9.29.1. Brief introduction ¶
General-purpose applications are designed for iPhone and iPad in a single binary file. This helps code reuse and helps to update faster.
9.29.2. Instance step ¶
1、创建一个简单的View based application(视图应用程序)
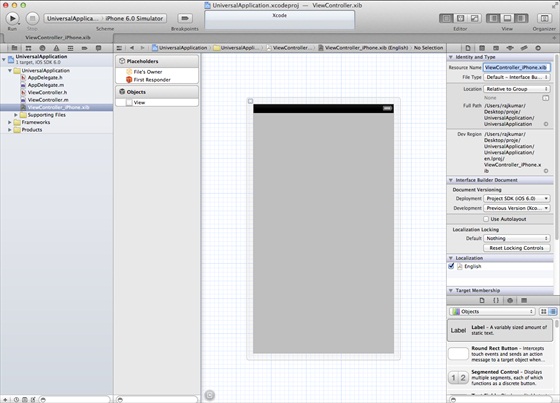
2、在文件查看器的右边,将文件ViewController.xib的文件名称更改为ViewController_iPhone.xib,如下所示
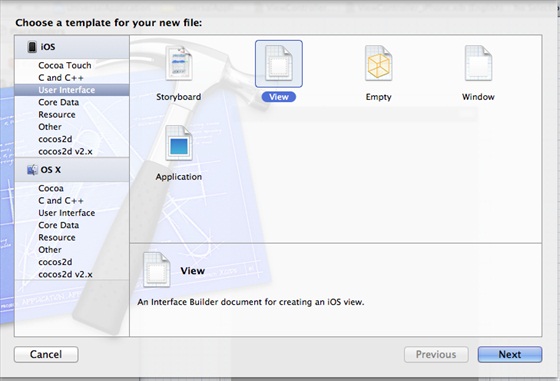
3、选择”File -> New -> File… “,然后选择User Interface,再选择View,单击下一步
4、选择iPad作为设备,单击下一步:
5、将该文件另存为ViewController_iPad.xib,然后选择创建
6、在ViewController_iPhone.xib和ViewController_iPad.xibd的屏幕中心添加标签
7、在ViewController_iPhone.xib中选择identity inspector,设置custom class为ViewController
8、更新AppDelegate.m中的 application:DidFinishLaunching:withOptions方法
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions
{
self.window = [[UIWindow alloc] initWithFrame:[[UIScreen
mainScreen] bounds]];
// Override point for customization after application launch.
if (UI_USER_INTERFACE_IDIOM() == UIUserInterfaceIdiomPhone) {
self.viewController = [[ViewController alloc]
initWithNibName:@"ViewController_iPhone" bundle:nil];
}
else{
self.viewController = [[ViewController alloc] initWithNibName:
@"ViewController_iPad" bundle:nil];
}
self.window.rootViewController = self.viewController;
[self.window makeKeyAndVisible];
return YES;
}
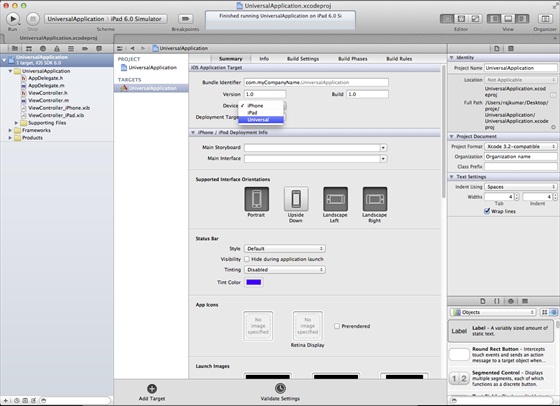
9、在项目摘要中更新设备中为universal,如下所示:
9.29.3. Output ¶
When we run the application, we will see the following output
Running the application in the iPad simulator, we get the following output: