7.13.1. Aggregate query (aggregate) ¶
Aggregate query functions perform calculations on a set of values and return a single value.
Django needs to introduce Avg, Max, Min, Count, Sum (uppercase initials) from django.db.models before using aggregate queries.
from django.db.models import Avg,Max,Min,Count,Sum # 引入函数
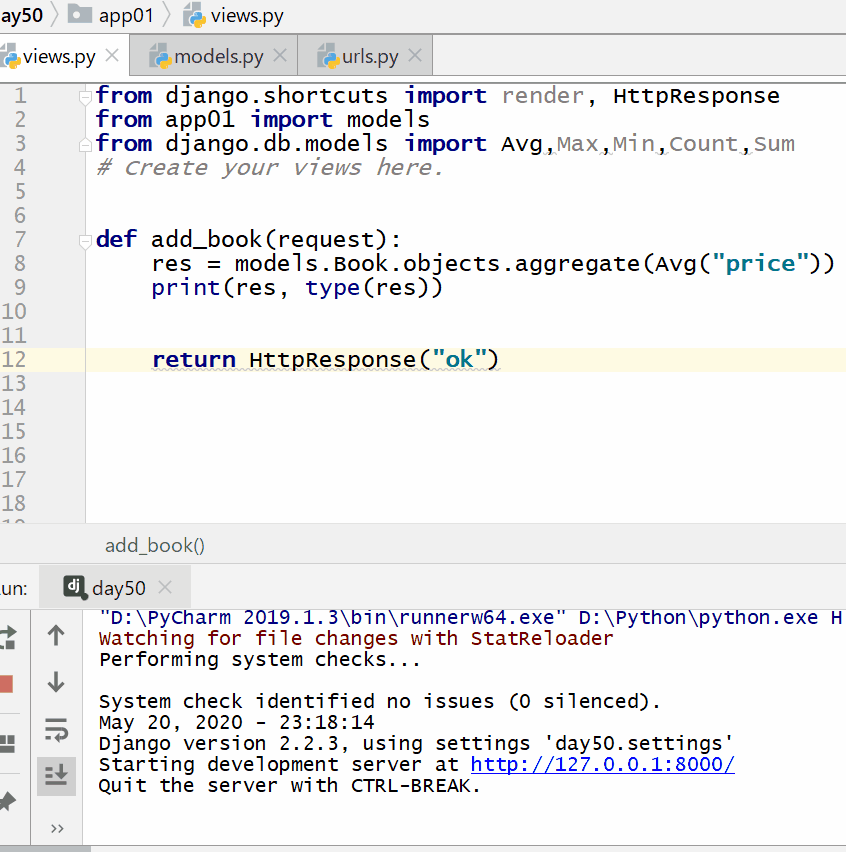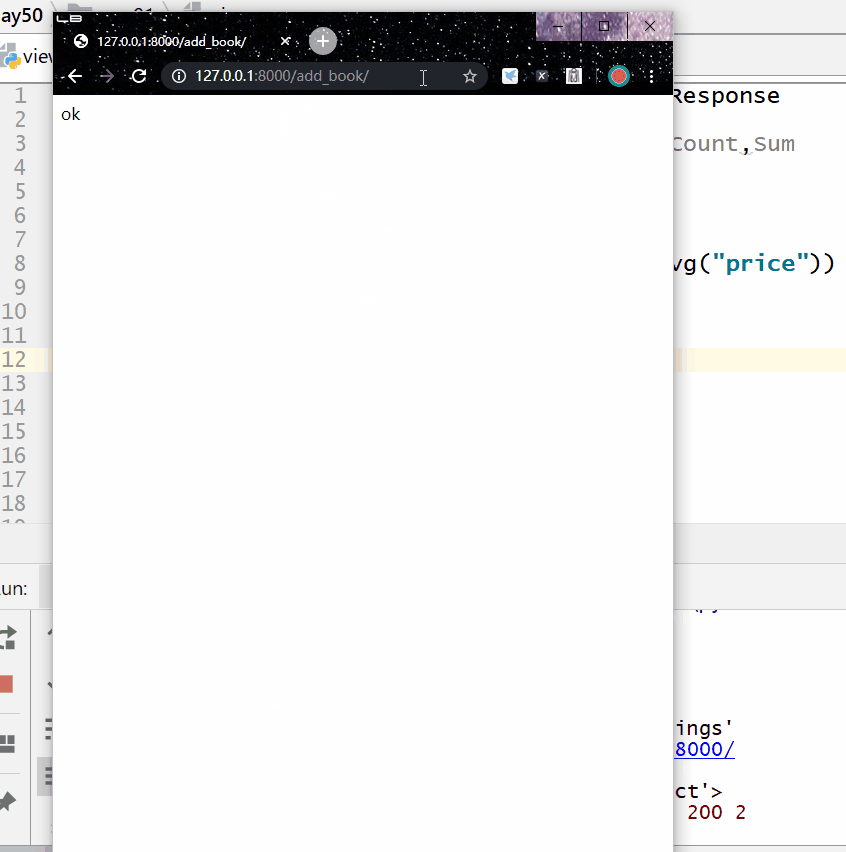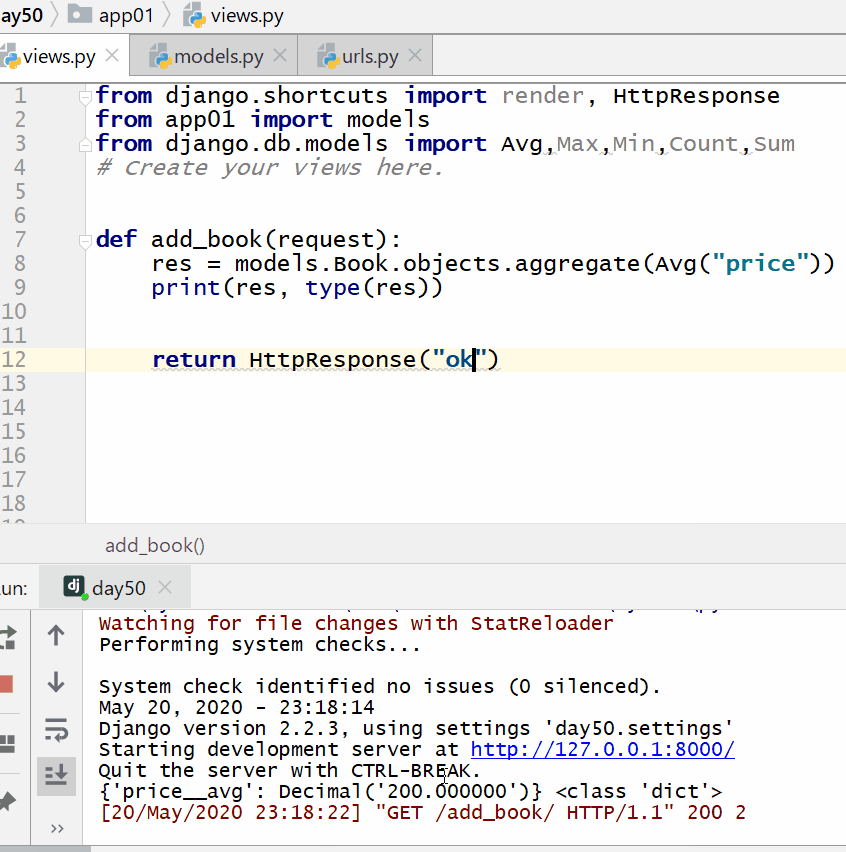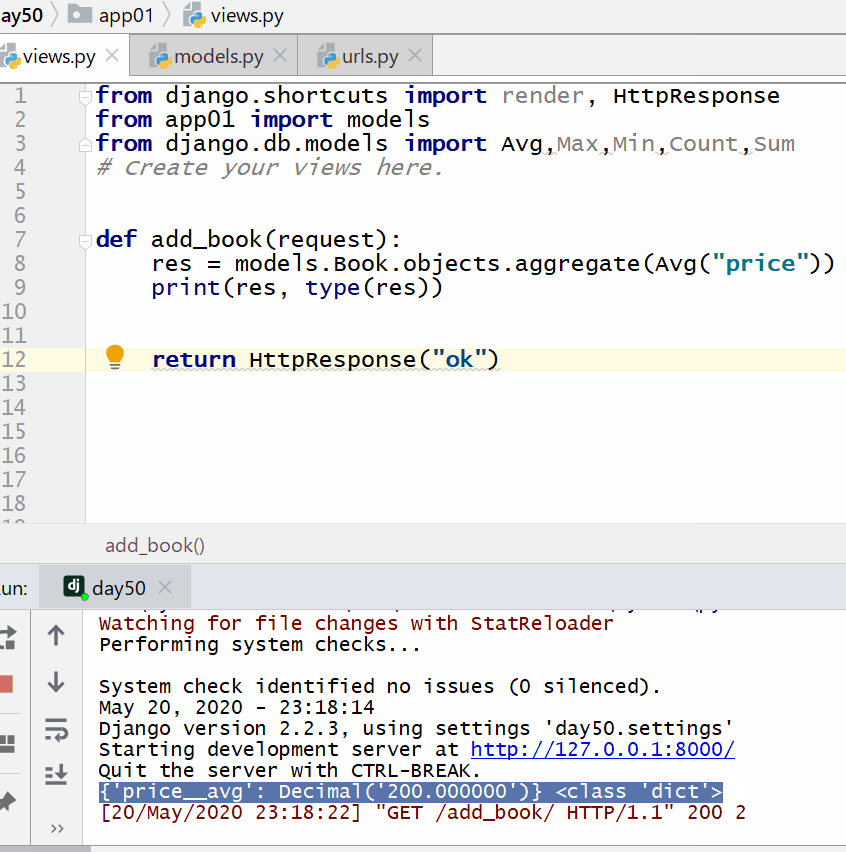
The data type of the return value of the aggregate query is a dictionary.
