKDIR /code
ENV FLASK_APP app.py
ENV FLASK_RUN_HOST 0.0.0.0
RUN apk add --no-cache gcc musl-dev linux-headers
COPY requirements.txt requirements.txt
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
COPY . .
CMD ["flask", "run"]
Dockerfile 内容解释:
FROM python:3.7-alpine : build the image from the Python 3.7image.
WORKDIR /code Set the working directory to / code
ENV FLASK_APP app.py
ENV FLASK_RUN_HOST 0.0.0.0
设置 flask 命令使用的环境变量。
RUN apk add –no-cache gcc musl-dev linux-headers Install gcc so that Python packages such as MarkupSafe and SQLAlchemy can be compiled and accelerated
COPY requirements.txt requirements.txt
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
复制 requirements.txt 并安装 Python 依赖项。
COPY . . Will. Copy the current directory in the project to. The working directory in the mirror.
CMD [“flask”, “run”] The default execution command provided by the container is flask run.
2.15.6. 3. Create docker-compose.yml ¶
Create a file named docker-compose.yml in the test directory and paste the following:
Docker-compose.yml profile
# yaml 配置
version:'3'
services:
web:
build:.
ports:
- "5000:5000"
redis:
image:"redis:alpine"
The Compose file defines two services: web and redis.
web The web service uses an image built from the current directory of Dockerfile It then binds the container and host to the exposed port 5000. This sample service uses the default port 5000 of the Flask Web server.
redis The redis service uses a public Redis image of Docker Hub
2.15.7. 4. Use Compose commands to build and run your application ¶
In the test directory, execute the following command to start the application:
docker-compose up
If you want to run the service in the background, you can add the-d parameter:
docker-compose up -d
Yml configuration instruction reference ¶
2.15.8. Version ¶
Specifies which version of the compose this yml depends on.
2.15.9. Build ¶
Specify as the build image context path:
For example, the webapp service is specified as an image built from the context path. / dir/Dockerfile:
version: "3.7"
services:
webapp:
build: ./dir
Or, as an object with a path specified in the context, and optionally Dockerfile and args:
version: "3.7"
services:
webapp:
build:
context: ./dir
dockerfile: Dockerfile-alternate
args:
buildno: 1
labels:
- "com.example.description=Accounting webapp"
- "com.example.department=Finance"
- "com.example.label-with-empty-value"
target: prod
Context: context path.
Dockerfile: specifies the name of the Dockerfile file to build the image.
Args: add build parameters, which are environment variables that can only be accessed during the build process.
Labels: sets the label for building images.
Target: multi-tier build, you can specify which layer to build.
2.15.10. cap_add,cap_drop ¶
Add or remove the host kernel functions owned by the container.
cap_add:
- ALL # 开启全部权限
cap_drop:
- SYS_PTRACE # 关闭 ptrace权限
2.15.11. cgroup_parent ¶
Specifying a parent cgroup group for the container means that the resource limits of that group will be inherited.
cgroup_parent: m-executor-abcd
2.15.12. Command ¶
Overrides the default command started by the container.
command: ["bundle", "exec", "thin", "-p", "3000"]
2.15.13. container_name ¶
Specifies the custom container name instead of the generated default name.
container_name: my-web-container
2.15.14. depends_on ¶
Set dependencies.
Docker-compose up: start services in dependency order. In the following example, db and redis are started before web is started.
Docker-compose up SERVICE: automatically includes dependencies for SERVICE. In the following example, docker-compose up web will also create and start db and redis.
Docker-compose stop: stops the service in dependency order. In the following example, web stops before db and redis.
version: "3.7"
services:
web:
build: .
depends_on:
- db
- redis
redis:
image: redis
db:
image: postgres
Note: the web service does not wait for redis db to start completely.
2.15.15. Deploy ¶
Specify the configuration related to the deployment and operation of the service. It is only useful in swarm mode.
version: "3.7"
services:
redis:
image: redis:alpine
deploy:
mode:replicated
replicas: 6
endpoint_mode: dnsrr
labels:
description: "This redis service label"
resources:
limits:
cpus: '0.50'
memory: 50M
reservations:
cpus: '0.25'
memory: 20M
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
delay: 5s
max_attempts: 3
window: 120s
You can select parameters:
endpoint_mode How to access the cluster service
endpoint_mode: vip
# Docker 集群服务一个对外的虚拟 ip。所有的请求都会通过这个虚拟 ip 到达集群服务内部的机器。
endpoint_mode: dnsrr
# DNS 轮询(DNSRR)。所有的请求会自动轮询获取到集群 ip 列表中的一个 ip 地址。
labels : set a label on the service Can be overridden with labels on the container (configuration at the same level as deploy)
deploy
Under
labels
.
mode Specifies the mode provided by the service
replicated Copy the service, copy the specified service to the machine in the cluster.
global Global service, which will be deployed to each node of the cluster
Illustration: the yellow square in the following figure is the operation of replicated mode, and the gray square is the operation of global mode.
