The Maven build life cycle defines a project build and release process.
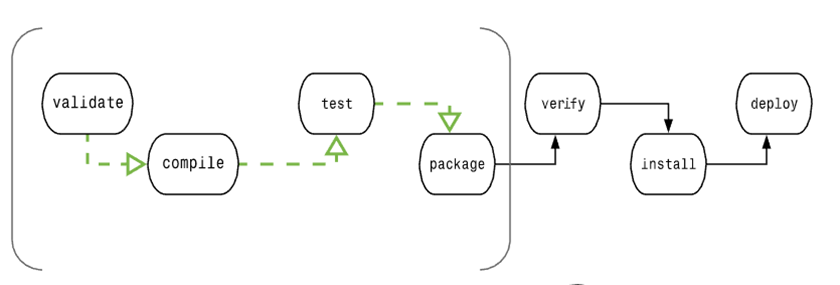
A typical Maven build (build) life cycle consists of a sequence of the following phases:
Stage | Deal with | Description |
|---|---|---|
Verify validate | Validate the project | Verify that the project is correct and that all required information is available |
Compile compile | Perform compilation | Source code compilation is completed at this stage |
Test Test | test | Run the tests using the appropriate unit test framework, such as JUnit. |
Packaging package | Packing | Create JAR/WAR packages such as those mentioned in the definition of pom.xml |
Check verify | Check | Check the results of the integration test to ensure that the quality is up to standard |
Install install | Installation | Install the packaged project to the local warehouse for use by other projects |
Deploy deploy | Deployment | Copy the final project package to the remote warehouse to share with other developers and projects |
In order to complete the default lifecycle, these phases (including other lifecycle phases not listed above) will be executed sequentially.
Maven has three standard lifecycles:
clean : handling of project cleanup
default(或 build) Processing of project deployment
site Processing of project site document creation
11.4.1. The build phase consists of plug-in goals. ¶
A plug-in goal represents a specific task (more refined than the build phase), which helps build and manage the project. These goals may be bound to multiple phases or unbound. Goals that are not bound to any build phase can be executed through direct calls outside the build life cycle. The order in which these goals are executed depends on the order of the invocation target and the build phase.
For example, consider the following command:
Clean and pakage are the construction phase, and dependency:copy-dependencies is the target
mvn clean dependency:copy-dependencies package
The clean phase here will be executed first, then the dependency:copy-dependencies goal will be executed, and finally the package phase will be executed.
11.4.2. Clean lifecycle ¶
When we execute the mvn post-clean command, Maven calls the clean lifecycle, which consists of the following phases:
Pre-clean: perform some work that needs to be done before clean
Clean: removes all files generated by the last build
Post-clean: perform some work that needs to be done immediately after clean
The clean in mvn clean is the clean above. In a lifecycle, when you run a phase, all previous phases are run, that is, if you execute mvn clean, you will run the following two lifecycle phases:
pre-clean, clean
If we run mvn post-clean, we run the following three lifecycle phases:
pre-clean, clean, post-clean
We can modify the operational behavior of this part by defining goals at any stage of the clean lifecycle above.
In the following example, we add the maven-antrun-plugin:run target to the pre-clean, clean, and post-clean phases. This allows us to display text messages at all stages of the clean lifecycle.
We have created a pom.xml file in the C:MVNproject directory.
<projectxmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><groupId>com.companyname.projectgroup</groupId><artifactId>project</artifactId><version>1.0</version><build><plugins><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-antrun-plugin</artifactId><version>1.1</version><executions><execution><id>id.pre-clean</id><phase>pre-clean</phase><goals><goal>run</goal></goals><configuration><tasks><echo>pre-clean
phase</echo></tasks></configuration></execution><execution><id>id.clean</id><phase>clean</phase><goals><goal>run</goal></goals><configuration><tasks><echo>clean
phase</echo></tasks></configuration></execution><execution><id>id.post-clean</id><phase>post-clean</phase><goals><goal>run</goal></goals><configuration><tasks><echo>post-clean
phase</echo></tasks></configuration></execution></executions></plugin></plugins></build></project>
Now open the command console, jump to the directory where pom.xml is located, and execute the following mvn command.
C:\MVN\project>mvn post-clean
Maven will begin to process and display all phases of the clean life cycle.
[INFO] Scanning for projects...