The aggregate function aggregate () is a termination clause of QuerySet that generates a summary value equivalent to count ().
After using aggregate (), the data type becomes a dictionary, and some API of the QuerySet data type can no longer be used.
Date data types (DateField) can be used with Max and Min.
返回的字典中:键的名称默认是(属性名称加上__聚合函数名),值是计算出来的聚合值。
If you want to customize the name of the key that returns the dictionary, you can give it an alias:
aggregate(别名 = 聚合函数名("属性名称"))
Calculate the average price of all books: Calculate the number, most expensive and cheapest prices of all books:Example ¶
from django.db.models import Avg,Max,Min,Count,Sum # 引入函数
...
res = models.Book.objects.aggregate(Avg("price"))
print(res, type(res))
...
7.13.2. Example ¶
Res=models.Book.objects.aggregate (c=Count (“id”), max=Max (“price”), min=Min (“price”) print (res,type (res))
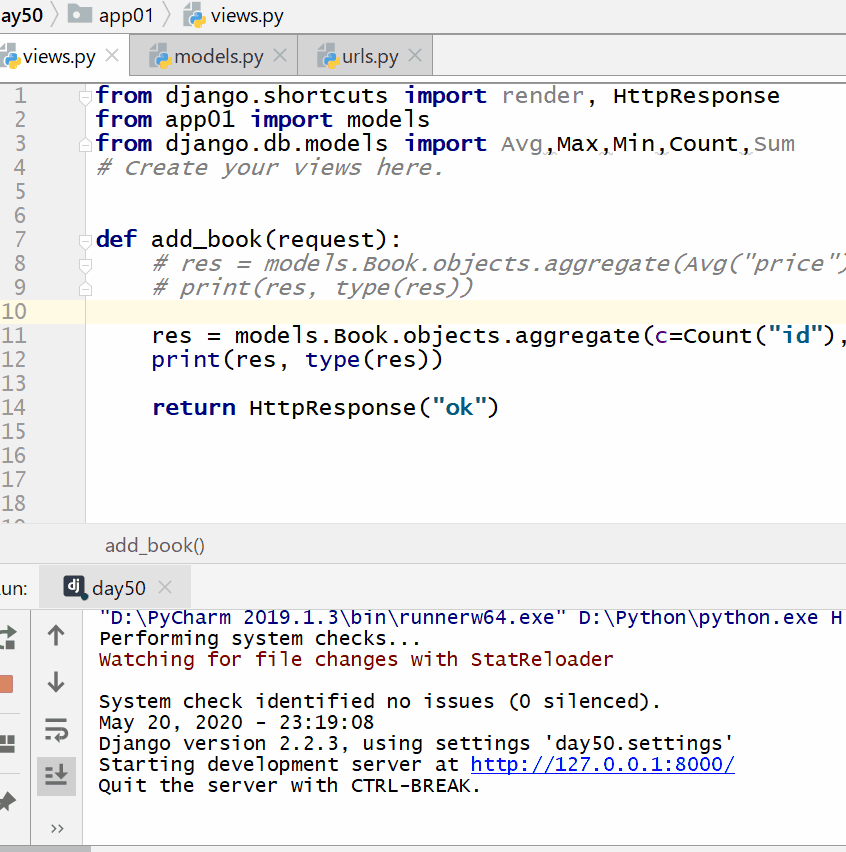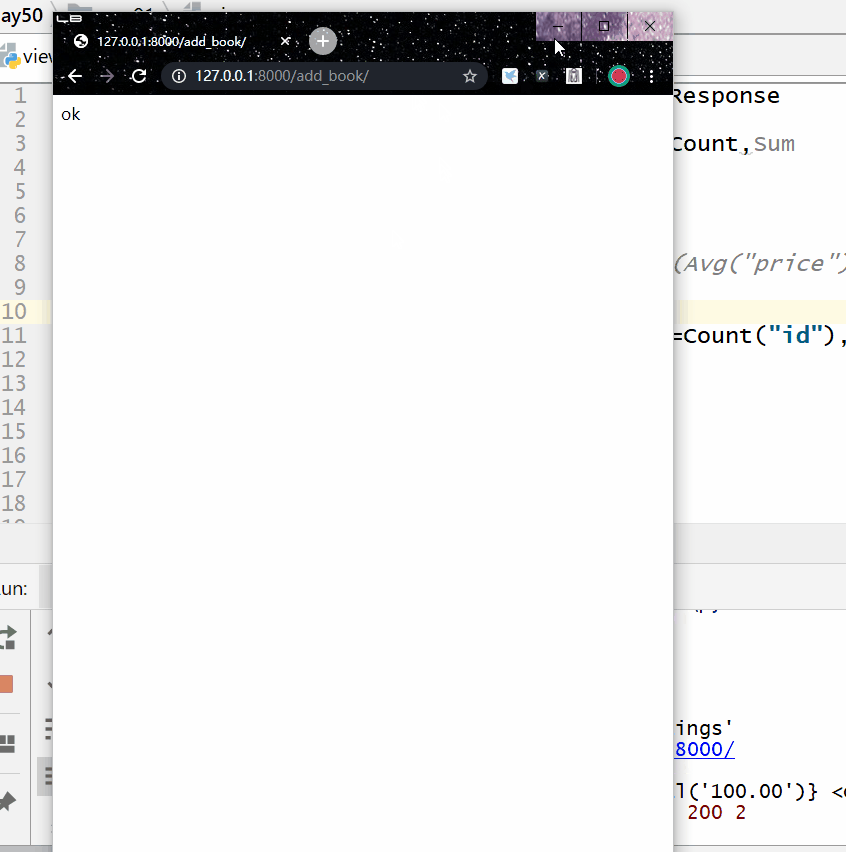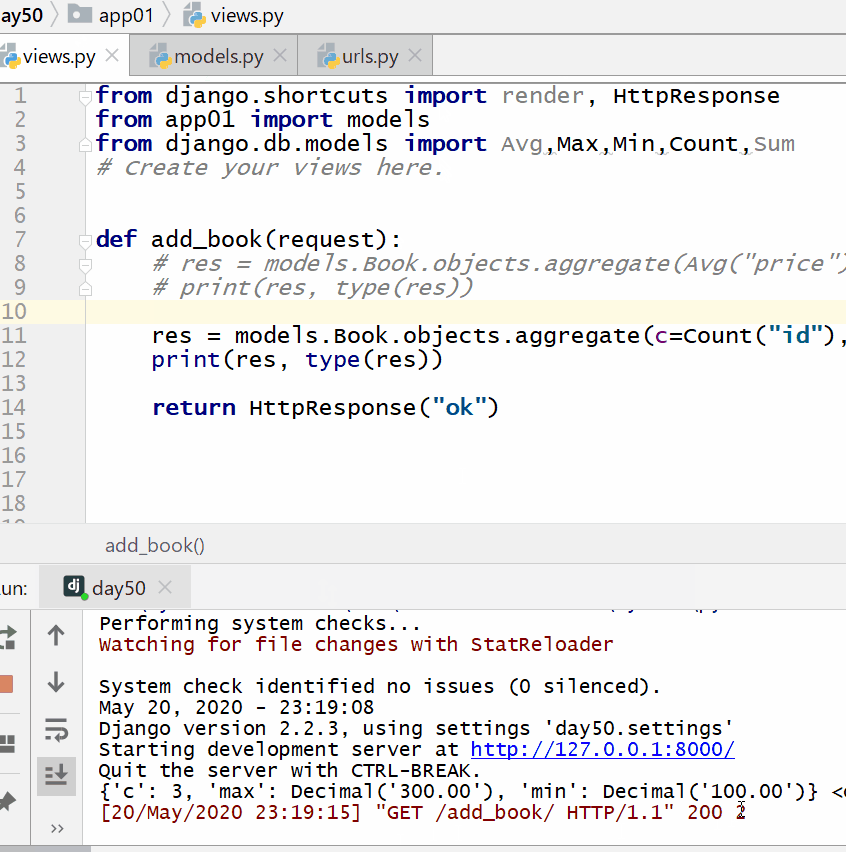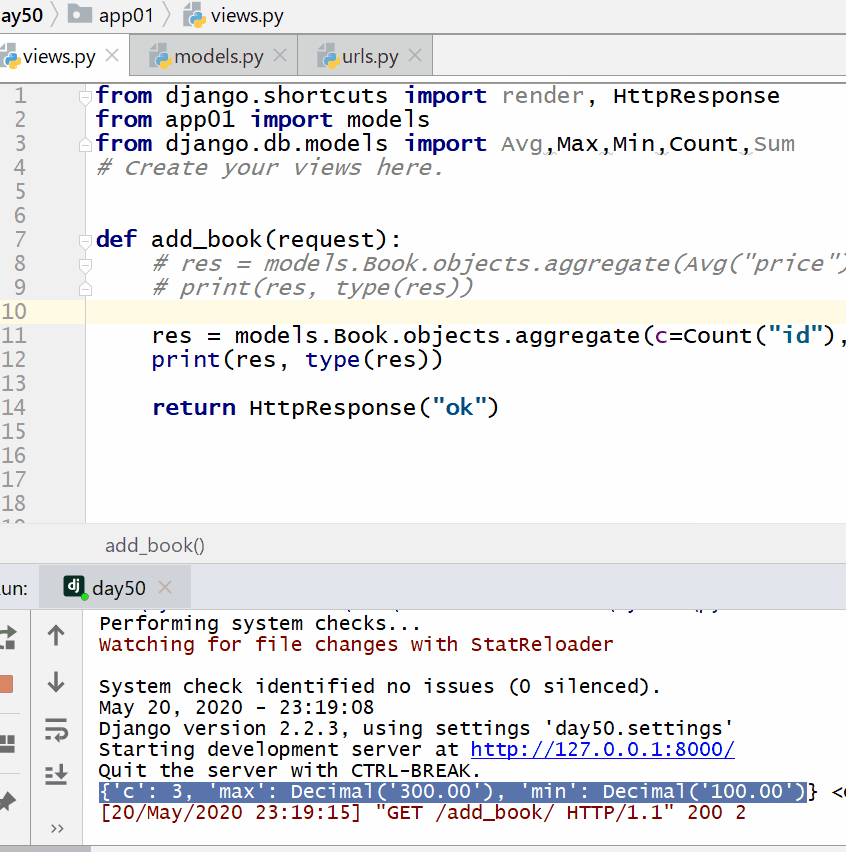
7.13.3. Group query (annotate) ¶
Aggregate functions are generally used in grouping queries, so introduce Avg,Max,Min,Count,Sum (uppercase initials) from django.db.models before using it.
from django.db.models import Avg,Max,Min,Count,Sum # 引入函数
返回值:
After grouping, the value is taken with values, and the return value is a dictionary in the QuerySet data type.
After grouping, use values_list to take the value, then the return value is a tuple in the QuerySet data type.
The limit in MySQL is equivalent to a slice of the QuerySet data type in ORM.
注意:
Aggregate functions are included in annotate.
values 或者 values_list 放在 annotate 前面: Values or values_list declares what fields to group, and annotate performs the grouping.
values 或者 values_list 放在annotate后面: Annotate indicates grouping directly based on the competition of the current table, and values or values_list indicates which fields to query, and aliases the aggregate function in annotate and writes its alias in values or values_list.
