For a set of data, the lookup set mainly supports two actions:
Union (ppen Q)-connects the two elements p and Q.
Find (p)-queries which collection the p element is in.
IsConnected (pquotiq)-check to see if the p and Q elements are connected.
In the previous section, we used the id The formal representation of the array and look up the set, and the time complexity of the search in the actual operation is O(1) But the connection efficiency is not high
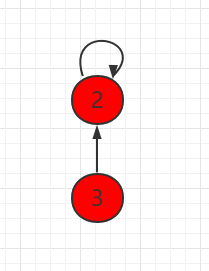
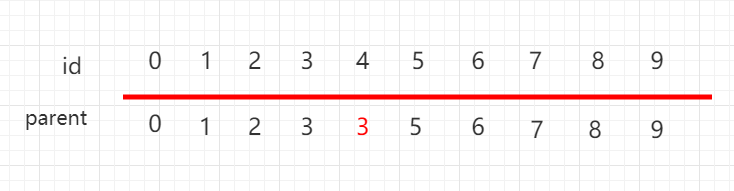
In this section, we will implement and look up the set in another way. Think of each element as a node and point to its parent node, and the root node points to itself. As shown in the following figure, node 3 points to node 2, which means that 3 and 2 are connected together, and node 2 itself is the root node, so it points to itself.
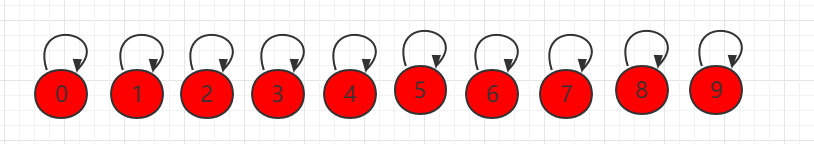
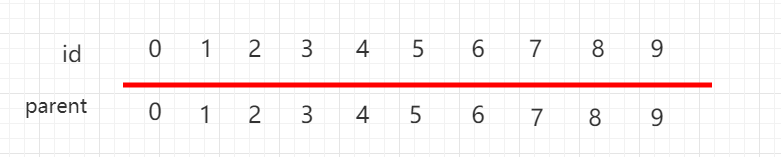
It is also represented by an array and looks up the set, but the following set of elements uses the parent Represents the parent node that the current element points to, and each element points to itself and is independent.
If you manipulate union (4Pol 3) at this time, point element 4 to element 3:
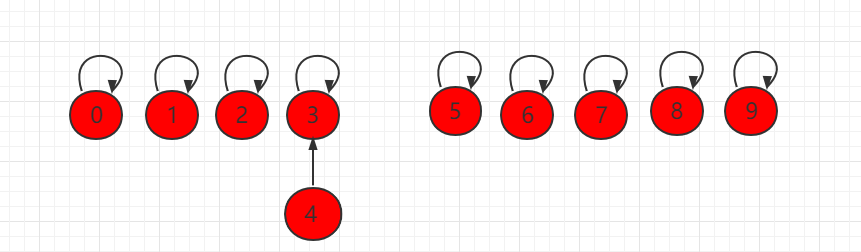
The array is also changed accordingly:
To determine whether the two elements are connected, you only need to determine whether the root node is the same.
As shown in the following figure, the root nodes of nodes 4 and 9 are both 8, so they are connected.
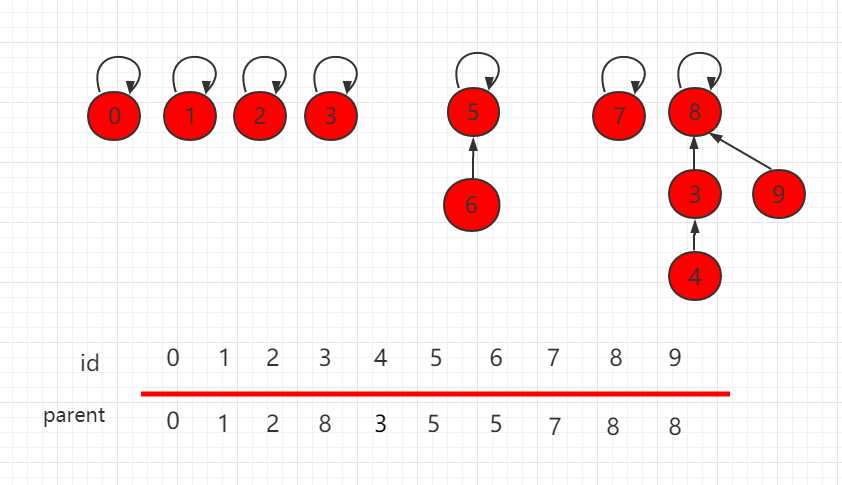
To connect two elements, you only need to find their corresponding root node and connect the root node, then they are connected nodes.
Suppose that to connect 6 and 4 in the above figure, you only need to point the root node 5 of 6 to the root node 8 of 4.

Build this tree structure pointing to the parent node, and use an array to build a tree pointing to the parent node, parent [i] Represents the parent node that the I element points to.
...
private int[] parent;
private int count; // 数据个数
...
Search process, find the set number corresponding to element p, and keep querying your parent node until you reach the root node, the characteristic parent of the root node [p] H is the height of the tree.
...
private int find(int p){
assert( p >= 0 && p < count );
while( p != parent[p] )
p = parent[p];
return p;
}
...
Merge the collections to which elements p and Q belong, query the root nodes of the two elements respectively, so that one of the root nodes points to the other root node, and the two sets are merged. This operation is the time complexity of O (h), where h is the height of the tree.
public void unionElements(int p, int q){
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if( pRoot == qRoot )
return;
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
}
5.24.1. Java instance code ¶
源码包下载: Download UnionFind2.java file code: ¶
package runoob.union;
/*\*
\* 第二版unionFind
*/
public class UnionFind2 {
// 我们的第二版Union-Find, 使用一个数组构建一棵指向父节点的树
// parent[i]表示第一个元素所指向的父节点
private int[] parent;
private int count; // 数据个数
// 构造函数
public UnionFind2(int count){
parent = new int[count];
this.count = count;
// 初始化, 每一个parent[i]指向自己,
表示每一个元素自己自成一个集合
for( int i = 0 ; i < count ; i ++ )
parent[i] = i;
}
// 查找过程, 查找元素p所对应的集合编号
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
private int find(int p){
assert( p >= 0 && p < count );
// 不断去查询自己的父亲节点, 直到到达根节点
// 根节点的特点: parent[p] == p
while( p != parent[p] )
p = parent[p];
return p;
}
// 查看元素p和元素q是否所属一个集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
public boolean isConnected( int p , int q ){
return find(p) == find(q);
}
// 合并元素p和元素q所属的集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
public void unionElements(int p, int q){
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if( pRoot == qRoot )
return;
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
}
}