5.14.1. I. the concept and its introduction ¶
Index heap is the optimization of the data structure of heap.
The index heap uses a new array of int types to hold index information.
Compared with heap, the advantages are as follows:
The consumption of exchange elements is optimized.
The position of the added data is fixed, so it is easy to find.
5.14.2. II. Applicable instructions ¶
If the elements stored in the heap are large, it takes a lot of time to swap, which can be replaced by the data structure of the index heap. The index of the array is stored in the heap, and we operate on the index accordingly.
5.14.3. III. Structural diagram ¶
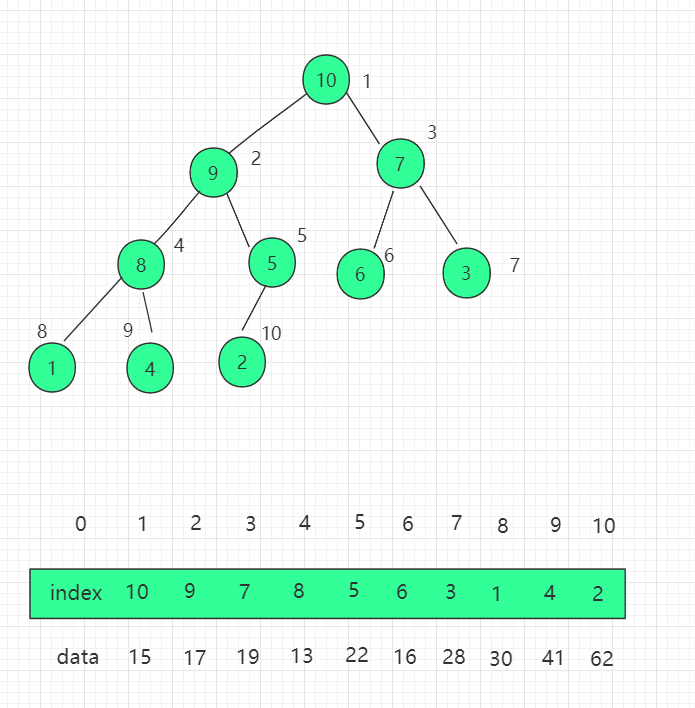
We need to modify the code implementation of the previous heap with the idea of directly manipulating the index. First, the constructor adds the indexed array attribute indexes.
protected T[] data; // 最大索引堆中的数据
protected int[] indexes; // 最大索引堆中的索引
protected int count;
protected int capacity;
The corresponding constructor is adjusted to add an array of initialized indexes.
...
public IndexMaxHeap(int capacity){
data = (T[])new Comparable[capacity+1];
indexes = new int[capacity+1];
count = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
}
...
Adjust the insert operation. The element added to the indexes array is the index indexes of the real data array. [count+1] = I.
...
// 向最大索引堆中插入一个新的元素, 新元素的索引为i, 元素为item
// 传入的i对用户而言,是从0索引的
public void insert(int i, Item item){
assert count + 1 <= capacity;
assert i + 1 >= 1 && i + 1 <= capacity;
i += 1;
data[i] = item;
indexes[count+1] = i;
count ++;
shiftUp(count);
}
...
Adjust the shift up operation: compare the size of the parent node data in the data array, so it needs to be expressed as data [index[k/2] ] < data [indexs[k] Exchange the index of the index array without any change to the data array, the same goes for shift down.
...
//k是堆的索引
// 索引堆中, 数据之间的比较根据data的大小进行比较, 但实际操作的是索引
private void shiftUp(int k){
while( k > 1 && data[indexes[k/2]].compareTo(data[indexes[k]]) < 0
){
swapIndexes(k, k/2);
k /= 2;
}
}
...
Fetch the element from the index heap and data the root element for the large element [index[1] And then exchange index locations for shift down operations.
...
public T extractMax(){
assert count > 0;
T ret = data[indexes[1]];
swapIndexes( 1 , count );
count --;
shiftDown(1);
return ret;
}
...
You can also directly fetch the data array index value of the maximum value
...
// 从最大索引堆中取出堆顶元素的索引
public int extractMaxIndex(){
assert count > 0;
int ret = indexes[1] - 1;
swapIndexes( 1 , count );
count --;
shiftDown(1);
return ret;
}
...
Modify index location data
...
