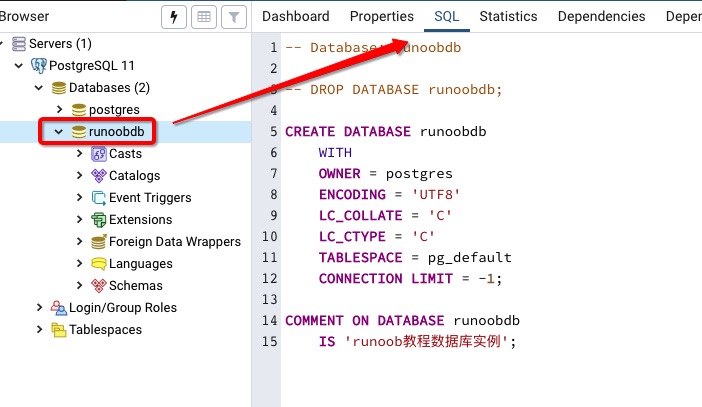
In the previous section, we talked about how to create a database, and then we discussed how to select the database we created. In the PostgreSQL command window, we can enter the SQL statement at the command prompt: Usel to view existing databases: Next we can usec + database name to enter the database: From the command line of the system, we can add the database name after the connection to the database to select the database: The pgAdmin tool is easier. Just click on the database to select it. You can also view some additional information about the database: 5.8.1. The command window of the database ¶
postgres=#
postgres=# \l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
-----------+----------+----------+---------+-------+-----------------------
postgres | postgres | UTF8 | C | C |
runoobdb | postgres | UTF8 | C | C |
template0 | postgres | UTF8 | C | C | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template1 | postgres | UTF8 | C | C | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
(4 rows)
postgres=# \c runoobdb
You are now connected to database "runoobdb" as user "postgres".
runoobdb=#
5.8.2. System command line window ¶
$ psql -h localhost -p 5432 -U postgres runoobdb
Password for user postgres: ****
psql (11.3)
Type "help" for help.
You are now connected to database "runoobdb" as user "postgres".
runoobdb=#
5.8.3. PgAdmin tool ¶