The relationships between tables can be divided into the following three categories:
一对一 Each person corresponds to an ID card number, and the data field sets unique.
一对多 There are multiple people in a family, which is generally realized through foreign keys.
多对多 A student has multiple courses, a course has many students, and the association is usually achieved through the third table.
Next, let’s take a look at multiple tables and multiple instances. 说明: 1、EmailField 数据类型是邮箱格式,底层继承 CharField,进行了封装,相当于 MySQL 中的 varchar。 2、Django1.1 版本不需要联级删除:on_delete=models.CASCADE,Django2.2 需要。 3、一般不需要设置联级更新. 4、外键在一对多的多中设置:models.ForeignKey(“关联类名”, on_delete=models.CASCADE)。 5、OneToOneField = ForeignKey(…,unique=True)设置一对一。 6、若有模型类存在外键,创建数据时,要先创建外键关联的模型类的数据,不然创建包含外键的模型类的数据时,外键的关联模型类的数据会找不到。 书籍表 Book Title, price, pub_date, publish (foreign key, many-to-one), authors (many-to-many) 出版社表 Publish : name 、 city 、 email 作者表 Author : name, age, au_detail (one to one) 作者详情表 AuthorDetail : gender 、 tel 、 addr 、 birthday The following is a description of the table association: https://www.runoob.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Django-orm2_1.png We perform the following SQL insert operation in MySQL: 方式一: Pass the form of the object, the data type of the return value is the object, the book object. 步骤: Get publisher object Pulish the publishing house attribute of the book to the publishing house object Method 2: pass the form of the object id (since the data passed is generally id, it is commonly used to pass the object id). In an one-to-many class (multiple tables) that set foreign key properties, the field names displayed in MySQL are: 外键属性名_id . The data type of the return value is object, book object. 步骤: Get the id of the publisher object The associated publishing house field for the book pulish_id passes the id of the publishing house object 方式一: Pass in the form of an object with no return value. 步骤: Get the author object Get book object Use the add method to pass the author object to the authors property of the book object 方式二: The object is in the form of id and no return value is returned. 步骤: Get the id of the author object Get book object Use the add method to pass the id of the author object to the authors property of the book object 前提: Many-to-many (there is an association manager in both directions) One-to-many (only the object of the more than one class has an association manager, that is, in reverse) 语法格式: 注意: One to many can only be reversed. 常用方法: add() : for many-to-many, adding the specified model object to the associated object set (relational table). 注意: Method 1: pass the object 反向:小写表名_set create() Create a new object and add it to the associated object set at the same time Returns the newly created object. remove() Removes the executed model object from the associated object set For ForeignKey objects, this method exists only when null=True (which can be null) and no return value is returned. clear() Remove all objects from the associated object set, delete the association, and do not delete the object. For ForeignKey objects, this method exists only when null=True (which can be null). No return value. Object-based cross-table query. Query the city where the publisher of the book with the primary key of 1 is located (forward). Query the title of the book published by Mingjiao Publishing House (reverse). Reverse: object. The lowercase class name _ set (pub.book_set) can jump to the associated table (book table). pub.book_set.all() Take out all the book objects in the book list, and traverse the book objects in a QuerySet. Inquire Linghu Chong’s phone number (positive) Forward: object. The attribute (author.au_detail) can jump to the associated table (author details table) Check the names of all authors whose addresses are in Blackwood Cliff (reverse). One-to-one reverse, with 对象.小写类名 No need to add_ set. Reverse: object. The lowercase class name (addr.author) can jump to the associated table (author table). The names and mobile phone numbers of all the authors of the rookie tutorial (positive). Positive: 对象.属性(book.authors) You can jump to the associated table (author table). The author’s phone number is not in the author’s table, so it is passed again. 对象.属性(i.au_detail) Jump to the associated table (author details table). Inquire about the names of all the books I have published (in reverse). Forward: attribute name _ _ across table attribute name reverse: lowercase class name _ _ across table attribute name Find out the names and prices of all books published by Cainiao Publishing House. Reverse: through small 写类名__跨表的属性名称(book__title,book__price) Get data across tables. Inquire about the names of all the books that I have published. Forward: obtain data across tables through attribute name _ _ cross-table attribute name (authors__name): Reverse: obtain data across tables by using lowercase class name _ _ cross-table attribute name (book__title): Check the mobile phone number of any bank. Forward: through 属性名称__跨表的属性名称(au_detail__tel) Get data across tables. Reversing: through 小写类名__跨表的属性名称(author__name) Get data across tables.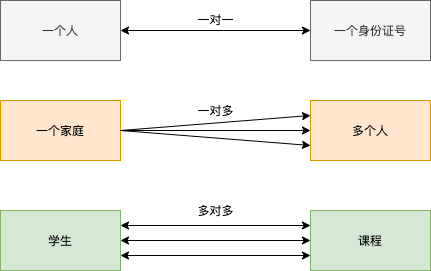
7.12.1. Create a model ¶
Example ¶
class Book(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=32)
price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=5, decimal_places=2)
pub_date = models.DateField()
publish = models.ForeignKey("Publish", on_delete=models.CASCADE)
authors = models.ManyToManyField("Author")
class Publish(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
city = models.CharField(max_length=64)
email = models.EmailField()
class Author(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
age = models.SmallIntegerField()
au_detail = models.OneToOneField("AuthorDetail",
on_delete=models.CASCADE)
class AuthorDetail(models.Model):
gender_choices = (
(0, "女"),
(1, "男"),
(2, "保密"),
)
gender = models.SmallIntegerField(choices=gender_choices)
tel = models.CharField(max_length=32)
addr = models.CharField(max_length=64)
birthday = models.DateField()
7.12.2. Table structure ¶
7.12.3. Insert data ¶
insert into app01_publish(name,city,email) values ("华山出版社", "华山", "hs@163.com"), ("明教出版社", "黑木崖", "mj@163.com")
# 先插入 authordetail 表中多数据
insert into app01_authordetail(gender,tel,addr,birthday) values (1,13432335433,"华山","1994-5-23"), (1,13943454554,"黑木崖","1961-8-13"), (0,13878934322,"黑木崖","1996-5-20")
# 再将数据插入 author,这样 author 才能找到 authordetail
insert into app01_author(name,age,au_detail_id) values ("令狐冲",25,1), ("任我行",58,2), ("任盈盈",23,3)

