It is generally used to switch between subtasks, views, or models in the same view.
An example of the tab bar is as follows:
Important attribute
BackgroundImage
Items
SelectedItem
Sample code and steps
1. 创建一个新的项目,选择 Tabbed Application 替代视图应用程序 ,点击下一步, 输入项目名称和选择 create .
Here two view controllers and tab bars are created by default to add to our application.
AppDelegate.m didFinishLaunchingWithOptions The methods are as follows:
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions
{
self.window = [[UIWindow alloc] initWithFrame:[[UIScreen mainScreen]
bounds]];
// Override point for customization after application launch.
UIViewController *viewController1 = [[FirstViewController alloc]
initWithNibName:@"FirstViewController" bundle:nil];
UIViewController *viewController2 = [[SecondViewController alloc]
initWithNibName:@"SecondViewController" bundle:nil];
self.tabBarController = [[UITabBarController alloc] init];
self.tabBarController.viewControllers = @[viewController1,
viewController2];
self.window.rootViewController = self.tabBarController;
[self.window makeKeyAndVisible];
return YES;
}
Two view controllers are used to assign view controllers as tab bar controllers
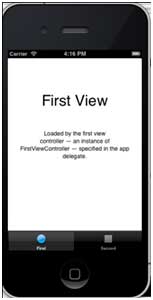
Run the application and get the following results: