5.2.1. I. the concept and its introduction ¶
Insert sort (InsertionSort), also known as direct insert sort.
It is an effective algorithm for sorting a small number of elements. Insert sort is the simplest sort method, its basic idea is to insert a record into an ordered table that has been sorted, thus a new ordered table with an increase of 1 in the number of records.
. In its implementation process, a double-layer loop is used, the outer loop looks for all elements except the first element, and the inner loop looks up and moves the ordered table in front of the current element.
5.2.2. II. Applicable instructions ¶
The average time complexity of insertion sorting is also O (n ^ 2), and the space complexity is constant O (1). The specific time complexity is also related to the ordering of the array.
In the insertion sort, when the array to be sorted is ordered, it is the best case. You only need to compare the current number with the previous number. In this case, you need to compare Nmure once, and the time complexity is O (N). In the worst case, the array to be sorted is in reverse order, which requires the most comparisons, and in the worst case, O (n ^ 2).
5.2.3. III. Process diagram ¶
Assume that the previous nmur1 (where n>=2 ) the number is already in order, and now the first n Insert the number into the previously arranged sequence, and then find the right position, so that the sequence with the nth number is also in order.
The process of inserting all elements in this way until the entire sequence is ordered is called insertion sorting.
The whole process of insertion sorting from small to large is shown in the figure:
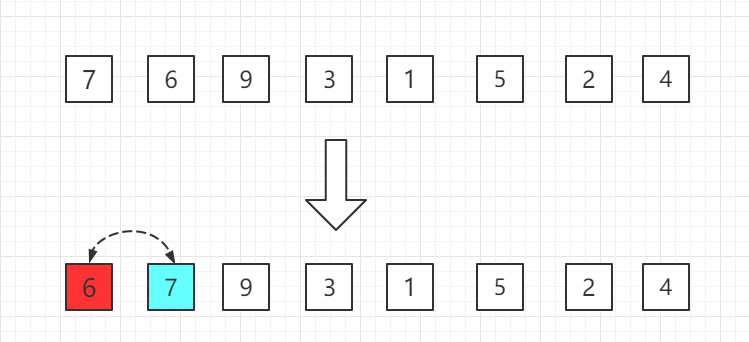
第一轮: Start with 6 in the second position, which is smaller than the previous 7, and switch places.
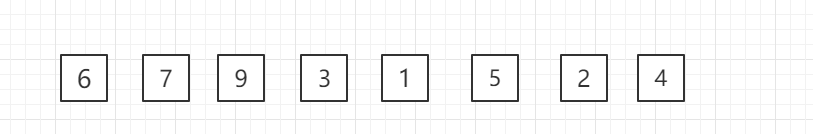
第二轮: The 9 of the third position is larger than the 7 of the previous position, and there is no need to change places.
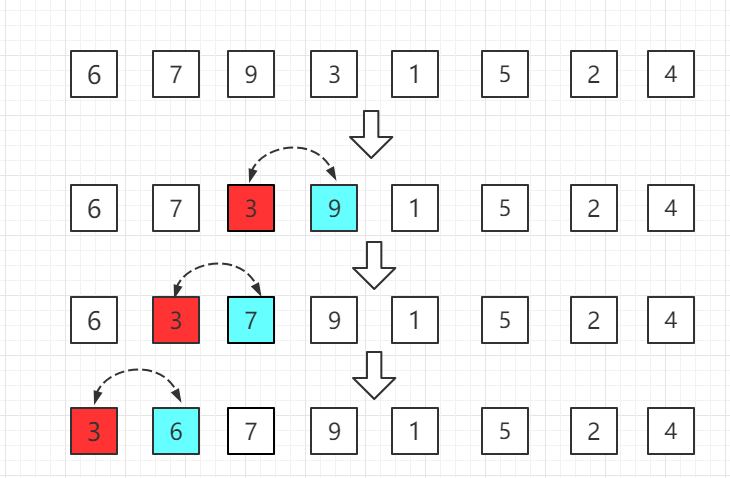
第三轮: The 3 of the fourth position is smaller than the 9 of the previous position, and the comparison is made forward in turn.
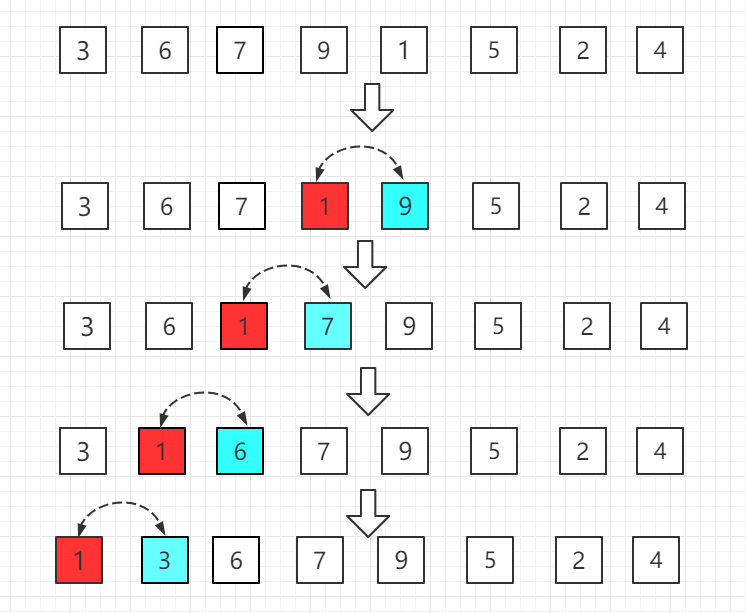
第四轮: The 1 of the fifth position is smaller than the 9 of the previous position, switch places, and then compare forward in turn.
So compare to the last element in turn.
5.2.4. 4. Java instance code ¶
源码包下载: Download
Part of the code:InsertionSort.java file code: ¶
package runoob;
/*\*
\* 插入排序
*/
public class InsertionSort {
//核心代码---开始
public static void sort(Comparable[] arr){
int n = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 寻找元素 arr[i] 合适的插入位置
for( int j = i ; j > 0 ; j -- )
if( arr[j].compareTo( arr[j-1] ) < 0 )
swap( arr, j , j-1 );
else
break;
}
}
//核心代码---结束
private static void swap(Object[] arr, int i, int j) {
Object t = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = t;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 20000;
Integer[] arr = SortTestHelper.generateRandomArray(N, 0,
100000);
InsertionSort.sort(arr);
for( int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i ++ ){
System.out.print(arr[i]);
System.out.print(' ');
}
}
}