7.12.4. ORM-add data ¶
7.12.5. One to many (foreign key ForeignKey) ¶
App01/views.py file code: ¶
def add_book(request):
# 获取出版社对象
pub_obj = models.Publish.objects.filter(pk=1).first()
# 给书籍的出版社属性publish传出版社对象
book = models.Book.objects.create(title="菜鸟教程", price=200,
pub_date="2010-10-10", publish=pub_obj)
print(book, type(book))
return HttpResponse(book)

App01/views.py file code: ¶
def add_book(request):
# 获取出版社对象
pub_obj = models.Publish.objects.filter(pk=1).first()
# 获取出版社对象的id
pk = pub_obj.pk
# 给书籍的关联出版社字段 publish_id 传出版社对象的id
book = models.Book.objects.create(title="冲灵剑法", price=100,
pub_date="2004-04-04", publish_id=pk)
print(book, type(book))
return HttpResponse(book)

7.12.6. Many-to-many (ManyToManyField): add data to the third relational table ¶
App01/views.py file code: ¶
def add_book(request):
# 获取作者对象
chong = models.Author.objects.filter(name="令狐冲").first()
ying = models.Author.objects.filter(name="任盈盈").first()
# 获取书籍对象
book = models.Book.objects.filter(title="菜鸟教程").first()
# 给书籍对象的 authors 属性用 add 方法传作者对象
book.authors.add(chong, ying)
return HttpResponse(book)

App01/views.py file code: ¶
def add_book(request):
# 获取作者对象
chong = models.Author.objects.filter(name="令狐冲").first()
# 获取作者对象的id
pk = chong.pk
# 获取书籍对象
book = models.Book.objects.filter(title="冲灵剑法").first()
# 给书籍对象的 authors 属性用 add 方法传作者对象的id
book.authors.add(pk)

7.12.7. Association Manager (object invocation) ¶
正向:属性名
反向:小写类名加 _set
add()
In one-to-many (that is, foreign keys), only objects can be passed
*QuerySet
Data type), cannot be passed
id(*[id表])
.
*[
]
Use of:book_obj = models.Book.objects.get(id=10)
author_list = models.Author.objects.filter(id__gt=2)
book_obj.authors.add(\*author_list) # 将 id
大于2的作者对象添加到这本书的作者集合中
# 方式二:传对象 id
book_obj.authors.add(\*[1,3]) # 将 id=1 和 id=3
的作者对象添加到这本书的作者集合中
return HttpResponse("ok")

ying = models.Author.objects.filter(name="任盈盈").first()
book = models.Book.objects.filter(title="冲灵剑法").first()
ying.book_set.add(book)
return HttpResponse("ok")

pub = models.Publish.objects.filter(name="明教出版社").first()
wo = models.Author.objects.filter(name="任我行").first()
book = wo.book_set.create(title="吸星大法", price=300,
pub_date="1999-9-19", publish=pub)
print(book, type(book))
return HttpResponse("ok")

Example ¶
author_obj =models.Author.objects.get(id=1)
book_obj = models.Book.objects.get(id=11)
author_obj.book_set.remove(book_obj)
return HttpResponse("ok")

# 清空独孤九剑关联的所有作者
book = models.Book.objects.filter(title="菜鸟教程").first()
book.authors.clear()
7.12.8. ORM query ¶
正向:属性名称
反向:小写类名_set
7.12.9. One to many ¶
Example ¶
book = models.Book.objects.filter(pk=10).first()
res = book.publish.city
print(res, type(res))
return HttpResponse("ok")

Example ¶
pub = models.Publish.objects.filter(name="明教出版社").first()
res = pub.book_set.all()
for i in res:
print(i.title)
return HttpResponse("ok")

7.12.10. one-for-one ¶
Example ¶
author = models.Author.objects.filter(name="令狐冲").first()
res = author.au_detail.tel
print(res, type(res))
return HttpResponse("ok")

Example ¶
addr = models.AuthorDetail.objects.filter(addr="黑木崖").first()
res = addr.author.name
print(res, type(res))
return HttpResponse("ok")

7.12.11. Many to many ¶
Example ¶
book = models.Book.objects.filter(title="菜鸟教程").first()
res = book.authors.all()
for i in res:
print(i.name, i.au_detail.tel)
return HttpResponse("ok")

Example ¶
author = models.Author.objects.filter(name="任我行").first()
res = author.book_set.all()
for i in res:
print(i.title)
return HttpResponse("ok")

7.12.12. Cross-table query based on double underscore ¶
7.12.13. One to many ¶
Example ¶
res =
models.Book.objects.filter(publish__name="菜鸟出版社").values_list("title",
"price")

Example ¶
res =
models.Publish.objects.filter(name="菜鸟出版社").values_list("book__title","book__price")
return HttpResponse("ok")

7.12.14. Many to many ¶
res = models.Book.objects.filter(authors__name="任我行").values_list("title")
res = models.Author.objects.filter(name="任我行").values_list("book__title")

7.12.15. one-for-one ¶
res = models.Author.objects.filter(name="任我行").values_list("au_detail__tel")

res = models.AuthorDetail.objects.filter(author__name="任我行").values_list("tel")
