First, define a binary search tree. The Java code is as follows:
public class BST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
// 树中的节点为私有的类, 外界不需要了解二分搜索树节点的具体实现
private class Node {
private Key key;
private Value value;
private Node left, right;
public Node(Key key, Value value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
left = right = null;
}
}
// 根节点
private Node root;
// 树种的节点个数
private int count;
// 构造函数, 默认构造一棵空二分搜索树
public BST() {
root = null;
count = 0;
}
// 返回二分搜索树的节点个数
public int size() {
return count;
}
// 返回二分搜索树是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return count == 0;
}
}
Node represents nodes and count represents the number of nodes.
The following example inserts element 61 into the following binary search tree:

(1)需要插入的元素 61 比 42 大,比较 42 的右子树根节点。

(2)61 比 59 大,所以需要把 61 移动到 59 右子树相应位置,而此时为空,直接插入作为 59 的右子节点。
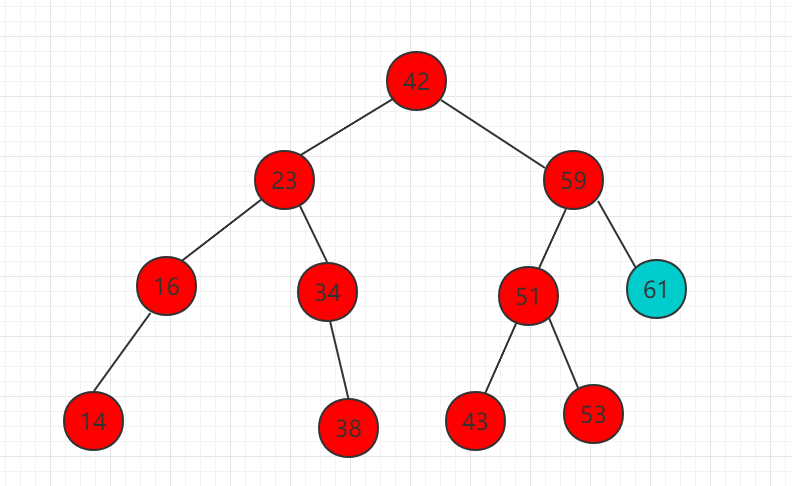
The insert operation is also a recursive process, which is divided into three cases, equal to, greater than, and less than. 源码包下载: Download 5.16.1. Java instance code ¶
Src/runoob/binary/BinarySearchTreeInsert.java file code: ¶
package runoob.binary;
/*\*
\* 二分搜索树插入新的元素
*/
public class BinarySearchTreeInsert<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value>
{
// 树中的节点为私有的类, 外界不需要了解二分搜索树节点的具体实现
private class Node {
private Key key;
private Value value;
private Node left, right;
public Node(Key key, Value value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
left = right = null;
}
}
private Node root; // 根节点
private int count; // 树种的节点个数
// 构造函数, 默认构造一棵空二分搜索树
public BinarySearchTreeInsert() {
root = null;
count = 0;
}
// 返回二分搜索树的节点个数
public int size() {
return count;
}
// 返回二分搜索树是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return count == 0;
}
// 向二分搜索树中插入一个新的(key, value)数据对
public void insert(Key key, Value value) {
root = insert(root, key, value);
}
//核心代码---开始
// 向以node为根的二分搜索树中, 插入节点(key, value), 使用递归算法
// 返回插入新节点后的二分搜索树的根
private Node insert(Node node, Key key, Value value) {
if (node == null) {
count++;
return new Node(key, value);
}
if (key.compareTo(node.key) == 0)
node.value = value;
else if (key.compareTo(node.key) < 0)
node.left = insert(node.left, key, value);
else // key > node->key
node.right = insert(node.right, key, value);
return node;
}
//核心代码---结束
}