This section describes how to add elements to a maximum heap called shift up .
Suppose we add a new element 52 to the largest heap below, placed in the last bit of the array, 52 is larger than the parent node 16, which does not meet the definition of the heap and needs to be adjusted.
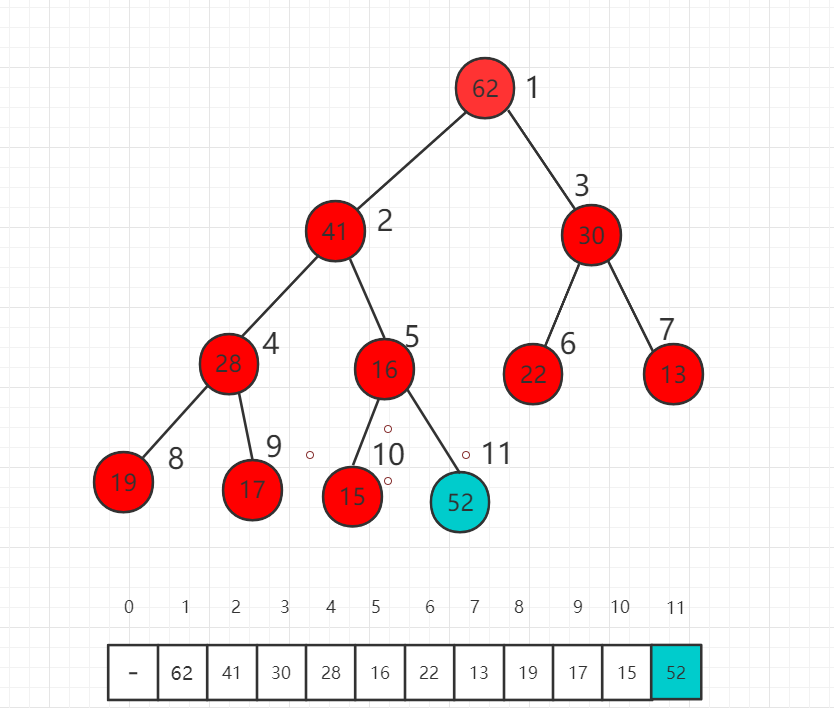
First, the swap index is the position of the values in the 5 and 11 arrays, that is, the 52 and 16 swap positions.
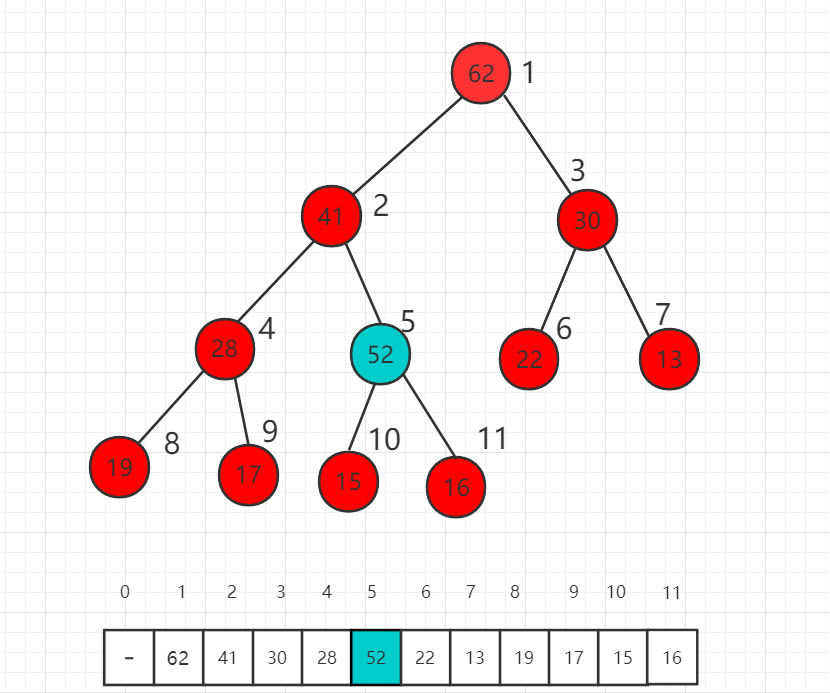
At this point, 52 is still larger than the value 41 with a parent node index of 2, and we need to move it further.