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Building Unnamed - com.companyname.projectgroup:project:jar:1.0
[INFO] task-segment: [post-clean]
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] [antrun:run {execution: id.pre-clean}]
[INFO] Executing tasks
[echo] pre-clean phase
[INFO] Executed tasks
[INFO] [clean:clean {execution: default-clean}]
[INFO] [antrun:run {execution: id.clean}]
[INFO] Executing tasks
[echo] clean phase
[INFO] Executed tasks
[INFO] [antrun:run {execution: id.post-clean}]
[INFO] Executing tasks
[echo] post-clean phase
[INFO] Executed tasks
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESSFUL
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Total time: < 1 second
[INFO] Finished at: Sat Jul 07 13:38:59 IST 2012
[INFO] Final Memory: 4M/44M
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------
You can try to modify the mvn clean command to display pre-clean and clean without doing anything during the post-clean phase.
11.4.3. Default (Build) lifecycle ¶
This is the main life cycle of Maven and is used to build applications, including the following 23 phases:
Life cycle stage | Description |
|---|---|
Validate (check) | Verify that the project is correct and that all the necessary information can complete the construction process of the project. |
Initialize (initialization) | Initialize the build state, such as setting property values. |
Generate-sources (generate source code) | Generate any source code included in the compilation phase. |
Process-sources (processing source code) | Deal with the source code, for example, to filter any value. |
Generate-resources (generate resource file) | Generate the resource files that will be included in the project package. |
Process-resources (processing resource files) | Copy and process resources to the target directory, best prepared for the packaging phase. |
Compile (compiled) | Compile the source code of the project. |
Process-classes (processing class files) | Deal with compiled files, such as bytecode improvement optimization for Java class files. |
Generate-test-sources (generate test source code) | Generate any test source code included in the compilation phase. |
Process-test-sources (processing test source code) | Deal with the test source code, for example, filter any value. |
Generate-test-resources (generate test resource files) | Create a resource file for the test. |
Process-test-resources (processing test resource files) | Copy and process test resources to the target directory. |
Test-compile (compile and test source code) | Compile the test source code to the test target directory. |
Process-test-classes (processing test class files) | Process the files generated by the test source code compilation. |
Test (Test) | Run the tests using the appropriate unit test framework (Juint is one of them). |
Prepare-package (ready to pack) | Perform any necessary actions to prepare for packaging before the actual packaging. |
Package (packaged) | Package the compiled code into files in a distributable format, such as JAR, WAR, or EAR files. |
Pre-integration-test (before integration testing) | Take the necessary actions before performing the integration test. For example, build the environment you need. |
Integration-test (integration testing) | Process and deploy the project to run the integrated test environment. |
Post-integration-test (after integration testing) | Take the necessary actions after the execution of the integration test is complete. For example, clean up the integrated test environment. |
Verify (Verification) | Run any checks to verify that the project package is valid and meets quality standards. |
Install (installation) | Install the project package to the local warehouse so that it can be used as a dependency for other local projects. |
Deploy (deployment) | Copy the final project package to the remote repository and share it with other developers and projects. |
There are some important concepts related to the Maven life cycle that need to be explained:
When a phase is called through the Maven command, such as mvn compile, only all phases before and including that phase are executed.
Different maven goals will be bound to different Maven lifecycle phases depending on the type of packaging (JAR / WAR / EAR).
In the following example, we add the maven-antrun-plugin:run goal to part of the Build lifecycle. In this way, we can display text information about the life cycle.
We have updated the pom.xml file in the C:MVNproject directory.
<projectxmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><groupId>com.companyname.projectgroup</groupId><artifactId>project</artifactId><version>1.0</version><build><plugins><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-antrun-plugin</artifactId><version>1.1</version><executions><execution><id>id.validate</id><phase>validate</phase><goals><goal>run</goal></goals><configuration><tasks><echo>validate
phase</echo></tasks></configuration></execution><execution><id>id.compile</id><phase>compile</phase><goals><goal>run</goal></goals><configuration><tasks><echo>compile
phase</echo></tasks></configuration></execution><execution><id>id.test</id><phase>test</phase><goals><goal>run</goal></goals><configuration><tasks><echo>test
phase</echo></tasks></configuration></execution><execution><id>id.package</id><phase>package</phase><goals><goal>run</goal></goals><configuration><tasks><echo>package
phase</echo></tasks></configuration></execution><execution><id>id.deploy</id><phase>deploy</phase><goals><goal>run</goal></goals><configuration><tasks><echo>deploy
phase</echo></tasks></configuration></execution></executions></plugin></plugins></build></project>
Now open the command console, jump to the directory where pom.xml is located, and execute the following mvn command.
C:\MVN\project>mvn compile
Maven will start processing and display the various stages of the build life cycle up to the compilation phase.
