The composite entity pattern (Composite Entity Pattern) is used in the EJB persistence mechanism. A composite entity is an EJB entity bean, which represents a diagram of the object. When you update a composite entity, the internal dependent objects beans are automatically updated because they are managed by the EJB entity bean. The following are the participants of the composite entity bean.
组合实体(Composite Entity) -it is the primary entity bean. It can be coarse-grained, or it can contain a coarse-grained object for persistent lifecycle.
粗粒度对象(Coarse-Grained Object) -this object contains dependent objects. It has its own life cycle, and it can also manage the life cycle of dependent objects.
依赖对象(Dependent Object) -A dependent object is an object whose persistent life cycle depends on coarse-grained objects.
策略(Strategies) -the policy represents how the composite entity is implemented.
6.30.1. Realize ¶
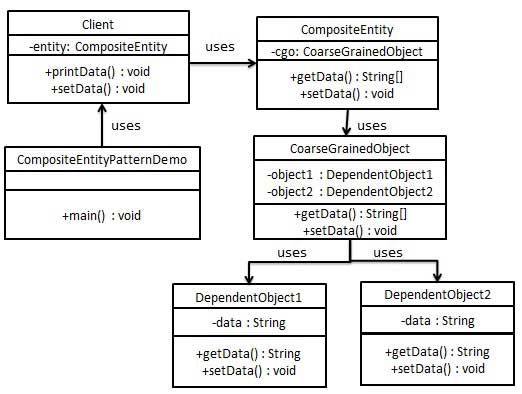
As a composite entity, we will create CompositeEntity Object. CoarseGrainedObject Is a class that contains dependent objects.
CompositeEntityPatternDemo Our demo class uses the Client Class to demonstrate the use of the composite entity pattern.
6.30.2. Step 1 ¶
Create dependent objects.DependentObject1.java ¶
publicclassDependentObject1{privateStringdata;publicvoidsetData(Stringdata){this.data=data;}publicStringgetData(){returndata;}}
DependentObject2.java ¶
publicclassDependentObject2{privateStringdata;publicvoidsetData(Stringdata){this.data=data;}publicStringgetData(){returndata;}}
6.30.3. Step 2 ¶
Create coarse-grained objects.CoarseGrainedObject.java ¶
publicclassCoarseGrainedObject{DependentObject1do1=newDependentObject1();DependentObject2do2=newDependentObject2();publicvoidsetData(Stringdata1,Stringdata2){do1.setData(data1);do2.setData(data2);}publicString[]getData(){returnnewString[]{do1.getData(),do2.getData()};}}
6.30.4. Step 3 ¶
Create a composite solid.CompositeEntity.java ¶
publicclassCompositeEntity{privateCoarseGrainedObjectcgo=newCoarseGrainedObject();publicvoidsetData(Stringdata1,Stringdata2){cgo.setData(data1,data2);}publicString[]getData(){returncgo.getData();}}
6.30.5. Step 4 ¶
Create a client class that uses composite entities.Client.java ¶
publicclassClient{privateCompositeEntitycompositeEntity=newCompositeEntity();publicvoidprintData(){for(inti=0;i<compositeEntity.getData().length;i++){System.out.println("Data:"+compositeEntity.getData()[i]);}}publicvoidsetData(Stringdata1,Stringdata2){compositeEntity.setData(data1,data2);}}
6.30.6. Step 5 ¶
Use Client To demonstrate the use of composite entity design patterns.CompositeEntityPatternDemo.java ¶
publicclassCompositeEntityPatternDemo{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){Clientclient=newClient();client.setData("Test","Data");client.printData();client.setData("Second
Test","Data1");client.printData();}}
6.30.7. Step 6 ¶
Execute the program and output the result:
Data: Test
Data: Data
Data: Second Test
Data: Data1