According to the idea of the previous section, we look up the following figure and do the union (4pr 9) operation.
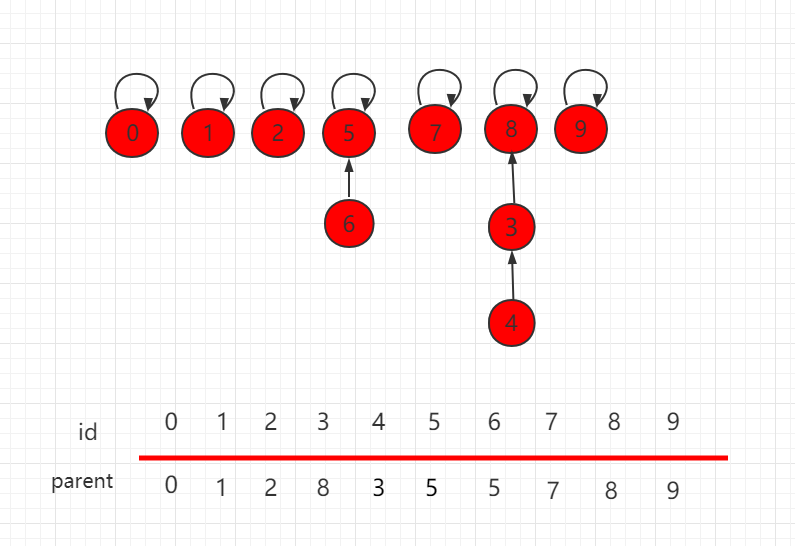
The structure after the merge operation is:

It can be found that the tree of this structure has a relatively high layer, and if the number of elements increases at this time, the consumption will be relatively large. To solve this problem is actually very simple, in the specific pointing operation, make a judgment first, point the set root node with fewer elements to the root node with more elements, which can generate a tree with lower layers with higher probability.
One more parameter is required when constructing and querying the set sz Array sz[i] Represented by i The number of elements in the collection that is the root.
// 构造函数
public UnionFind3(int count){
parent = new int[count];
sz = new int[count];
this.count = count;
// 初始化, 每一个parent[i]指向自己, 表示每一个元素自己自成一个集合
for( int i = 0 ; i < count ; i ++ ){
parent[i] = i;
sz[i] = 1;
}
}
In the merge operation, the merge direction is judged according to the different number of elements in the tree where the two elements are located.
public void unionElements(int p, int q){
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if( pRoot == qRoot )
return;
if( sz[pRoot] < sz[qRoot] ){
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
sz[qRoot] += sz[pRoot];
}
else{
parent[qRoot] = pRoot;
sz[pRoot] += sz[qRoot];
}
}
After optimization, the merge results are as follows, with 9 pointing to parent node 8.
源码包下载: Download 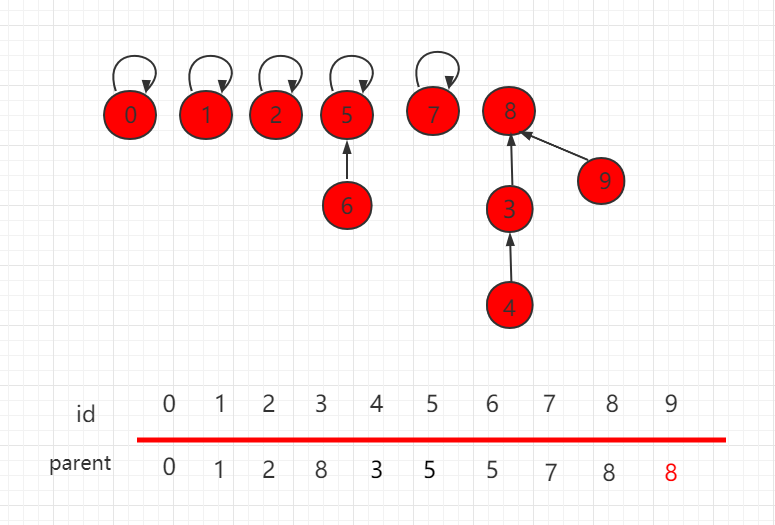
5.25.1. Java instance code ¶
UnionFind3.java file code: ¶
package runoob.union;
/*\*
\* 并查集size的优化
*/
public class UnionFind3 {
// parent[i]表示第一个元素所指向的父节点
private int[] parent;
// sz[i]表示以i为根的集合中元素个数
private int[] sz;
// 数据个数
private int count;
// 构造函数
public UnionFind3(int count){
parent = new int[count];
sz = new int[count];
this.count = count;
// 初始化, 每一个parent[i]指向自己,
表示每一个元素自己自成一个集合
for( int i = 0 ; i < count ; i ++ ){
parent[i] = i;
sz[i] = 1;
}
}
// 查找过程, 查找元素p所对应的集合编号
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
private int find(int p){
assert( p >= 0 && p < count );
// 不断去查询自己的父亲节点, 直到到达根节点
// 根节点的特点: parent[p] == p
while( p != parent[p] )
p = parent[p];
return p;
}
// 查看元素p和元素q是否所属一个集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
public boolean isConnected( int p , int q ){
return find(p) == find(q);
}
// 合并元素p和元素q所属的集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
public void unionElements(int p, int q){
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if( pRoot == qRoot )
return;
// 根据两个元素所在树的元素个数不同判断合并方向
// 将元素个数少的集合合并到元素个数多的集合上
if( sz[pRoot] < sz[qRoot] ){
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
sz[qRoot] += sz[pRoot];
}
else{
parent[qRoot] = pRoot;
sz[pRoot] += sz[qRoot];
}
}
}