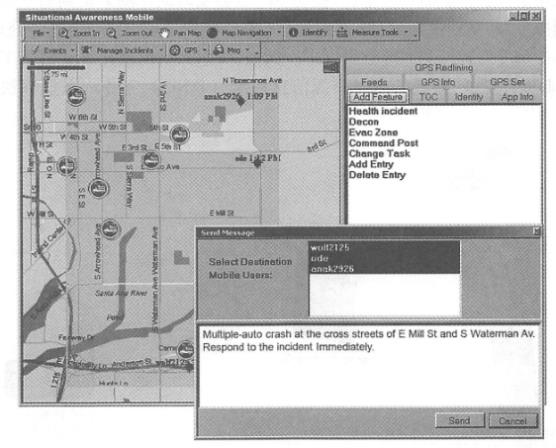
There are many methods to develop mobile GIS (Table 5. 1 ), including native application-based methods, browser-based methods, and short message-based methods (KaPoor, 2008). This section discusses the advantages and limitations of these methods, and describes how to choose the right method based on the purpose, requirements and user group of the application project.
表5.1对比不同的移动GIS开发方法
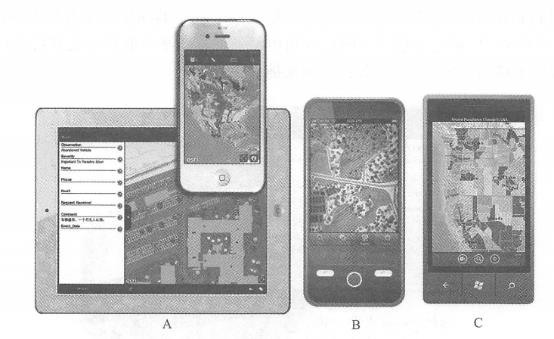
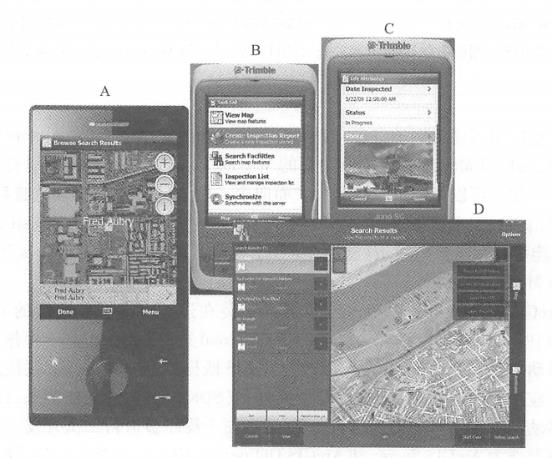
Native applications are software programs installed and running on mobile devices. This is an important mobile GIS application development method. the advantages include Friendly user experience: Native applications can be closely and perfectly integrated with the operating system, making full use of the unique or rich user interface provided by the mobile operating system to achieve the most friendly user interaction. Ability to directly use auxiliary equipment: for example, you can directly read the GPS receiver, so that you can perform differential calculations on coordinates measured by GPS. This feature is critical for many applications, such as surveying, navigation and one. Some professional applications, etc. Ability to use local files and data: Some projects need to continue working without a network, so data needs to be stored on the device. The shortcomings of local applications are that they require large investment in development, are poor cross-platform, the programming language relies on the operating system, and applications developed for one operating system often cannot run on other operating systems. For example, on the iOS platform, you need to use Objective C(Figure 5. 5)Use Java or C on the Android platform, use Silverlight(running outside the browser) on the Windows Phone platform, and use. NET Mobile on the Windows Mobile platform. At present, some “universal” methods have also emerged. For example,Adobe’s Flash Builder integrated development environment can compile the same program into iOS and Android versions (Figure 5.5 ). Although this method cannot make full use of the characteristics or unique interfaces of each mobile platform, it provides a convenient way to cross-platform development of mobile GIS. Fig. 58 (A)Adobe’s FlashBuilder integrated development environment can compile the same Flex program into iOS, Android and BlackBerry versions, providing a cross-mobile platform development method; (B) Apple’s recommended method for developing iOS applications is to use Apple’s computers (such as MadBookAir), XCode integrated development environment and Objective C language # There are many examples of native applications. For example, there are a large number of native applications that can be downloaded or purchased for free in Apple’s App Store, Google’s Android Market, and Microsoft’s Windows Phone Marketplace. Applications for individual users include car navigation systems, Google Maps (mobile version) and Foursquare mobile version. Applications for business users include Esri’s Arc-GIS smartphone and tablet versions (including ArcGIS for iOS, Android, and Windows Phone), ArcGIS Mobile, and ArcPad. ArcGIS smartphone and tablet versions can be installed on iPhones, iPads, and iPdTouch running the iOS operating system (Figure 5. 6), and on multiple mobile platforms running Android or Windows Phone operating systems. For each operating system,ArcGIS provides both a mobile GIS application that can be used directly, and a software development kit (SDK). The former can be downloaded and installed for free in the mobile application stores of Apple, Google, and Microsoft. The latter is convenient for programmers to conduct secondary development. Its primary role is as an ArcGIS Server and ArcGIS Online(ArcGIS. com), which can realize functions including querying and using map services and map applications in ArcGIS Online, displaying dynamic or tiled map services, combining multiple map services, collecting geographical and attribute data, performing map queries, place name address lookups, and invoking analytical tasks supported by ArcGIS Server. ArcGIS Mobile is a task-guided mobile application that requires a mobile device running on the Win¬dowsMobile operating system or a portable computer running on the Windows operating system (Figure 5. 7) 。 Fig. 59 ArcGIS for iPhone and iPad (A) ,Android (B) ,Windows Phone (C) (Acknowledgements: U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. Census Bureau) # Fig. 60 ArcGISMobile provides computing power and data from GIS servers to a variety of mobile devices, which can be used to (A) locate colleagues or devices;(B) perform assigned tasks through a task-oriented user interface; (C) edit attribute data and add photos; and (D) use its tablet-based night view interface. (Thanks:ANDAutomotive Navigation Data,Tele Atlas NorthAmerica, Inc., GeoEye, i-Cubed and Trimble) # It provides an application that can be flexibly configured and also provides a software development tool (SDK). Its main role is also as a client of ArcGIS Server, and can load geographical data and maps onto mobile devices, and has certain capabilities to run offline. Its functions include: Conduct map browsing, navigation and equipment and asset surveys in the wild; Collect and edit GIS data, and synchronize the collected data to the GIS server at any time; Query and manage dispatch orders; Rapid deployment and application without programming. Compared with the first two, ArcPad is suitable for field GIS applications with higher spatial accuracy requirements, especially field measurement, underground pipeline maintenance, etc.