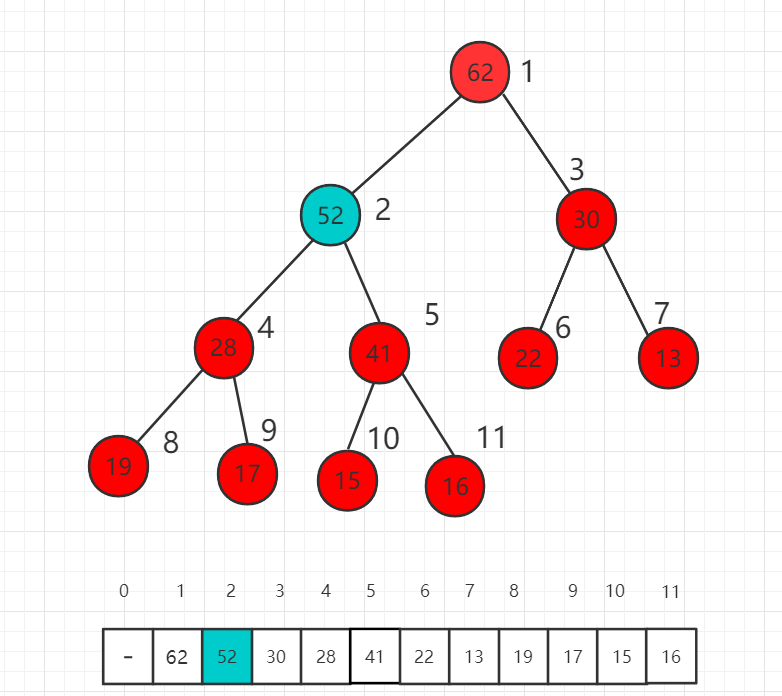
By this time, comparing the size of 52 and 62, 52 is already smaller than the parent node and does not need to rise any more, meeting the definition of maximum heap. We call this process the largest heap of shift up. 源码包下载: Download 5.10.1. Java instance code ¶
Src/runoob/heap/HeapShiftUp.java file code: ¶
package runoob.heap;
/*\*
\* 往堆中添加一元素
*/
public class HeapShiftUp<T extends Comparable> {
protected T[] data;
protected int count;
protected int capacity;
// 构造函数, 构造一个空堆, 可容纳capacity个元素
public HeapShiftUp(int capacity){
data = (T[])new Comparable[capacity+1];
count = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
}
// 返回堆中的元素个数
public int size(){
return count;
}
// 返回一个布尔值, 表示堆中是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return count == 0;
}
// 像最大堆中插入一个新的元素 item
public void insert(T item){
assert count + 1 <= capacity;
data[count+1] = item;
count ++;
shiftUp(count);
}
// 交换堆中索引为i和j的两个元素
private void swap(int i, int j){
T t = data[i];
data[i] = data[j];
data[j] = t;
}
//*******************\*
//\* 最大堆核心辅助函数
//*******************\*
private void shiftUp(int k){
while( k > 1 && data[k/2].compareTo(data[k]) < 0 ){
swap(k, k/2);
k /= 2;
}
}
// 测试 HeapShiftUp
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeapShiftUp<Integer> heapShiftUp = new
HeapShiftUp<Integer>(100);
int N = 50; // 堆中元素个数
int M = 100; // 堆中元素取值范围[0, M)
for( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ )
heapShiftUp.insert( new Integer((int)(Math.random() \* M))
);
System.out.println(heapShiftUp.size());
}
}