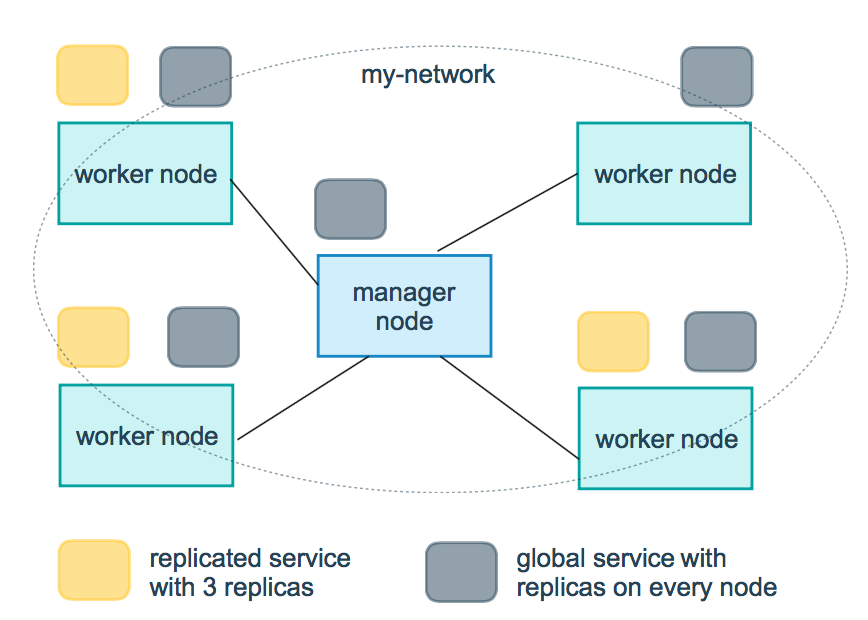
replicas:mode When replicated, you need to use this parameter to configure the specific number of nodes running.
resources Configure the restrictions on the use of server resources, for example, the percentage of cpu and memory footprint required to configure the redis cluster to run. Avoid exceptions that take up too much resources.
restart_policy Configure how to restart the container when exiting
Condition: optional none,on-failure or any (default: any).
Delay: how long to restart after setting (default: 0).
max_attempts:尝试重新启动容器的次数,超出次数,则不再尝试(默认值:一直重试)。
Window: sets the container restart timeout (default: 0).
rollback_config Configure how to roll back the service if the update fails
parallelismThe number of containers to be rolled back at a time. If set to 0, all containers are rolled back at the same time.delayThe time to wait between rollbacks of each container group (default is 0s).failure_actionWhat to do if the rollback fails One of the continue or pause (the default pause).monitorAfter each container is updated, keep watching to see if it fails (ns |us| Ms |s| M | h) (default is 0s).max_failure_ratioThe failure rate that can be tolerated during the rollback (default is 0).orderThe order of operations during the rollback One of these is stop-first (serial rollback), or start-first (parallel rollback) (default stop-first).
update_config Configure how the service should be updated, which is useful for configuring rolling updates
parallelismThe number of containers updated at a time.delayThe amount of time to wait between updating a set of containersfailure_actionWhat to do if the update fails One of the continue,rollback or pause (default: pause).monitorAfter each container is updated, keep watching to see if it fails (ns |us| Ms |s| M | h) (default is 0s).max_failure_ratioThe failure rate that can be tolerated during the update processorderThe order of operations during the rollback One of these is stop-first (serial rollback), or start-first (parallel rollback) (default stop-first).
注 Only V3.4 and later are supported.
2.15.16. Devices ¶
Specifies the list of device mappings.
devices:
- "/dev/ttyUSB0:/dev/ttyUSB0"
2.15.17. Dns ¶
Custom DNS server, which can be a single value or multiple values of a list.
dns: 8.8.8.8
dns:
- 8.8.8.8
- 9.9.9.9
2.15.18. dns_search ¶
Customize the DNS search domain. Can be a single value or a list.
dns_search: example.com
dns_search:
- dc1.example.com
- dc2.example.com
2.15.19. Entrypoint ¶
Overrides the container default entrypoint.
entrypoint: /code/entrypoint.sh
It can also be in the following format:
entrypoint:
- php
- -d
- zend_extension=/usr/local/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-non-zts-20100525/xdebug.so
- -d
- memory_limit=-1
- vendor/bin/phpunit
2.15.20. env_file ¶
Add environment variables from the file. Can be a single value or multiple values of a list.
env_file: .env
It can also be in list format:
env_file:
- ./common.env
- ./apps/web.env
- /opt/secrets.env
2.15.21. Environment ¶
Add environment variables. You can use an array or dictionary, any Boolean value, which needs to be enclosed in quotation marks to ensure that the YML parser does not convert it to
True
Or
False
.
environment:
RACK_ENV: development
SHOW: 'true'
2.15.22. Expose ¶
The port is exposed, but not mapped to the host, and is only accessed by the connected service.