(Figure 5. 8)。It provides outdoor geographical information collection, editing and display capabilities. The data it collects can be submitted to the main database of the server through ArcGIS desktop software after returning to the office, or can be submitted at any time through ArcGIS Server through wireless communication. Fig. 61 GeoCollector is a professional handheld GPS terminal device that integrates ArcPad and Trimble, which can achieve outdoor surveying accuracy of 1 foot. (Thanks:Tele Atlas North America,Inc. and Trimble) # Web browsers on mobile devices are also known as “mobile browsers” or “micro-browsers.” Mobile GIS can be implemented based on HTML, JavaScript and browser plug-ins. Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) WAP is an international standard whose main intention is to enable low-end mobile phones to browse the web, so its functions are limited. WAP 1.0 formulated the WML( Wireless Markup Language) language to write WAP web pages. WML has been widely criticized for its incompatibility with the widely used HTML. WAP2. 0 has improved this and formulated XHTML-MP( extensible HTML mobile pro file, a subset of HTML), which is recommended as the language for developing WAP web pages. WAP pages can be displayed on high-end and low-end mobile devices, so they can cover a large user base. However, the user interface of WAP web pages is often relatively simple, making it difficult to develop friendly and rich GIS functions. Full version of HTML With the development of mobile platforms, Web browsers such as Apple’s iPhone, Google’s Android and Windows Phone have become close to the functions of desktop computer browsers. They can support complete HTML, CSS, JaVaScriPt and AJAX. Developers can adopt these commonly used and familiar development languages without having to learn relatively unfamiliar WAP or relatively difficult local development methods. Or you can modify the existing HTMiyjavaScript WebGIS application (mainly modify the interface to adapt to the small screen of mobile devices, and the application logic layer on the server side often does not need to be significantly changed), so you can support both desktop Web browsers and mobile clients of multiple operating systems, achieving better cross-platform performance (Figure 5. 9)。Through some packages, such as the JavaScript program provided by Esri for platforms such as iOS Fig. 62 In the resource center of the ArcGIS API for JavaScript, there are many examples for mobile GIS on the iOS platform (A) ; ArcGISOnline (ArcGIS. com) is based on HTML and JavaScript and can run on smartphones and tablets, such as iPad (B); run a mobile map based on the ArcGIS API for JavaScript on Android (C). (Acknowledgement: U.S. Census Bureau) # The package can also achieve a user interface close to the local development method and achieve a better user experience. Mobile browser plugin On desktop computer platforms, Web browser plug-ins such as Flash and Silverlight are commonly used and highly expressive WebGIS development technologies. However, at present, mobile platforms do not support plug-ins enough and are not unified. Steve Jobs(2010), former president of Apple, once wrote an article pointing out that Flash plug-ins consume more CPU resources and consume power on the iOS mobile platform, and refused to support Flash on iOS. Adobe also stated that it would stop the development of Hash plug-ins in mobile browsers and focus on developing Flash and Air as native application development methods on mobile platforms and the development of Flash in desktop browsers (Winokur, 2011), making the future of this method based on mobile browser plug-ins unclear. SMS is a service supported by both high-end mobile phones. Using SMS methods to develop WebGIS applications can deliver geographical information to the largest user group. For example, Yahoo and Google have allowed users to query and collect business lists, weather and navigation information about nearby places via text messages. The disadvantage of this method is that the user experience is poor, and the content is generally limited to text and is not intuitive. SMS can also be combined with other methods. For example, some sites allow users to use a desktop computer to query locations and driving directions, and send the results to their mobile phones via text messages. In addition, Esri Situational Awareness Bundle and Lomarinda University Medical Center advanced emergency GIS applications Fig. 63 Region-based group text message technology can send group text messages to people in the field in a selected area on the screen. (Thanks:Tele Atlas North America, Inc.) # Ability to provide region-based group messaging function. Through the app, field personnel can report their location, and the command center can also send text messages to all personnel located in an area (Figure 5. 10)。This method has special value in emergency situations, especially when it is difficult to obtain communication numbers of field personnel.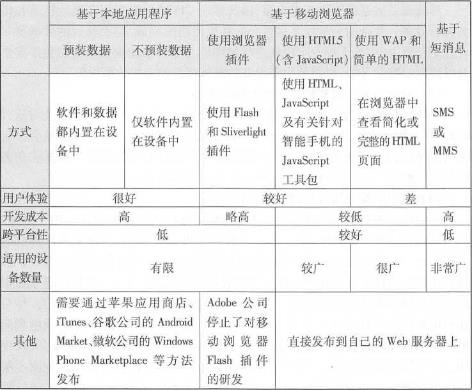
Native application approach #


Web browser-based development method #

SMS based approach #