7.13.4. Prepare data and create models ¶
models.py ¶
class Emp(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
age = models.IntegerField()
salary = models.DecimalField(max_digits=8, decimal_places=2)
dep = models.CharField(max_length=32)
province = models.CharField(max_length=32)
class Emps(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
age = models.IntegerField()
salary = models.DecimalField(max_digits=8, decimal_places=2)
dep = models.ForeignKey("Dep", on_delete=models.CASCADE)
province = models.CharField(max_length=32)
class Dep(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=32)
Data:
Execute from the MySQL command line: ¶
INSERTINTO\`app01_emp\`(\`id\`,\`name\`,\`age\`,\`salary\`,\`dep\`,\`province\`)VALUES('1','令狐冲','24','6000.00','销售部','河南');INSERTINTO\`app01_emp\`(\`id\`,\`name\`,\`age\`,\`salary\`,\`dep\`,\`province\`)VALUES('2','任盈盈','18','8000.00','关公部','广东');INSERTINTO\`app01_emp\`(\`id\`,\`name\`,\`age\`,\`salary\`,\`dep\`,\`province\`)VALUES('3','任我行','56','10000.00','销售部','广东');INSERTINTO\`app01_emp\`(\`id\`,\`name\`,\`age\`,\`salary\`,\`dep\`,\`province\`)VALUES('4','岳灵珊','19','6000.00','关公部','河南');INSERTINTO\`app01_emp\`(\`id\`,\`name\`,\`age\`,\`salary\`,\`dep\`,\`province\`)VALUES('5','小龙女','20','8000.00','关公部','河北');INSERTINTO\`app01_dep\`(\`id\`,\`title\`)VALUES('1','销售部');INSERTINTO\`app01_dep\`(\`id\`,\`title\`)VALUES('2','关公部');INSERTINTO\`app01_emps\`(\`id\`,\`name\`,\`age\`,\`salary\`,\`province\`,\`dep_id\`)VALUES('2','令狐冲','24','8000.00','河南','1');INSERTINTO\`app01_emps\`(\`id\`,\`name\`,\`age\`,\`salary\`,\`province\`,\`dep_id\`)VALUES('3','任盈盈','18','9000.00','广东','2');INSERTINTO\`app01_emps\`(\`id\`,\`name\`,\`age\`,\`salary\`,\`province\`,\`dep_id\`)VALUES('4','任我行','57','10000.00','广东','1');INSERTINTO\`app01_emps\`(\`id\`,\`name