In the heap sorting in the previous section, we opened up additional space to construct and sort the heap. In this section, we optimize using in-situ heap sorting.
For a maximum heap, first exchange the starting position data with the value at the end of the array, then the end of the array is the largest element, then shift down the W element to regenerate the maximum heap, and then swap the newly generated maximum number with the penultimate position of the entire array, which is the penultimate big data everywhere, and so on.
The whole process can be shown in the following figure:
源码包下载: Download 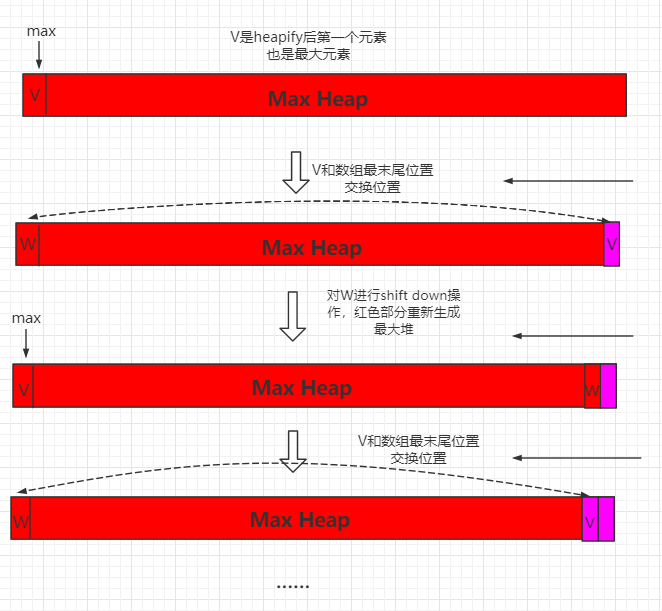
5.13.1. Java instance code ¶
Src/runoob/heap/HeapSort.java file code: ¶
package runoob.heap;
import runoob.sort.SortTestHelper;
/*\*
\* 原地堆排序
*/
public class HeapSort<T extends Comparable> {
public static void sort(Comparable[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
// 注意,此时我们的堆是从0开始索引的
// 从(最后一个元素的索引-1)/2开始
// 最后一个元素的索引 = n-1
for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
shiftDown(arr, n, i);
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--) {
swap(arr, 0, i);
shiftDown(arr, i, 0);
}
}
// 交换堆中索引为i和j的两个元素
private static void swap(Object[] arr, int i, int j) {
Object t = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = t;
}
// 原始的shiftDown过程
private static void shiftDown(Comparable[] arr, int n, int k) {
while (2 \* k + 1 < n) {
//左孩子节点
int j = 2 \* k + 1;
//右孩子节点比左孩子节点大
if (j + 1 < n && arr[j + 1].compareTo(arr[j]) > 0)
j += 1;
//比两孩子节点都大
if (arr[k].compareTo(arr[j]) >= 0) break;
//交换原节点和孩子节点的值
swap(arr, k, j);
k = j;
}
}
// 测试 HeapSort
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 100;
Integer[] arr = SortTestHelper.generateRandomArray(N, 0,
100000);
sort(arr);
// 将heapify中的数据逐渐使用extractMax取出来
// 取出来的顺序应该是按照从大到小的顺序取出来的
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
// 确保arr数组是从大到小排列的
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++)
assert arr[i - 1] >= arr[i];
}
}