5.9.1. I. the concept and its introduction ¶
Heap is a general term for a special kind of data structure in computer science.
A heap is usually an array object that can be thought of as a complete binary tree.
The heap satisfies the following properties:
The value of a node in the heap is never greater than or less than the value of its parent node.
The heap is always a complete binary tree.
5.9.2. II. Applicable instructions ¶
Heap uses the structure of complete binary tree to maintain a set of data, and then carries out related operations. generally, the time complexity of one operation is between O (1) and O (logn). Heap is usually used to dynamically allocate and release objects used by programs.
If it is a priority queue scenario, ordinary array or sequential array, the worst case is O (n ^ 2), the data structure of heap can also improve the efficiency of entering and leaving the queue.
Join the team | Get out of the team | |
|---|---|---|
Ordinary array | O (1) | O (n) |
Sequential array | O (n) | O (1) |
Heap | O (logn) | O (log) |
5.9.3. III. Structural diagram ¶
The binary heap is a complete binary tree, and the value of a node in the heap is always no more than that of its parent node. The depth of the complete binary tree is k. Except for the k layer, the number of nodes in other layers (1~k-1) reaches the maximum, and all the nodes in the k layer are continuously concentrated on the far left.
The root node of the heap is called the maximum heap, as shown in the following figure:

We can use an array to store the binary heap, and the label on the right is the index of the array.
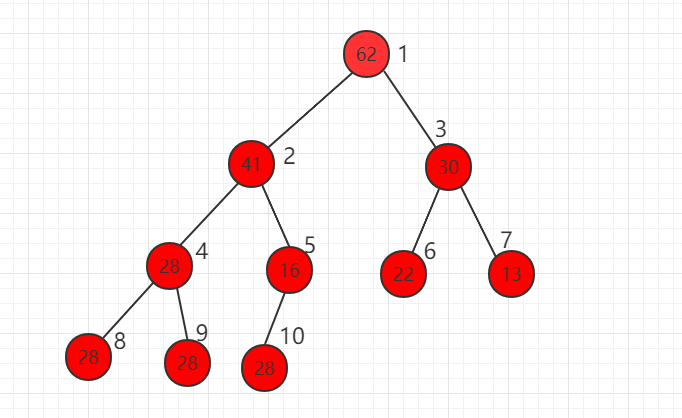
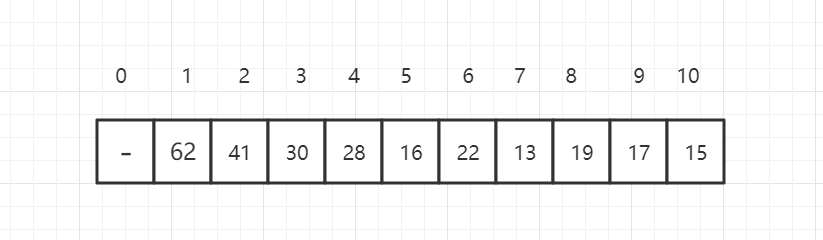
Assuming that the index position of the current element is I, you can get the rule:
parent(i) = i/2(取整)
left child(i) = 2*i
right child(i) = 2*i +1
5.9.4. 4. Java instance code ¶
源码包下载: Download Src/runoob/heap/MaxHeap.java file code: ¶
package runoob.heap;
/*\*
\* 堆定义
*/
public class MaxHeap<T> {
private T[] data;
private int count;
// 构造函数, 构造一个空堆, 可容纳capacity个元素
public MaxHeap(int capacity){
data = (T[])new Object[capacity+1];
count = 0;
}
// 返回堆中的元素个数
public int size(){
return count;
}
// 返回一个布尔值, 表示堆中是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return count == 0;
}
// 测试 MaxHeap
public static void main(String[] args) {
MaxHeap<Integer> maxHeap = new MaxHeap<Integer>(100);
System.out.println(maxHeap.size());
}
}