\`,\`age\`,\`salary\`,\`province\`,\`dep_id\`)VALUES('5','岳灵珊','19','6000.00','河南','2');INSERTINTO\`app01_emps\`(\`id\`,\`name\`,\`age\`,\`salary\`,\`province\`,\`dep_id\`)VALUES('6','小龙女','20','8000.00','河北','2');
Count the prices of the cheapest books in each publisher:
Example ¶
res = models.Publish.objects.values("name").annotate(in_price =
Min("book__price"))
print(res)
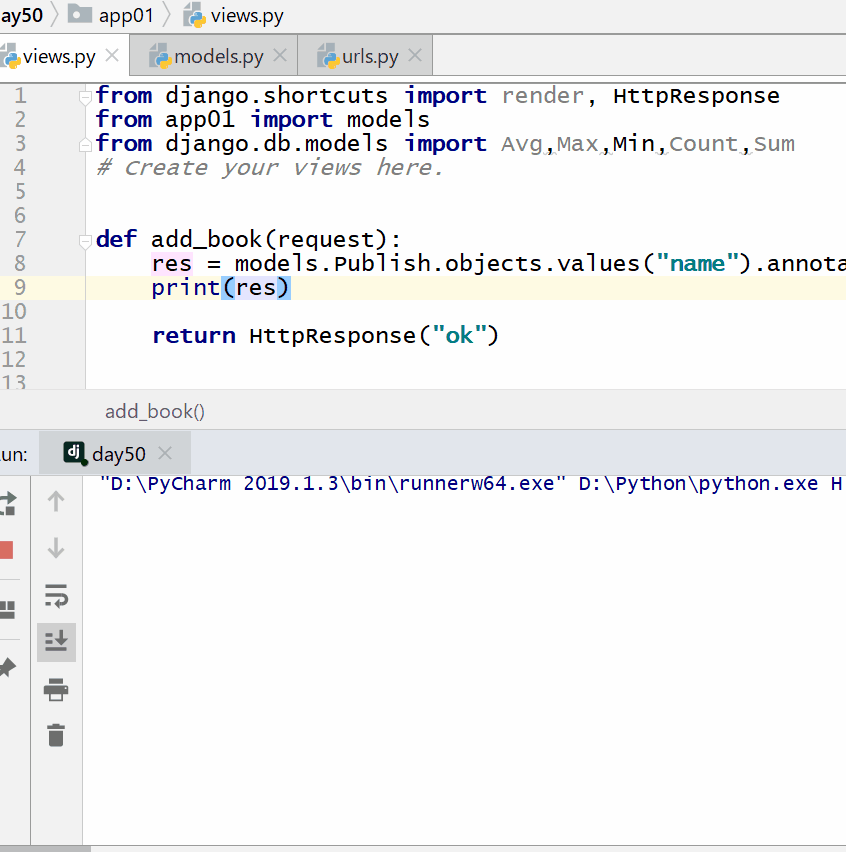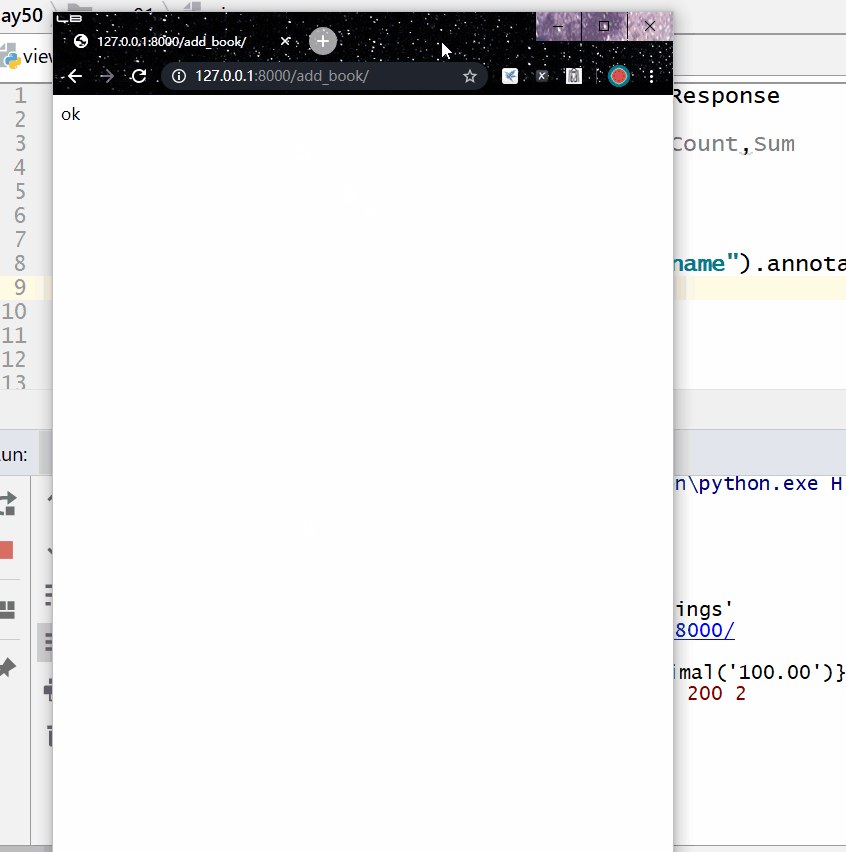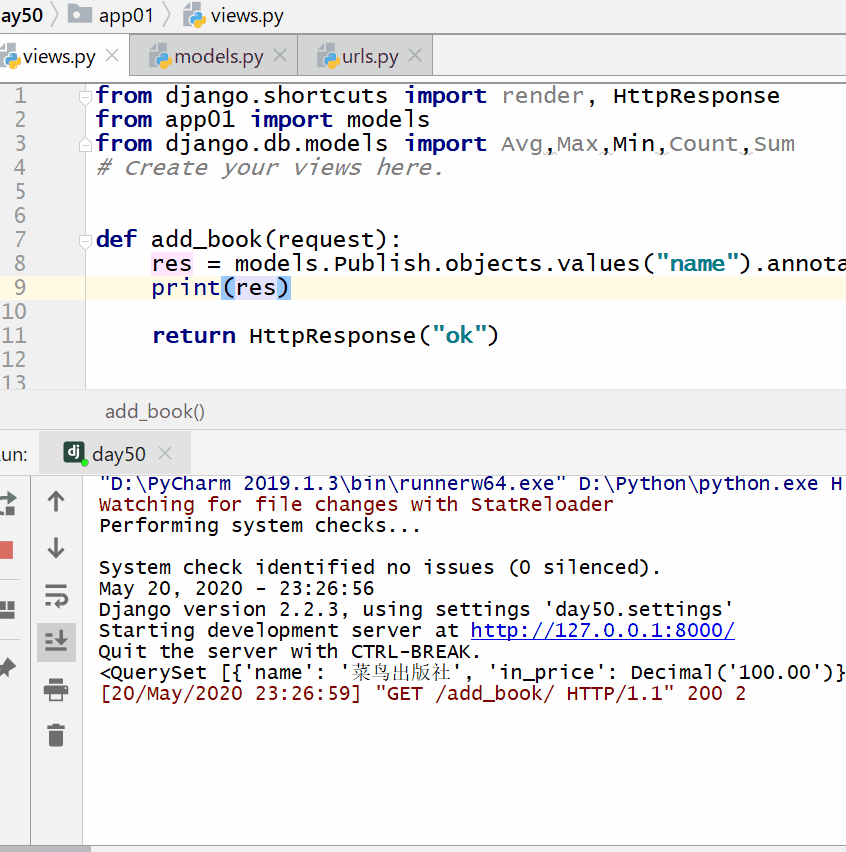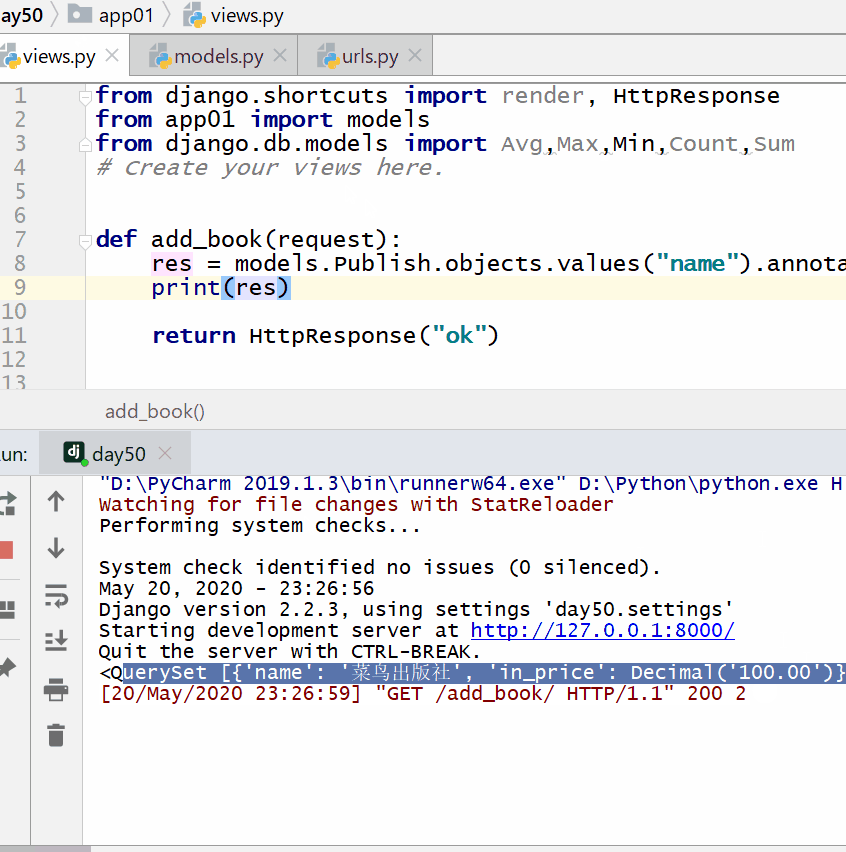
The following output can be seen on the command line:
<QuerySet [{'name': '菜鸟出版社', 'in_price': Decimal('100.00')}, {'name': '明教出版社', 'in_price': Decimal('300.00')}]>
Count the number of authors of each book:
Example ¶
res = models.Book.objects.annotate(c =
Count("authors__name")).values("title","c")
print(res)
The following output can be seen on the command line: