This tutorial introduces you to the syntax and examples of the MySQL UNION operator. The MySQL UNION operator is used to connect more than two MySQL UNION operator syntax format: expression1, expression2, … expression_n The column to retrieve tables: The data table to retrieve. WHERE conditions: Optional, search conditions. DISTINCT: Optionally, delete duplicate data in the result set. By default, the UNION operator has removed duplicate data, so the DISTINCT modifier has little effect on the result. ALL: Optionally, returns all result sets, including duplicate data. In this tutorial, we will use the RUNOOB sample database. Here is the data selected from the “Websites” table: Here is the data for “apps” APP: The following SQL statement selects all from the “Websites” and “apps” tables 不同的 Country (only different values): Example The output of executing the above SQL is as follows: 注释: UNION cannot be used to list all country in two tables. If some websites and APP are from the same country, each country will only be listed once. UNION only selects different values. Please use UNION ALL to select duplicate values! The following SQL statement uses UNION ALL to select from the “Websites” and “apps” tables 所有的 Country (there are also duplicate values): Example The output of executing the above SQL is as follows: The following SQL statement uses UNION ALL to select from the “Websites” and “apps” tables 所有的 China (CN) data (there are also duplicate values): Example The output of executing the above SQL is as follows:Description ¶
SELECT
The results of the statement are combined into a result set Multiple
SELECT
Statement deletes duplicate data.Grammar ¶
SELECT expression1, expression2, ... expression_n
FROM tables
[WHERE conditions]
UNION [ALL | DISTINCT]
SELECT expression1, expression2, ... expression_n
FROM tables
[WHERE conditions];
Parameters. ¶
Demo database ¶
mysql> SELECT * FROM Websites;
+----+--------------+---------------------------+-------+---------+
| id | name | url | alexa | country |
+----+--------------+---------------------------+-------+---------+
| 1 | Google | https://www.google.cm/ | 1 | USA |
| 2 | 淘宝 | https://www.taobao.com/ | 13 | CN |
| 3 | 菜鸟教程 | http://www.runoob.com/ | 4689 | CN |
| 4 | 微博 | http://weibo.com/ | 20 | CN |
| 5 | Facebook | https://www.facebook.com/ | 3 | USA |
| 7 | stackoverflow | http://stackoverflow.com/ | 0 | IND |
+----+---------------+---------------------------+-------+---------+
mysql> SELECT * FROM apps;
+----+------------+-------------------------+---------+
| id | app_name | url | country |
+----+------------+-------------------------+---------+
| 1 | QQ APP | http://im.qq.com/ | CN |
| 2 | 微博 APP | http://weibo.com/ | CN |
| 3 | 淘宝 APP | https://www.taobao.com/ | CN |
+----+------------+-------------------------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
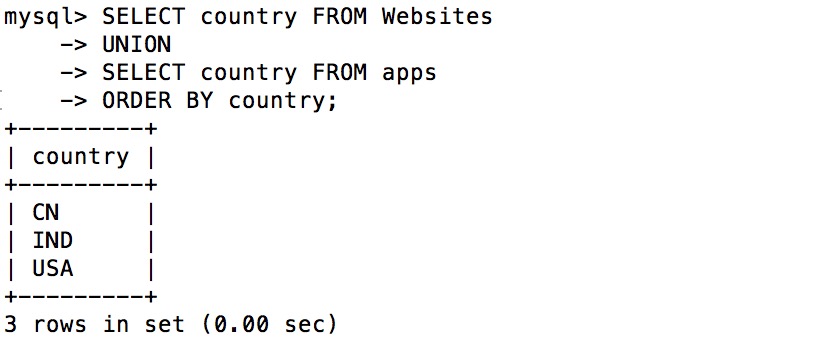
SQL UNION instance ¶
SELECT country FROM Websites
UNION
SELECT country FROM apps
ORDER BY country;
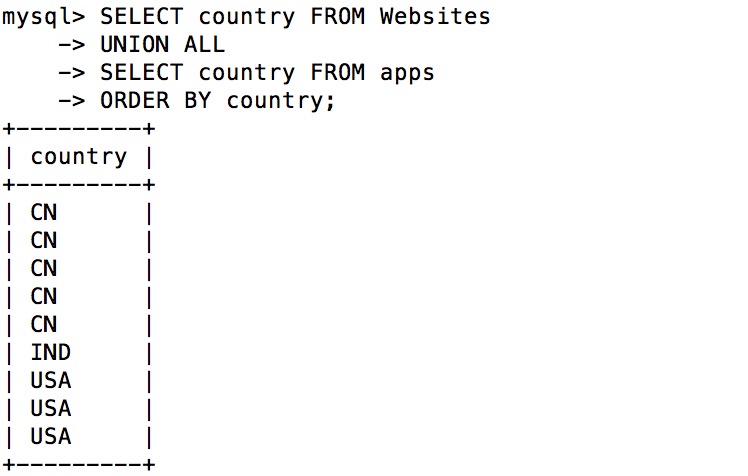
SQL UNION ALL instance ¶
SELECT country FROM Websites
UNION ALL
SELECT country FROM apps
ORDER BY country;
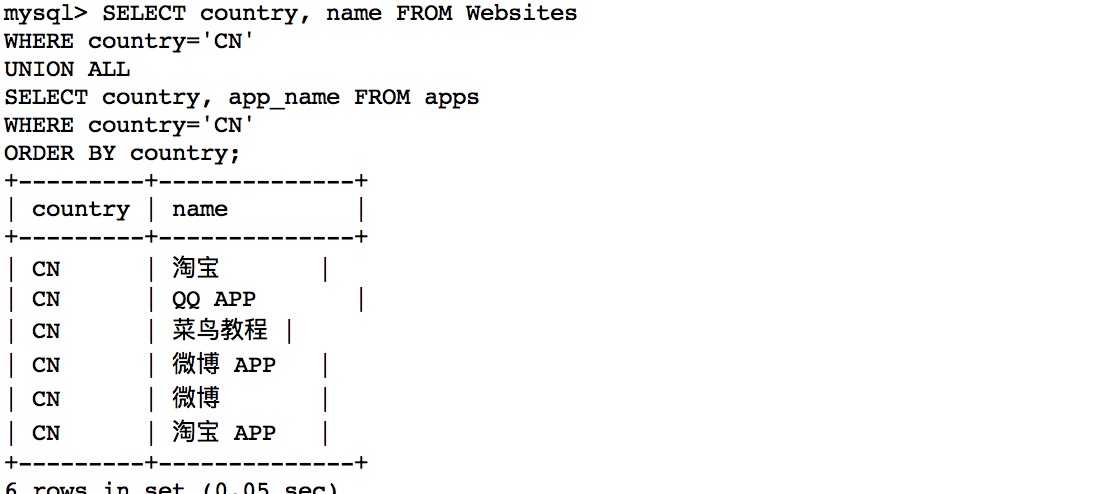
SQL UNION ALL with WHERE ¶
SELECT country, name FROM Websites
WHERE country='CN'
UNION ALL
SELECT country, app_name FROM apps
WHERE country='CN'
ORDER BY country;