// 将最大索引堆中索引为i的元素修改为newItem
public void change( int i , Item newItem ){
i += 1;
data[i] = newItem;
// 找到indexes[j] = i, j表示data[i]在堆中的位置
// 之后shiftUp(j), 再shiftDown(j)
for( int j = 1 ; j <= count ; j ++ )
if( indexes[j] == i ){
shiftUp(j);
shiftDown(j);
return;
}
}
...
5.14.4. 4. Java instance code ¶
源码包下载: Download The above modification index location in the search index location we use traversal, the efficiency is not high. We can also optimize it again to maintain a set of reverse [i] Array, which represents the position of index I in the indexes (heap), reducing the time complexity of the search to O (1). It has the following properties:Src/runoob/heap/IndexMaxHeap.java file code: ¶
package runoob.heap;
import java.util.Arrays;
/*\*
\* 索引堆
*/
// 最大索引堆,思路:元素比较的是data数据,元素交换的是索引
public class IndexMaxHeap<T extends Comparable> {
protected T[] data; // 最大索引堆中的数据
protected int[] indexes; // 最大索引堆中的索引
protected int count;
protected int capacity;
// 构造函数, 构造一个空堆, 可容纳capacity个元素
public IndexMaxHeap(int capacity){
data = (T[])new Comparable[capacity+1];
indexes = new int[capacity+1];
count = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
}
// 返回索引堆中的元素个数
public int size(){
return count;
}
// 返回一个布尔值, 表示索引堆中是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return count == 0;
}
// 向最大索引堆中插入一个新的元素, 新元素的索引为i, 元素为item
// 传入的i对用户而言,是从0索引的
public void insert(int i, T item){
assert count + 1 <= capacity;
assert i + 1 >= 1 && i + 1 <= capacity;
i += 1;
data[i] = item;
indexes[count+1] = i;
count ++;
shiftUp(count);
}
// 从最大索引堆中取出堆顶元素, 即索引堆中所存储的最大数据
public T extractMax(){
assert count > 0;
T ret = data[indexes[1]];
swapIndexes( 1 , count );
count --;
shiftDown(1);
return ret;
}
// 从最大索引堆中取出堆顶元素的索引
public int extractMaxIndex(){
assert count > 0;
int ret = indexes[1] - 1;
swapIndexes( 1 , count );
count --;
shiftDown(1);
return ret;
}
// 获取最大索引堆中的堆顶元素
public T getMax(){
assert count > 0;
return data[indexes[1]];
}
// 获取最大索引堆中的堆顶元素的索引
public int getMaxIndex(){
assert count > 0;
return indexes[1]-1;
}
// 获取最大索引堆中索引为i的元素
public T getItem( int i ){
assert i + 1 >= 1 && i + 1 <= capacity;
return data[i+1];
}
// 将最大索引堆中索引为i的元素修改为newItem
public void change( int i , T newItem ){
i += 1;
data[i] = newItem;
// 找到indexes[j] = i, j表示data[i]在堆中的位置
// 之后shiftUp(j), 再shiftDown(j)
for( int j = 1 ; j <= count ; j ++ )
if( indexes[j] == i ){
shiftUp(j);
shiftDown(j);
return;
}
}
// 交换索引堆中的索引i和j
private void swapIndexes(int i, int j){
int t = indexes[i];
indexes[i] = indexes[j];
indexes[j] = t;
}
//*******************\*
//\* 最大索引堆核心辅助函数
//*******************\*
//k是堆的索引
// 索引堆中, 数据之间的比较根据data的大小进行比较,
但实际操作的是索引
private void shiftUp(int k){
while( k > 1 && data[indexes[k/2]].compareTo(data[indexes[k]]) <
0 ){
swapIndexes(k, k/2);
k /= 2;
}
}
// 索引堆中, 数据之间的比较根据data的大小进行比较,
但实际操作的是索引
private void shiftDown(int k){
while( 2\*k <= count ){
int j = 2\*k;
if( j+1 <= count &&
data[indexes[j+1]].compareTo(data[indexes[j]]) > 0 )
j ++;
if( data[indexes[k]].compareTo(data[indexes[j]]) >= 0 )
break;
swapIndexes(k, j);
k = j;
}
}
// 测试 IndexMaxHeap
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 1000000;
IndexMaxHeap<Integer> indexMaxHeap = new
IndexMaxHeap<Integer>(N);
for( int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ )
indexMaxHeap.insert( i , (int)(Math.random()\*N) );
}
}

indexes[i] = j
reverse[j] = i
indexes[reverse[i]] = i
reverse[indexes[i]] = i