Maven uses archetype (prototype) to create a custom project structure to form a Maven project template.
In the previous section, we learned that Maven uses the following command to quickly create a java project:
mvn archetype:generate
11.11.1. What is archetype? ¶
Archetype, or prototype, is a Maven plug-in, to be exact, a project template whose task is to create a project structure based on the template. We will use the quickstart prototype plug-in to create a simple java application.
11.11.2. Use project templates ¶
Let’s open the command console, jump to the C:> MVN directory and execute the following mvn command:
C:\MVN> mvn archetype:generate
Maven will start processing and require you to select the desired prototype:
[INFO] Scanning for projects...
[INFO] Searching repository for plugin with prefix: 'archetype'.
[INFO] -------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Building Maven Default Project
[INFO]task-segment: [archetype:generate] (aggregator-style)
[INFO] -------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Preparing archetype:generate
...
600: remote -> org.trailsframework:trails-archetype (-)
601: remote -> org.trailsframework:trails-secure-archetype (-)
602: remote -> org.tynamo:tynamo-archetype (-)
603: remote -> org.wicketstuff.scala:wicket-scala-archetype (-)
604: remote -> org.wicketstuff.scala:wicketstuff-scala-archetype
Basic setup for a project that combines Scala and Wicket,
depending on the Wicket-Scala project.
Includes an example Specs test.)
605: remote -> org.wikbook:wikbook.archetype (-)
606: remote -> org.xaloon.archetype:xaloon-archetype-wicket-jpa-glassfish (-)
607: remote -> org.xaloon.archetype:xaloon-archetype-wicket-jpa-spring (-)
608: remote -> org.xwiki.commons:xwiki-commons-component-archetype
(Make it easy to create a maven project for creating XWiki Components.)
609: remote -> org.xwiki.rendering:xwiki-rendering-archetype-macro
(Make it easy to create a maven project for creating XWiki Rendering Macros.)
610: remote -> org.zkoss:zk-archetype-component (The ZK Component archetype)
611: remote -> org.zkoss:zk-archetype-webapp (The ZK wepapp archetype)
612: remote -> ru.circumflex:circumflex-archetype (-)
613: remote -> se.vgregion.javg.maven.archetypes:javg-minimal-archetype (-)
614: remote -> sk.seges.sesam:sesam-annotation-archetype (-)
Choose a number or apply filter
(format: [groupId:]artifactId, case sensitive contains): 203:
Press Enter Select the default option (203:maven-archetype-quickstart).
11.11.3. Maven will ask for the version of the prototype ¶
Choose org.apache.maven.archetypes:maven-archetype-quickstart version:
1: 1.0-alpha-1
2: 1.0-alpha-2
3: 1.0-alpha-3
4: 1.0-alpha-4
5: 1.0
6: 1.1
Choose a number: 6:
Press Enter Select the default option (6:maven-archetype-quickstart:1.1)
Maven will ask for project details. Enter project details as required. Press Enter directly if you want to use the default value. You can also enter your own value.
Define value for property 'groupId': : com.companyname.insurance
Define value for property 'artifactId': : health
Define value for property 'version': 1.0-SNAPSHOT
Define value for property 'package': com.companyname.insurance
Maven will ask for confirmation of project details, press Enter Or press Y
Confirm properties configuration:
groupId: com.companyname.insurance
artifactId: health
version: 1.0-SNAPSHOT
package: com.companyname.insurance
Y:
Now Maven will begin to create the project structure, which is shown as follows:
[INFO] -----------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Using following parameters for creating project
from Old (1.x) Archetype: maven-archetype-quickstart:1.1
[INFO] -----------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Parameter: groupId, Value: com.companyname.insurance
[INFO] Parameter: packageName, Value: com.companyname.insurance
[INFO] Parameter: package, Value: com.companyname.insurance
[INFO] Parameter: artifactId, Value: health
[INFO] Parameter: basedir, Value: C:\MVN
[INFO] Parameter: version, Value: 1.0-SNAPSHOT
[INFO] project created from Old (1.x) Archetype in dir: C:\MVN\health
[INFO] -----------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESSFUL
[INFO] -----------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Total time: 4 minutes 12 seconds
[INFO] Finished at: Fri Jul 13 11:10:12 IST 2012
[INFO] Final Memory: 20M/90M
[INFO] -----------------------------------------------------------------------
11.11.4. Project created ¶
Now go to the C:> MVN directory. You will see a java application project named health, just like the artifactId name created when the project was created. Maven will create a project with a standard directory layout, as follows:
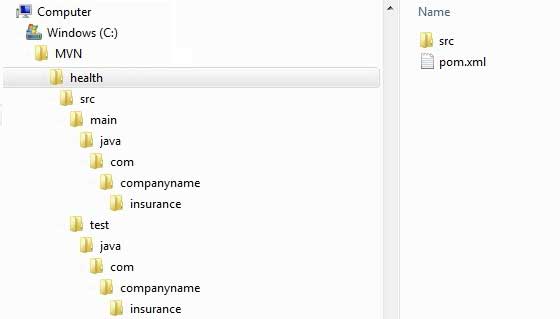
11.11.5. Create pom.xml ¶
Maven automatically generates a pom.xml file for the project, as shown below:
<projectxmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><groupId>com.companyname.insurance</groupId><artifactId>health</artifactId><version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version><packaging>jar</packaging><name>health</name><url>http://maven.apache.org</url><properties><project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding></properties><dependencies><dependency><groupId>junit</groupId><artifactId>junit</artifactId><version>3.8.1</version><scope>test</scope></dependency></dependencies></project>
11.11.6. App.java ¶
Maven automatically generates a test java file, App.java.
路径: C:MVNconsumerBankingsrcmainjavacomcompanynamebank
packagecom.companyname.insurance;/\*\* \* Hello world!
\*\*/publicclassApp{publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args){System.out.println("Hello
World!");}}
11.11.7. AppTest.java ¶
Maven automatically generates a java file, AppTest.java.
路径为: C:MVNconsumerBankingsrctestjavacomcompanynamebank
packagecom.companyname.insurance;importjunit.framework.Test;importjunit.framework.TestCase;importjunit.framework.TestSuite;/\*\*
\* Unit test for simple App.\*/publicclassAppTestextendsTestCase{/\*\*
\* Create the test case \* \*@paramtestName name of the test
case\*/publicAppTest(StringtestName){super(testName);}/\*\* \*@returnthe
suite of tests being
tested\*/publicstaticTestsuite(){returnnewTestSuite(AppTest.class);}/\*\*
\* Rigourous Test :-)\*/publicvoidtestApp(){assertTrue(true);}}
That’s all. Now you can see the power of Maven. You can create any type of project with maven simple commands, and you can start your development.