5.7.1. I. the concept and its introduction ¶
Three-way quick sorting is a further improved version of two-way quick sorting. The three-way sorting algorithm divides the sorted data into three parts, which are less than v, equal to v, and greater than v, respectively. Among the three parts of data, the data equal to v will no longer need to be sorted in the next recursion, and a lot of cases will not occur in the data less than v and greater than v) In this way, the performance of the three-way quick sorting algorithm is better.
5.7.2. II. Applicable instructions ¶
Time and space complexity are the same as randomized quick sorting.
The three-way quick sorting algorithm uses the three-way partition strategy to divide the array, which is very effective in improving the fast sorting process for the array dealing with a large number of repetitive elements. It adds logic that the processing is equal to dividing the value of the element, bringing all the values equal to the dividing element together.
三、过程图示
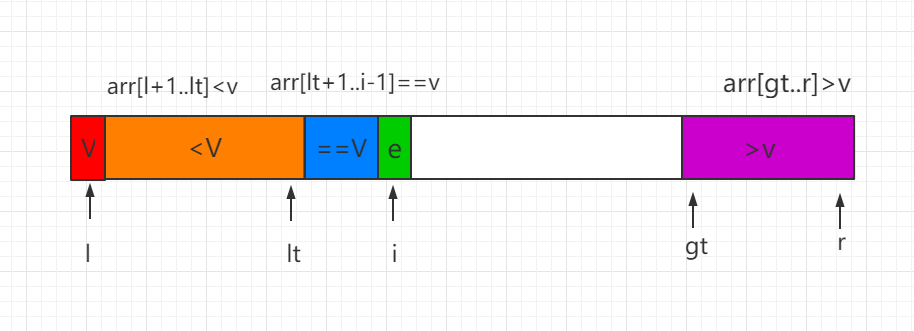
We discuss the partiton process in three cases, where I represents the current index location traversed:
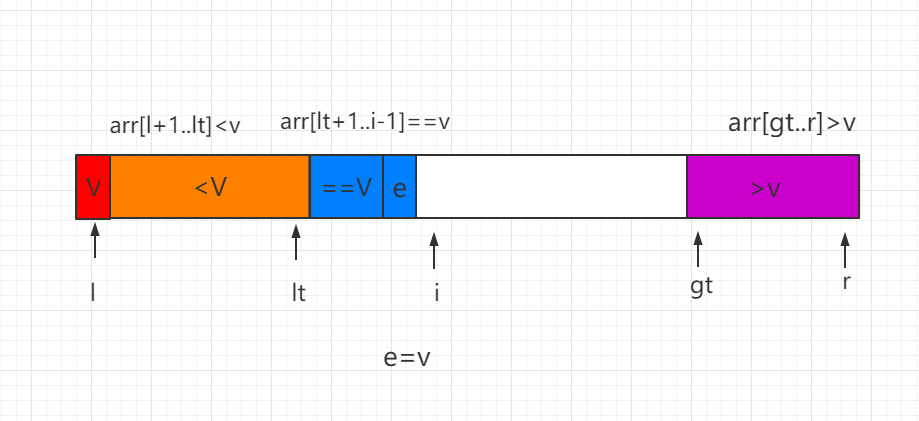
(1)当前处理的元素 e=V,元素 e 直接纳入蓝色区间,同时i向后移一位。
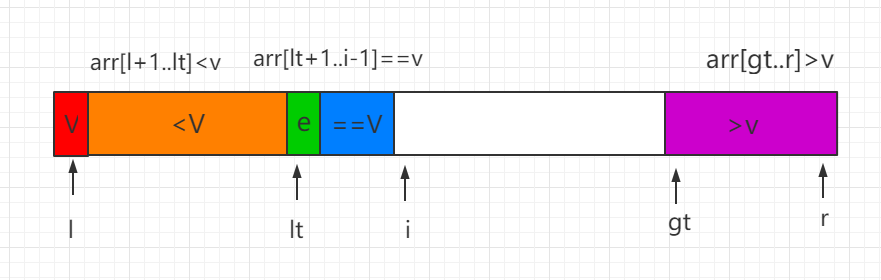
(2)当前处理元素 e<v,e 和等于 V 区间的第一个位置数值进行交换,同时索引 lt 和 i 都向后移动一位
(3)当前处理元素 e>v,e 和 gt-1 索引位置的数值进行交换,同时 gt 索引向前移动一位。
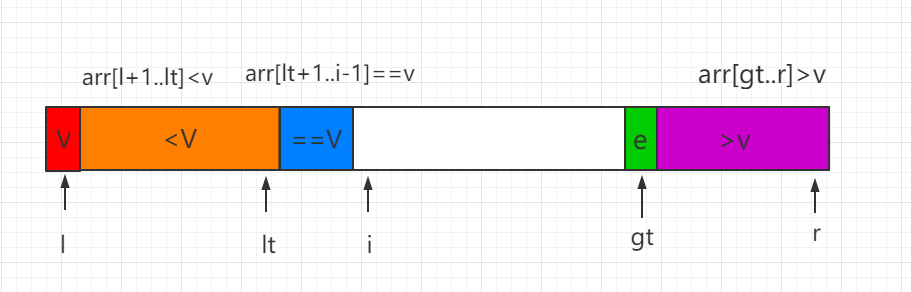
Finally, when you i=gt, you end the traversal and exchange the values pointed to by v and index lt, so that the sorting process is complete, and then sort the array parts of < V and > V recursively in the same way.
5.7.3. 4. Java instance code ¶
源码包下载: Download QuickSort3Ways.java file code: ¶
package runoob;
/*\*
\* 三路快速排序
*/
public class QuickSort3Ways {
//核心代码---开始
// 递归使用快速排序,对arr[l...r]的范围进行排序
private static void sort(Comparable[] arr, int l, int r){
if (l >= r) {
return;
}
// 随机在arr[l...r]的范围中, 选择一个数值作为标定点pivot
swap( arr, l, (int)(Math.random()\*(r-l+1)) + l );
Comparable v = arr[l];
int lt = l; // arr[l+1...lt] < v
int gt = r + 1; // arr[gt...r] > v
int i = l+1; // arr[lt+1...i) == v
while( i < gt ){
if( arr[i].compareTo(v) < 0 ){
swap( arr, i, lt+1);
i ++;
lt ++;
}
else if( arr[i].compareTo(v) > 0 ){
swap( arr, i, gt-1);
gt --;
}
else{ // arr[i] == v
i ++;
}
}
swap( arr, l, lt );
sort(arr, l, lt-1);
sort(arr, gt, r);
}
//核心代码---结束
public static void sort(Comparable[] arr){
int n = arr.length;
sort(arr, 0, n-1);
}
private static void swap(Object[] arr, int i, int j) {
Object t = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = t;
}
// 测试 QuickSort3Ways
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 三路快速排序算法也是一个O(nlogn)复杂度的算法
// 可以在1秒之内轻松处理100万数量级的数据
int N = 1000000;
Integer[] arr = SortTestHelper.generateRandomArray(N, 0,
100000);
sort(arr);
SortTestHelper.printArray(arr);
}
}