Only internal ports can be specified as parameters:
expose:
- "3000"
- "8000"
2.15.23. extra_hosts ¶
Add a hostname mapping. Similar to docker client-add-host.
extra_hosts:
- "somehost:162.242.195.82"
- "otherhost:50.31.209.229"
The above will create a mapping with ip address and hostname in the internal container / etc/hosts of this service:
162.242.195.82 somehost
50.31.209.229 otherhost
2.15.24. Healthcheck ¶
Used to detect whether the docker service is running healthily.
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://localhost"] # 设置检测程序
interval: 1m30s # 设置检测间隔
timeout: 10s # 设置检测超时时间
retries: 3 # 设置重试次数
start_period: 40s # 启动后,多少秒开始启动检测程序
2.15.25. Image ¶
Specifies the image in which the container runs. The following formats are available:
image: redis
image: ubuntu:14.04
image: tutum/influxdb
image: example-registry.com:4000/postgresql
image: a4bc65fd # 镜像id
2.15.26. Logging ¶
Logging configuration for the service.
Driver: specifies the logging driver for the service container. The default value is json-file. There are three options
driver: "json-file"
driver: "syslog"
driver: "none"
Under the json-file driver only, the following parameters can be used to limit the number and size of logs.
logging:
driver: json-file
options:
max-size: "200k" # 单个文件大小为200k
max-file: "10" # 最多10个文件
When the file limit is reached, the old file will be deleted automatically.
Under the syslog driver, you can use syslog-address to specify the log receiving address.
logging:
driver: syslog
options:
syslog-address: "tcp://192.168.0.42:123"
2.15.27. network_mode ¶
Sets the network mode.
network_mode: "bridge"
network_mode: "host"
network_mode: "none"
network_mode: "service:[service name]"
network_mode: "container:[container name/id]"
Networks
Configure the network to which the container is connected, referencing entries under the top-level networks.
services:
some-service:
networks:
some-network:
aliases:
- alias1
other-network:
aliases:
- alias2
networks:
some-network:
# Use a custom driver
driver: custom-driver-1
other-network:
# Use a custom driver which takes special options
driver: custom-driver-2
aliases Other containers on the same network can use the service name or this alias to connect to the service of the corresponding container
2.15.28. Restart ¶
No: is the default restart policy, and the container will not be restarted under any circumstances.
Always: the container always restarts.
On-failure: the container will be restarted only when the container exits abnormally (the exit status is not 0).
Unless-stopped: always restart the container when it exits, but do not consider the container that was stopped when the Docker daemon started
restart: "no"
restart: always
restart: on-failure
restart: unless-stopped
Note: swarm cluster mode, please use it instead
restart_policy
.
2.15.29. Secrets ¶
Store sensitive data, such as passwords:
version: "3.1"
services:
mysql:
image: mysql
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD_FILE: /run/secrets/my_secret
secrets:
- my_secret
secrets:
my_secret:
file: ./my_secret.txt
2.15.30. security_opt ¶
Modify the default schema tag of the container.
security-opt:
- label:user:USER # 设置容器的用户标签
- label:role:ROLE # 设置容器的角色标签
- label:type:TYPE # 设置容器的安全策略标签
- label:level:LEVEL # 设置容器的安全等级标签
2.15.31. stop_grace_period ¶
Specifies how long to wait before sending a SIGKILL signal to close the container after the container cannot process SIGTERM (or any stop_signal signal).
stop_grace_period: 1s # 等待 1 秒
stop_grace_period: 1m30s # 等待 1 分 30 秒
The default wait time is 10 seconds.
2.15.32. stop_signal ¶
Sets an alternative signal to stop the container. SIGTERM is used by default.
The following example uses SIGUSR1 instead of the signal SIGTERM to stop the container.
stop_signal: SIGUSR1
2.15.33. Sysctls ¶
Set the kernel parameters in the container, either in array or dictionary format.
sysctls:
net.core.somaxconn: 1024
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies: 0
sysctls:
- net.core.somaxconn=1024
- net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies=0
2.15.34. Tmpfs ¶
Install a temporary file system in the container. Can be a single value or multiple values of a list.
tmpfs: /run
tmpfs:
- /run
- /tmp
2.15.35. Ulimits ¶
Overrides the container default ulimit.
ulimits:
nproc: 65535
nofile:
soft: 20000
hard: 40000
2.15.36. Volumes ¶
Mount the host’s data volume or file into the container.
version: "3.7"
services:
db:
image: postgres:latest
volumes:
- "/localhost/postgres.sock:/var/run/postgres/postgres.sock"
- "/localhost/data:/var/lib/postgresql/data"