7.2.1. Basic introduction ¶
Django is an open source Web application framework written by Python.
Using Django, Python programmers can easily complete most of the content needed by a formal website with very little code, and further develop a full-function Web service Django itself based on MVC model, that is, Model (model) + View (view) + Controller (controller) design pattern. MVC pattern simplifies subsequent modifications and extensions of the program, and makes it possible to reuse a certain part of the program.
MVC advantages:
Low coupling
Quick development
Easy to deploy
High reusability
Low maintenance cost
…
Python plus Django is the best combination for rapid development, design and deployment of websites.
7.2.2. Characteristics ¶
Powerful database function
Comes with powerful background functions.
Elegant web site
7.2.3. MVC and MTV model ¶
7.2.4. MVC model ¶
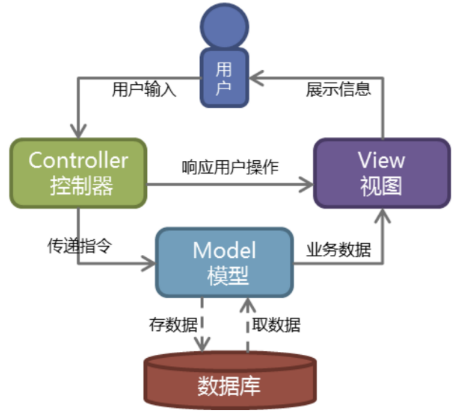
MVC pattern (Model-view-controller) is a software architecture pattern in software engineering, which divides the software system into three basic parts: Model, View and Controller.
MVC are connected together in a plug-in, loosely coupled manner.
Model (M)-the function of writing a program, which is responsible for mapping business objects to databases (ORM).
View (V)-graphical interface, responsible for interaction with the user (page).
Controller (C)-responsible for forwarding requests and processing requests.
Simple figure:

User operation flow chart:
7.2.5. MTV model ¶
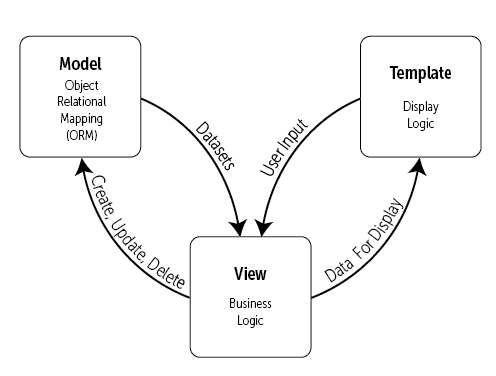
The MTV mode of Django is essentially the same as that of MVC, and it is also for the purpose of maintaining a loosely coupled relationship between components, except that the definition is slightly different. The MTV of Django refers to:
M representation model (Model): the function of writing a program, which is responsible for mapping business objects to databases (ORM).
T represents template (Template): responsible for how to display the page (html) to the user.
V represents the view (View): responsible for the business logic and calling Model and Template when appropriate.
In addition to the above three layers, you also need a URL dispatcher, which is used to distribute URL page requests to different View processing. The response mode of View calling the corresponding Model and Template,MTV is as follows:
Simple figure:
User operation flow chart:
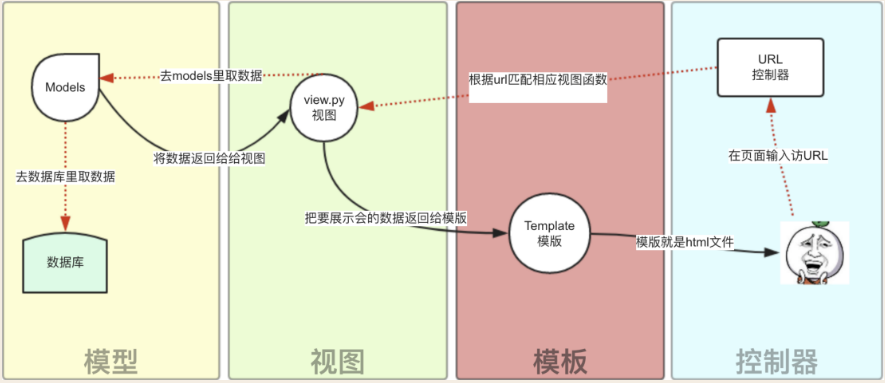
解析:
The user initiates a request (request) to our server through the browser, which accesses the view function:
a.如果不涉及到数据调用,那么这个时候视图函数直接返回一个模板也就是一个网页给用户。
b.如果涉及到数据调用,那么视图函数调用模型,模型去数据库查找数据,然后逐级返回。
The view function fills the returned data into the spaces in the template and finally returns the web page to the user.
Reference address: