Breadth-first traversal starts from a vertex v, first visits the node and marks it as visited, then sequentially accesses all the unaccessed adjacencies {vi,..,vj} of node v and marks them as visited, and then repeats the access method of node v for each node in {vi,…,vj} until all nodes have been visited.
We can divide it into three steps:
(1)使用一个辅助队列 q,首先将顶点 v 入队,将其标记为已访问,然后循环检测队列是否为空。
(2)如果队列不为空,则取出队列第一个元素,并将与该元素相关联的所有未被访问的节点入队,将这些节点标记为已访问。
(3)如果队列为空,则说明已经按照广度优先遍历了所有的节点。
As shown in the following figure, the blue on the right shows the order of traversing nodes starting from 0, and the following is the distance of recording distance 0. It is known that breadth-first traversal can find the shortest path of the unauthorized graph.
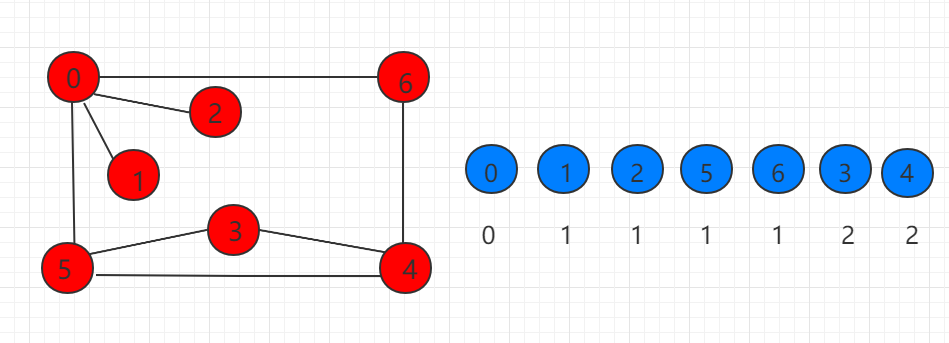
The following code shows how to use breadth-first traversal to complete traversal and query the shortest path. We add an array of global variables ord to the previous section of code to record the order of nodes in the path. Ord [i] Represents the order of I nodes in the path. At the same time, the constructor adjusts accordingly to ord each unaccessed node when traversing neighboring nodes. [i] = ord [v] + 1 record distance. The breadth-first traversal time complexity of adjacency table is O (VroomE), and the time complexity of adjacency matrix is O (V ^ 2).
...
// 构造函数, 寻路算法, 寻找图graph从s点到其他点的路径
public ShortestPath(Graph graph, int s){
// 算法初始化
G = graph;
assert s >= 0 && s < G.V();
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
from = new int[G.V()];
ord = new int[G.V()];
for( int i = 0 ; i < G.V() ; i ++ ){
visited[i] = false;
from[i] = -1;
ord[i] = -1;
}
this.s = s;
// 无向图最短路径算法, 从s开始广度优先遍历整张图
LinkedList<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.push( s );
visited[s] = true;
ord[s] = 0;
while( !q.isEmpty() ){
int v = q.pop();
for( int i : G.adj(v) )
if( !visited[i] ){
q.push(i);
visited[i] = true;
from[i] = v;
ord[i] = ord[v] + 1;
}
}
}
...
Check the shortest path length from s point to w point. If it is unreachable from s to w, return-1.
...
public int length(int w){
assert w >= 0 && w < G.V();
return ord[w];
}
...
5.32.1. Java instance code ¶
源码包下载: Download Src/runoob/graph/ShortestPath.java file code: ¶
package runoob.graph;
import runoob.graph.read.Graph;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.Vector;
/*\*
\* 广度优先遍历与最短路径
*/
public class ShortestPath {
// 图的引用
private Graph G;
// 起始点
private int s;
// 记录dfs的过程中节点是否被访问
private boolean[] visited;
// 记录路径, from[i]表示查找的路径上i的上一个节点
private int[] from;
// 记录路径中节点的次序。ord[i]表示i节点在路径中的次序。
private int[] ord;
// 构造函数, 寻路算法, 寻找图graph从s点到其他点的路径
public ShortestPath(Graph graph, int s){
// 算法初始化
G = graph;
assert s >= 0 && s < G.V();
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
from = new int[G.V()];
ord = new int[G.V()];
for( int i = 0 ; i < G.V() ; i ++ ){
visited[i] = false;
from[i] = -1;
ord[i] = -1;
}
this.s = s;
// 无向图最短路径算法, 从s开始广度优先遍历整张图
LinkedList<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.push( s );
visited[s] = true;
ord[s] = 0;
while( !q.isEmpty() ){
int v = q.pop();
for( int i : G.adj(v) )
if( !visited[i] ){
q.push(i);
visited[i] = true;
from[i] = v;
ord[i] = ord[v] + 1;
}
}
}
// 查询从s点到w点是否有路径
public boolean hasPath(int w){
assert w >= 0 && w < G.V();
return visited[w];
}
// 查询从s点到w点的路径, 存放在vec中
public Vector<Integer> path(int w){
assert hasPath(w) ;
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>();
// 通过from数组逆向查找到从s到w的路径, 存放到栈中
int p = w;
while( p != -1 ){
s.push(p);
p = from[p];
}
// 从栈中依次取出元素, 获得顺序的从s到w的路径
Vector<Integer> res = new Vector<Integer>();
while( !s.empty() )
res.add( s.pop() );
return res;
}
// 打印出从s点到w点的路径
public void showPath(int w){
assert hasPath(w) ;
Vector<Integer> vec = path(w);
for( int i = 0 ; i < vec.size() ; i ++ ){
System.out.print(vec.elementAt(i));
if( i == vec.size() - 1 )
System.out.println();
else
System.out.print(" -> ");
}
}
// 查看从s点到w点的最短路径长度
// 若从s到w不可达,返回-1
public int length(int w){
assert w >= 0 && w < G.V();
return ord[w];
}
}