3.25.1. MongoDB data backup ¶
In Mongodb, we use the mongodump command to back up MongoDB data. This command exports all data to the specified directory.
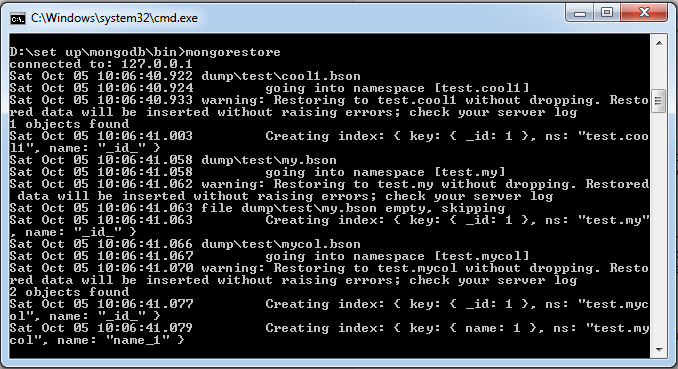
The mongodump command can specify the server for rollover of the exported data magnitude through parameters. The mongodump command script syntax is as follows: -h: The address of the server where MongoDB resides, for example: 127.0.0.1. Of course, you can also specify the port number: 127.0.0.1 27017. -d: Database instance that needs to be backed up, for example: test -o: The location of the backup data, for example: C:datadump. Of course, this directory needs to be established in advance. After the backup is completed, the system automatically creates a test directory under the dump directory, in which the backup data of the database instance is stored. Start your mongod service locally with 27017. Open a command prompt window and enter the command mongodump in the bin directory of the MongoDB installation directory: After executing the above command, the client connects to the MongoDB service with ip 127.0.0.1 port number 27017 and backs up all data to the bin/dump/ directory. The output of the command is as follows: The list of optional parameters for the mongodump command is as follows: Grammar Description Example Mongodump-host HOST_NAME-port PORT_NUMBER This command will back up all MongoDB data Mongodump-host runoob.com-port 27017 Mongodump-dbpath DB_PATH-out BACKUP_DIRECTORY Mongodump-dbpath / data/db/-out / data/backup/ Mongodump-collection COLLECTION-db DB_NAME This command backs up the collection of the specified database. Mongodump-collection mycol-db testGrammar ¶
>mongodump -h dbhost -d dbname -o dbdirectory
Example ¶
>mongodump
3.25.2. MongoDB data recovery ¶
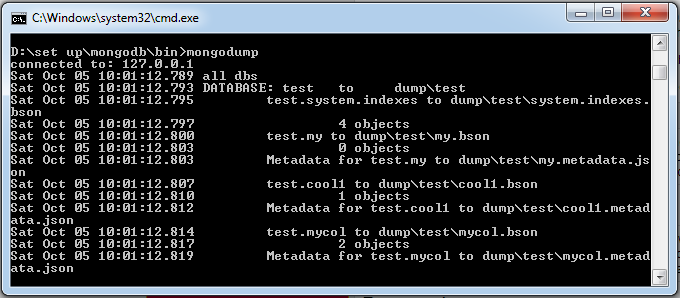
Mongodb uses the mongorestore command to restore backed-up data. The mongorestore command script syntax is as follows: –host <:port>, -h <:port>: Server address where MongoDB resides. Default is: localhost:27017 –db , -d : The database instance that needs to be restored, such as test. Of course, this name can be different from that of backup, such as test2. –drop: When restoring, delete the current data first, and then restore the backed-up data. That is to say, after recovery, the data added and modified after backup will be deleted, so use it with caution. <path>: The last parameter of mongorestore, which sets the location of the backup data, for example: C:datadumptest. You cannot specify both < path > and– dir options, and– dir can also set the backup directory. –dir: Specify the directory of the backup You cannot specify both < path > and– dir options. Next, let’s execute the following command: The output from the above command is as follows:Grammar ¶
>mongorestore -h <hostname><:port> -d dbname <path>
>mongorestore