[INFO] Scanning for projects...
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Building Unnamed - com.companyname.projectgroup:project:jar:1.0
[INFO] task-segment: [compile]
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] [antrun:run {execution: id.validate}]
[INFO] Executing tasks
[echo] validate phase
[INFO] Executed tasks
[INFO] [resources:resources {execution: default-resources}]
[WARNING] Using platform encoding (Cp1252 actually) to copy filtered resources,
i.e. build is platform dependent!
[INFO] skip non existing resourceDirectory C:\MVN\project\src\main\resources
[INFO] [compiler:compile {execution: default-compile}]
[INFO] Nothing to compile - all classes are up to date
[INFO] [antrun:run {execution: id.compile}]
[INFO] Executing tasks
[echo] compile phase
[INFO] Executed tasks
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESSFUL
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Total time: 2 seconds
[INFO] Finished at: Sat Jul 07 20:18:25 IST 2012
[INFO] Final Memory: 7M/64M
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------
11.4.4. Command line call ¶
In the development environment, use the following command to build and install the project to the local warehouse
mvn install
This command executes the phases of the default life cycle (validate,compile,package, etc.) sequentially before executing the install phase, and we only need to call the last phase, as in this case install.
In the build environment, use the following calls to cleanly build and deploy the project to the shared repository
mvn clean deploy
This command can also be used in the case of multiple modules, that is, projects with multiple subprojects, where Maven executes the clean command in each subproject, followed by the deploy command.
11.4.5. Site lifecycle ¶
Maven Site plug-ins are generally used to create new report documents, deploy sites, and so on.
Pre-site: perform some work that needs to be done before generating site documentation
Site: generate site documentation for the project
Post-site: perform some work that needs to be done after the site documentation is generated, and prepare for deployment
Site-deploy: deploy the generated site documents to a specific server
Site phase and site-deploy phase are often used here to generate and publish Maven sites, which is a very powerful function of Maven, Manager likes, documents and statistics are automatically generated, very good-looking. In the following example, we add the maven-antrun-plugin:run goal to all phases of the Site lifecycle. This way we can display all the text information for the life cycle.
We have updated the pom.xml file in the C:MVNproject directory.
<projectxmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><groupId>com.companyname.projectgroup</groupId><artifactId>project</artifactId><version>1.0</version><build><plugins><plugin><groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId><artifactId>maven-antrun-plugin</artifactId><version>1.1</version><executions><execution><id>id.pre-site</id><phase>pre-site</phase><goals><goal>run</goal></goals><configuration><tasks><echo>pre-site
phase</echo></tasks></configuration></execution><execution><id>id.site</id><phase>site</phase><goals><goal>run</goal></goals><configuration><tasks><echo>site
phase</echo></tasks></configuration></execution><execution><id>id.post-site</id><phase>post-site</phase><goals><goal>run</goal></goals><configuration><tasks><echo>post-site
phase</echo></tasks></configuration></execution><execution><id>id.site-deploy</id><phase>site-deploy</phase><goals><goal>run</goal></goals><configuration><tasks><echo>site-deploy
phase</echo></tasks></configuration></execution></executions></plugin></plugins></build></project>
Now open the command console, jump to the directory where pom.xml is located, and execute the following mvn command.
C:\MVN\project>mvn site
Maven will start processing and display the various stages of the site life cycle up to the site phase.
[INFO] Scanning for projects...
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Building Unnamed - com.companyname.projectgroup:project:jar:1.0
[INFO] task-segment: [site]
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] [antrun:run {execution: id.pre-site}]
[INFO] Executing tasks
[echo] pre-site phase
[INFO] Executed tasks
[INFO] [site:site {execution: default-site}]
[INFO] Generating "About" report.
[INFO] Generating "Issue Tracking" report.
[INFO] Generating "Project Team" report.
[INFO] Generating "Dependencies" report.
[INFO] Generating "Project Plugins" report.
[INFO] Generating "Continuous Integration" report.
[INFO] Generating "Source Repository" report.
[INFO] Generating "Project License" report.
[INFO] Generating "Mailing Lists" report.
[INFO] Generating "Plugin Management" report.
[INFO] Generating "Project Summary" report.
[INFO] [antrun:run {execution: id.site}]
[INFO] Executing tasks
[echo] site phase
[INFO] Executed tasks
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESSFUL
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Total time: 3 seconds
[INFO] Finished at: Sat Jul 07 15:25:10 IST 2012
[INFO] Final Memory: 24M/149M
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------```